Failure monitoring system and method of engine intake electronic decompression valve
A failure monitoring and engine technology, which is applied in the direction of engine components, machines/engines, mechanical equipment, etc., can solve problems such as single factors, limited use range, complex calculations, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
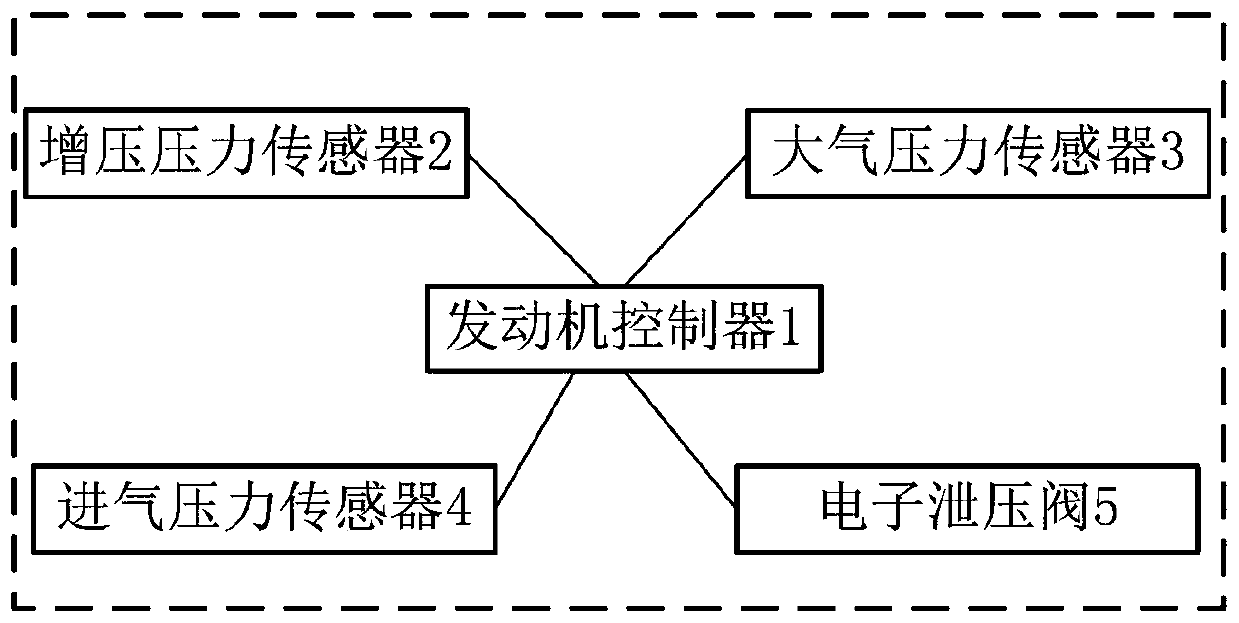
[0084] like figure 1 As shown, a failure monitoring system for an engine intake electronic pressure relief valve includes an engine controller 1 , a boost pressure sensor 2 , an atmospheric pressure sensor 3 , an intake pressure sensor 4 , and an electronic pressure relief valve 5 .
[0085] The engine controller 1 is the Engine Management System, referred to as EMS.
[0086] The boost pressure sensor 2 is arranged behind the engine intake compressor, used to detect the gas pressure at the outlet of the engine intake compressor, and is connected with the engine controller.
[0087] The atmospheric pressure sensor 3 is used to detect the atmospheric pressure and is connected with the engine controller.
[0088] The intake air pressure sensor 4 is arranged behind the throttle valve, is used for detecting the gas pressure behind the throttle valve, and is connected with the engine controller.
[0089] The electronic pressure relief valve 5 is used to guide the airflow to the fr...
