Flat-head Chinese zither for children
A flat head, children's technology, applied in the direction of stringed instruments, instruments, musical instruments, etc., can solve the problems of affecting the effect of practice and performance, the reduction of volume and timbre, and not suitable for learning pianos, etc., to achieve convenient placement of music scores, accurate timbre, and convenient carrying and collection Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
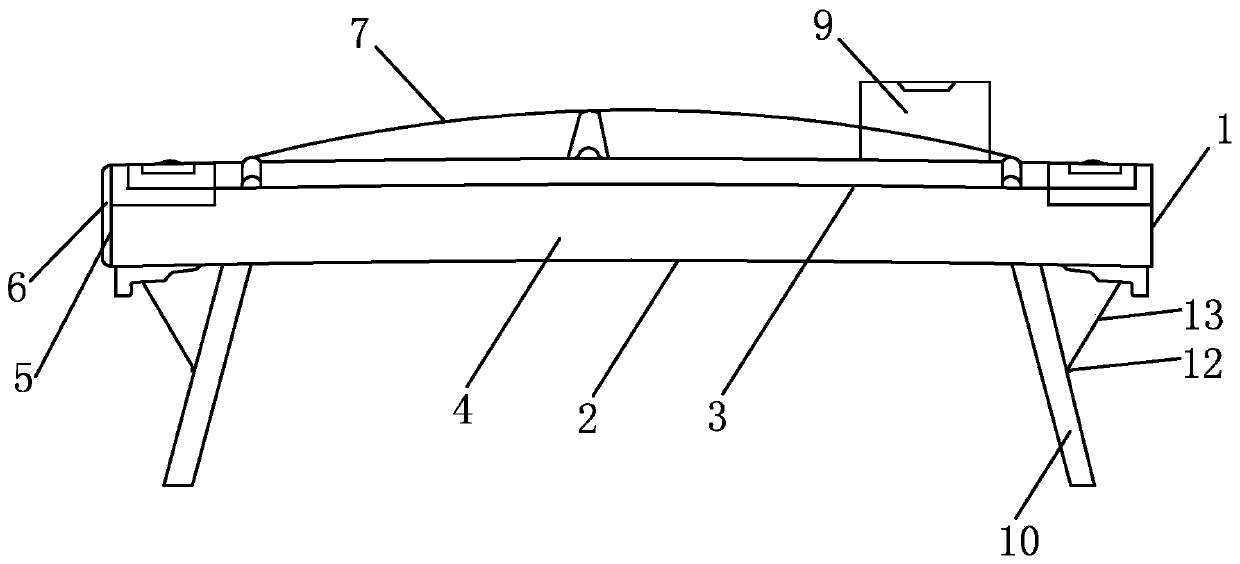
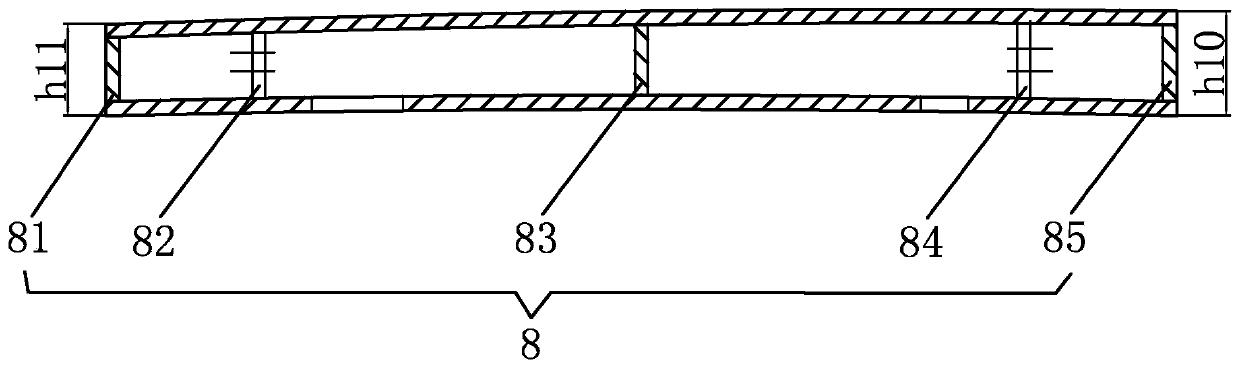
[0037] Embodiment 1: as Figure 1-Figure 5 As shown, a flat-headed zither for children comprises an inner frame 8, an outer side plate 4, a sound board 3, a bottom plate 2, a headboard 1, a tail plate 5, strings 7 and string codes, and the top of the inner frame 9 is arranged Soundboard 3, the base plate 2 is arranged at the bottom, the connecting bracket 10 is rotatable under the base plate 2, the string code is arranged on the soundboard 3, the outer panels 4 are arranged on both sides of the inner frame 9, the headboard 1 and the tailboard 5 are arranged at both ends, Such as Figure 7 As shown, the inner frame 9 is a frame structure surrounded by two inner plates 86 and two end plates. The sub-board I 82, the end plate II 82 near the headstock is provided with the sub-board II 84 for adjusting the tension of the strings 7, and the sound beam 83 is set in the middle between the sub-board I 82 and the sub-board II 84 in the frame structure, and the top of the sound beam 83 ...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Embodiment 2: This example is different from Embodiment 1 in that: the angle α between the slopes on both sides of the arc edge of the sound beam 83 described in this example and the horizontal plane is 55°, and the height h1 between the center of the arc edge and the bottom edge It is 106mm.
[0050] The thickness of the sound beam 83 is 12mm, and the two sound holes on it are symmetrical. The width M1 of the middle column between the two sound holes is 16mm. The distance from M3 is 16mm.
[0051] The maximum distance h2 between the arc-shaped top and the bottom of the sub-plate I 82 is 96 mm; the maximum distance h3 between the arc-shaped top and the bottom of the sub-plate II 84 is 106 mm.
[0052] The distance W1 between the Xiao sub-board I82 and the end board I81 of the piano tail is 95 mm; the distance W2 between the Xiao sub-board II 84 and the end board II 85 of the piano head is 112 mm, and the distance between the sound beam 83 and the Xiao sub-board I 82 an...
Embodiment 3
[0056] Embodiment 3: This example is different from Embodiment 1 in that: the angle α between the slopes on both sides of the arc edge of the sound beam 83 described in this example and the horizontal plane is 65°, and the height h1 between the center of the arc edge and the bottom edge It is 102mm.
[0057] The thickness of the sound beam 83 is 8mm, and the two sound holes on it are symmetrical, the width M1 of the middle column between the two sound holes is 12mm, the distance M2 between the two sound holes and the two ends of the sound beam is 8mm, and the distance between the sound holes and other boundaries The distance from M3 is 12mm.
[0058] The maximum distance h2 between the arc-shaped top and the bottom of the sub-plate I 82 is 92 mm; the maximum distance h3 between the arc-shaped top and the bottom of the sub-plate II 84 is 102 mm.
[0059] The distance W1 between the Xiao sub-board I82 and the end board I81 of the piano tail is 90mm; the distance W2 between the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com