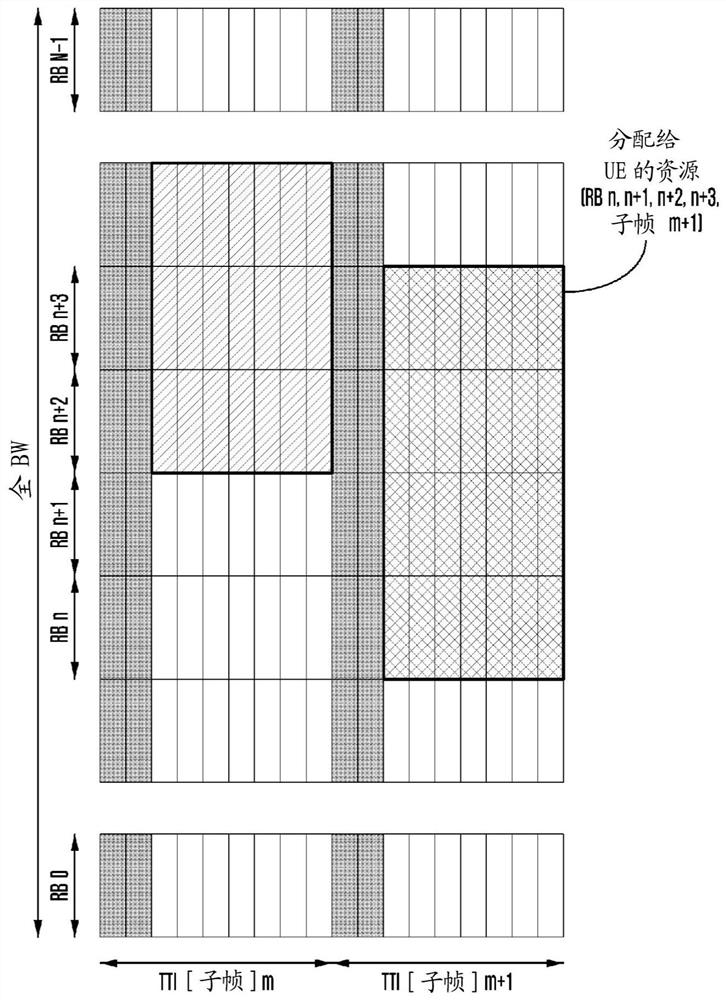
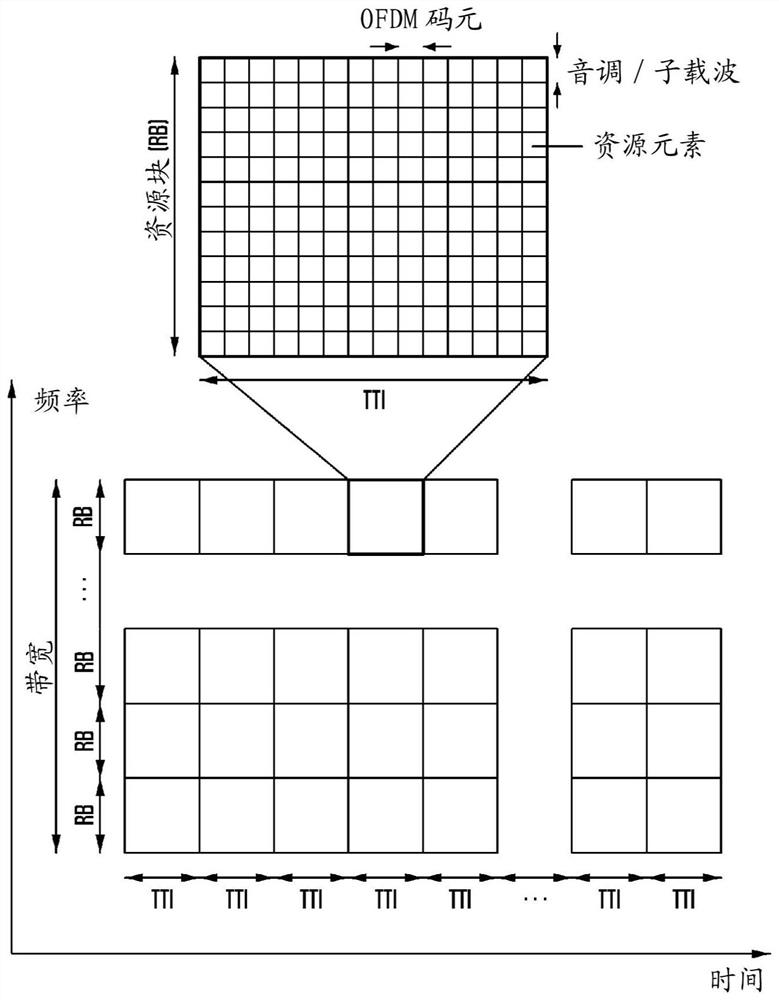
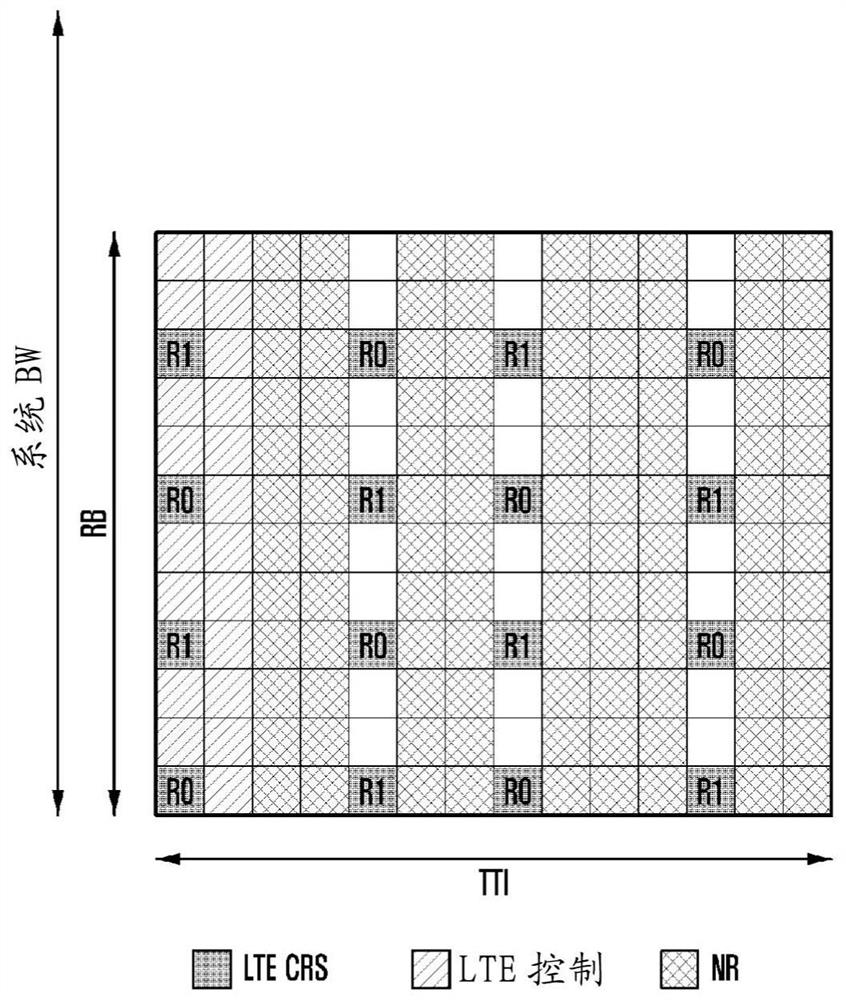
Method and device for data transmission in next generation cellular network
A technology for receiving data and downlinking, which is applied in the field of data transmission and can solve the problems of no judgment and no assertion.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0071] Embodiment 1: symbol bitmap
[0072] Figure 5 The figure shows an example of a configuration indicated based on a symbol bitmap according to an embodiment of the present disclosure.
[0073] refer to Figure 5 , if there are N symbols in a given TTI duration, then a bitmap {b 0 ,b 1 ,...,b n ,b n+1 ,...,b N-1} can be used e.g. by setting b n = 1 or 0 to explicitly indicate whether the nth symbol is allocated. This requires N bits for indicating each symbol. For example, if N=14, an indication with a 14-bit bitmap is necessary.
Embodiment 2
[0074] Embodiment 2: start symbol index, end symbol index (or the quantity of symbol)
[0075] Figure 6 Figure illustrates an example of a configuration-based indication of a start symbol and an end symbol according to an embodiment of the disclosure.
[0076] refer to Figure 6 , if there are N symbols in a given TTI duration, then (n start ,n symbol ) indication can be used to indicate that there are from n start start to n end The indexed symbols are assigned. Alternatively, (n start , n symbol ) indication can be used to indicate from nstart start n symbol consecutive symbols are assigned, i.e., until the index (n start +n symbol -1) until the code unit. In other words, information about the start symbol and the duration of the assigned consecutive symbols can be signaled. this requires bits are used for indication. For example, if N=14, an indication with 8 bits is necessary.
Embodiment 3
[0077] Embodiment 3: Indication of consecutively allocated symbols
[0078] Figure 7 The diagram illustrates an example of a configuration-based indication of consecutively allocated symbols according to an embodiment of the disclosure.
[0079] refer to Figure 7 , to further reduce overhead, a tree-based signaling method can be used to indicate if consecutive symbols are always assigned. A resource indication value (RIV) can be signaled in order to derive the index n of the starting symbol start and the number of assigned consecutive symbols n symbol . RIV and n start / n symbol The relationship between can be expressed as follows:
[0080] -if Then RIV=N(n symbol -1)+n start
[0081] - else (i.e., Then RIV=N(N-n symbol +1)+(N-1-n start )
[0082] this requires bits are used for indication. For example, if N=14, an indication with 7 bits is necessary. exist Figure 7 An example in the case of N=6 is shown in .
[0083] Frequency Domain Resource Co...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com