A data security method and system for MapReduce calculation
A mapreduce framework and data security technology, applied in the direction of digital data protection, computing, electronic digital data processing, etc., can solve the problem of unpredictable time-consuming
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
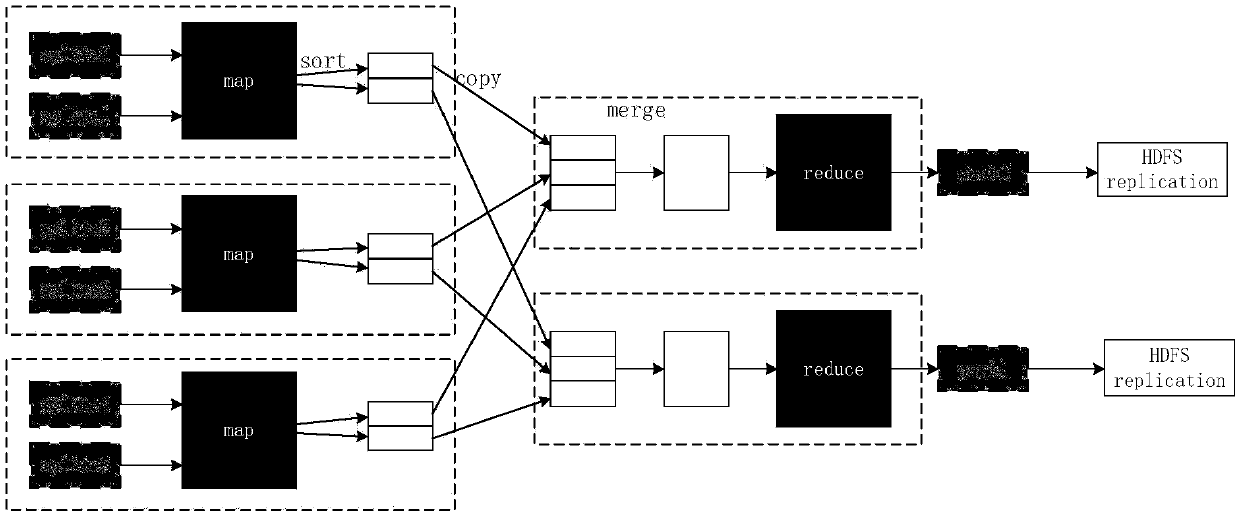
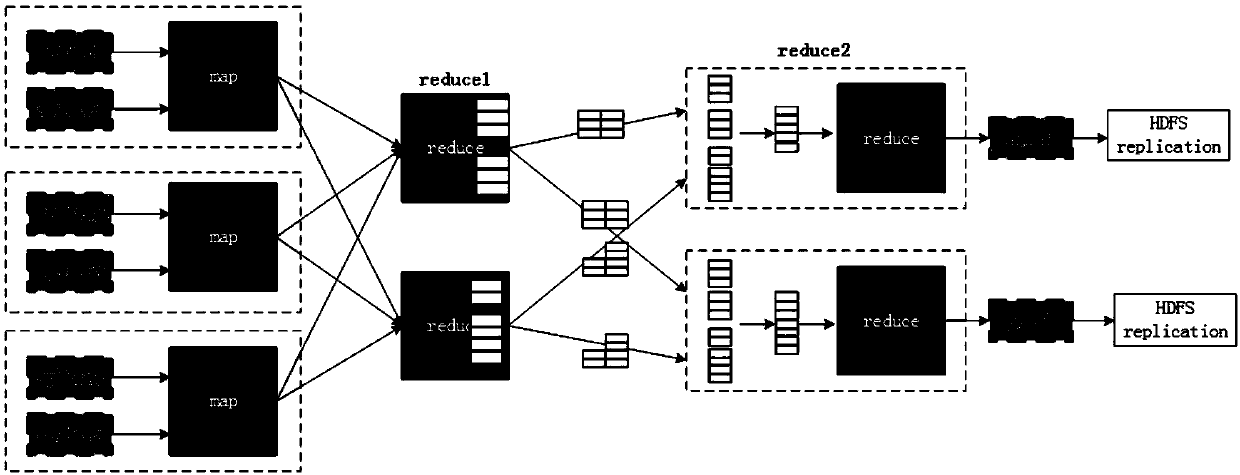
[0072] See image 3 As shown, compared with the standard MapReduce process, this embodiment mainly modifies the partition function of the map phase and adds another reduce phase in the rewriting of the MapReduce execution process. Another reduce stage added before the standard reduce is called reduce1, and the standard reduce is rewritten as reduce2 in the present invention. The rewritten MapReduce conforms to the indistinguishability of map output, and the amount of data received by each reduce task that conforms to the indistinguishability of the input at the reduce end is the same.
[0073] Suppose the data set input used by the user to submit the job is D, |D| represents the input data size, M represents the number of map tasks, R represents the number of reduce tasks in reduce1 and the number of reduce tasks in reduce2 (that is, the number of reduce tasks in reduce1 and reduce2 The number of reduce tasks is equal). The processing methods of the map phase, the reduce1 phase,...
Embodiment approach 2
[0079] This embodiment uses the method of adding fake data to realize the confidentiality of the data, and at the same time protects the number of key types K. In this embodiment, MapReduce is rewritten to meet the indistinguishability of the map output. The indistinguishability of the input at the reduce end is not equal, but after random addition and marking, it has no post-statistical speculation significance.
[0080] See Figure 4 As shown, compared with the standard MapReduce process, this embodiment mainly modifies the partition function of the map phase and adds another reduce phase in the rewriting of the MapReduce execution process. Another reduce stage added before the standard reduce is called reduce1, and the standard reduce is rewritten as reduce2 in the present invention.
[0081] Suppose the data set input used by the user to submit the job is D, |D| represents the input data size, M represents the number of map tasks, R represents the number of reduce tasks in redu...
Embodiment approach 3
[0090] This embodiment uses the method of adding fake data to realize data confidentiality, and at the same time protects the number of key types K. In this embodiment, MapReduce is rewritten to conform to the indistinguishability of the map output, and the amount of data received by each reduce task that conforms to the indistinguishability of the input at the reduce end is the same.
[0091] See Figure 5 As shown, compared with the standard MapReduce process, this embodiment mainly modifies the partition function of the map phase and adds another reduce phase in the rewriting of the MapReduce execution process. Another reduce stage added before the standard reduce is called reduce1, and the standard reduce is rewritten as reduce2 in the present invention.
[0092] Suppose the data set input used by the user to submit the job is D, |D| represents the input data size, M represents the number of map tasks, R represents the number of reduce tasks in reduce1 and the number of reduce ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com