Embodiment 2
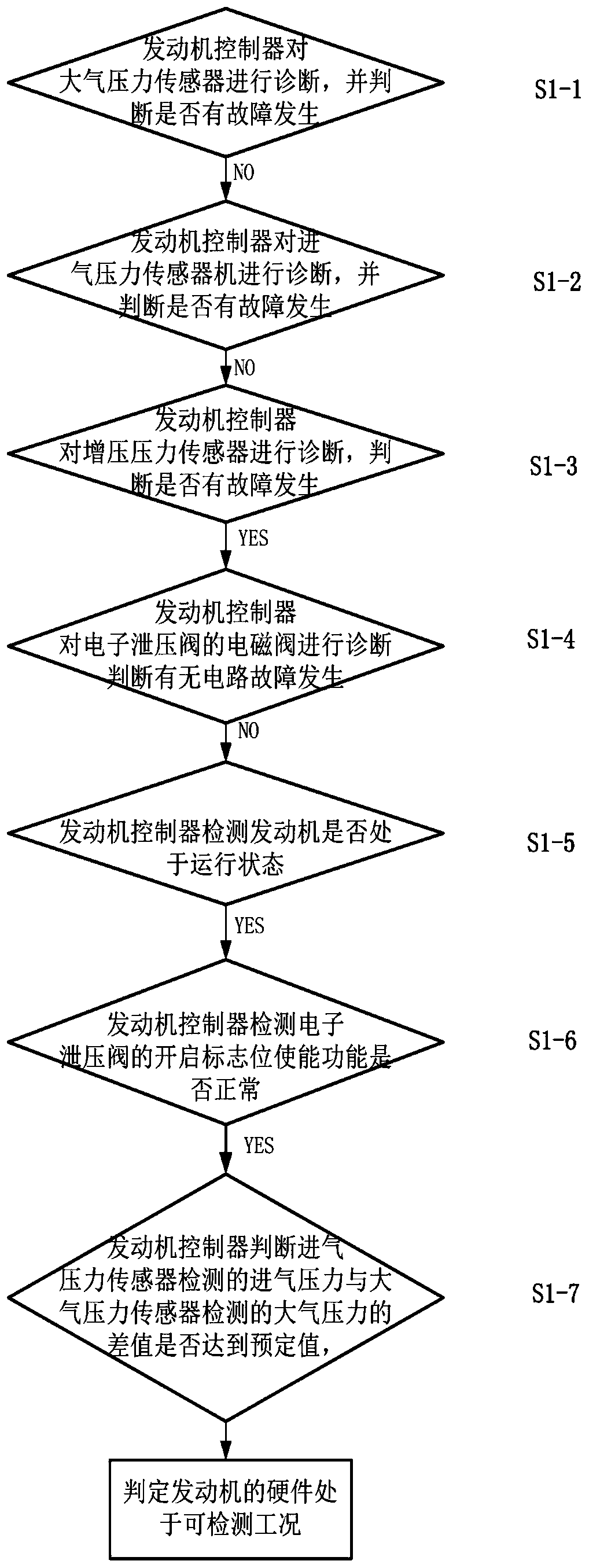
[0108] image 3 is a sub-step schematic diagram of step S1 in the embodiment of the present invention.
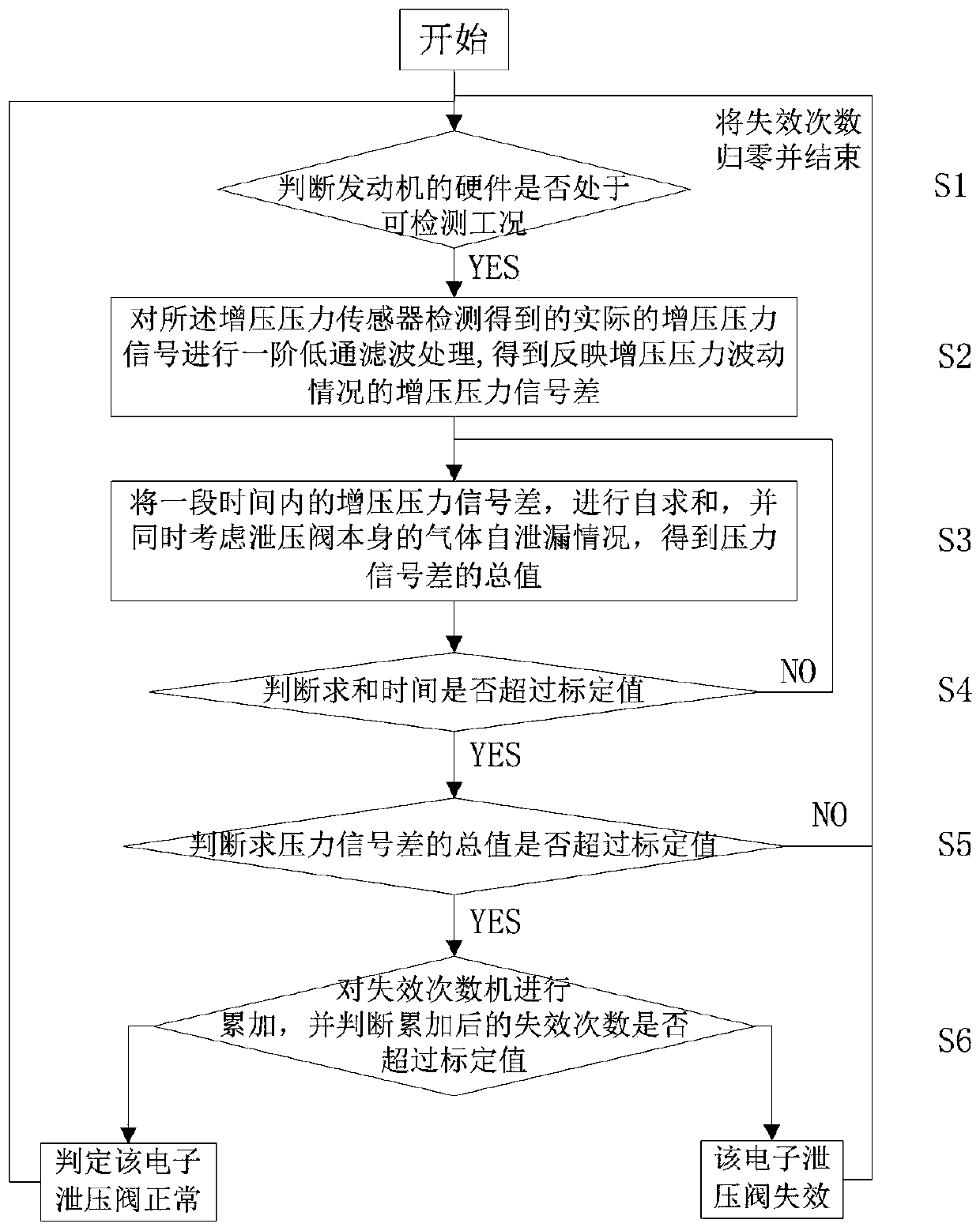
[0109] On the basis of Embodiment 1, this embodiment further optimizes the detection method of whether the engine is in a detectable working condition, specifically including:
[0110] Step S1-1, the engine controller diagnoses the atmospheric pressure sensor and judges whether there is a fault, if not, proceed to the next step;
[0111] Step S1-2, the engine controller diagnoses the intake pressure sensor, and further judges whether there is a fault, if not, proceed to the next step;
[0112] Step S1-3, the engine controller diagnoses the boost pressure sensor, and further judges whether there is a fault, and if so, proceed to the next step;
[0113] Step S1-4, the engine controller diagnoses the solenoid valve of the electronic pressure relief valve, and judges whether there is a circuit fault, and if not, proceed to the next step;
[0114] Step S1-5, the engine contro...
Embodiment 3
[0119] On the basis of Embodiment 1, this embodiment further optimizes the detection method of whether the engine is in a detectable working condition, when the following conditions are all satisfied:
[0120] The engine controller diagnoses the atmospheric pressure sensor, and no fault occurs;
[0121] The engine controller diagnoses the intake air pressure sensor, and no fault occurs;
[0122] The engine controller diagnoses the boost pressure sensor, and a fault occurs;
[0123] The engine controller diagnoses the solenoid valve of the electronic pressure relief valve, and no circuit failure occurs;
[0124] The engine controller detects that the engine is running;
[0125] The engine controller detects that the enable function of the open flag of the electronic pressure relief valve is normal;
[0126] The engine controller judges that the difference between the intake air pressure detected by the intake pressure sensor and the atmospheric pressure detected by the atmos...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com