A rendezvous and approach method with minimum velocity increment
A Speed, Rendezvous Technology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
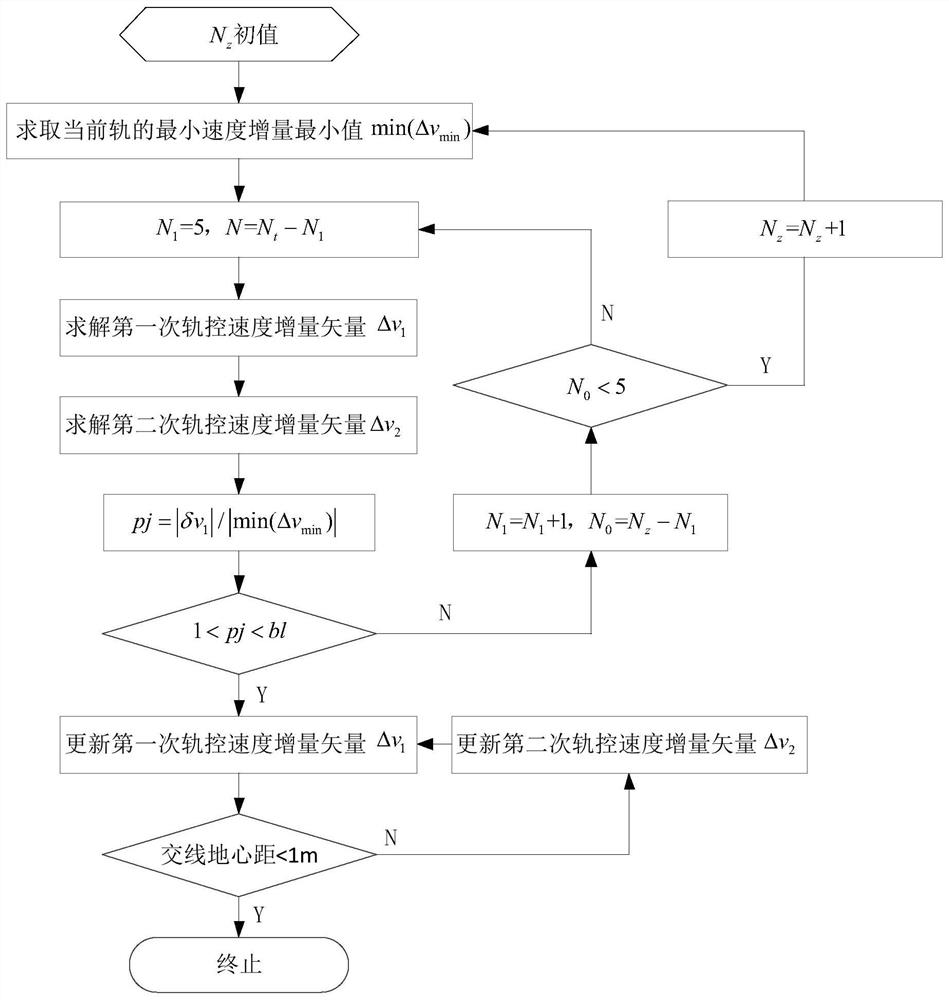
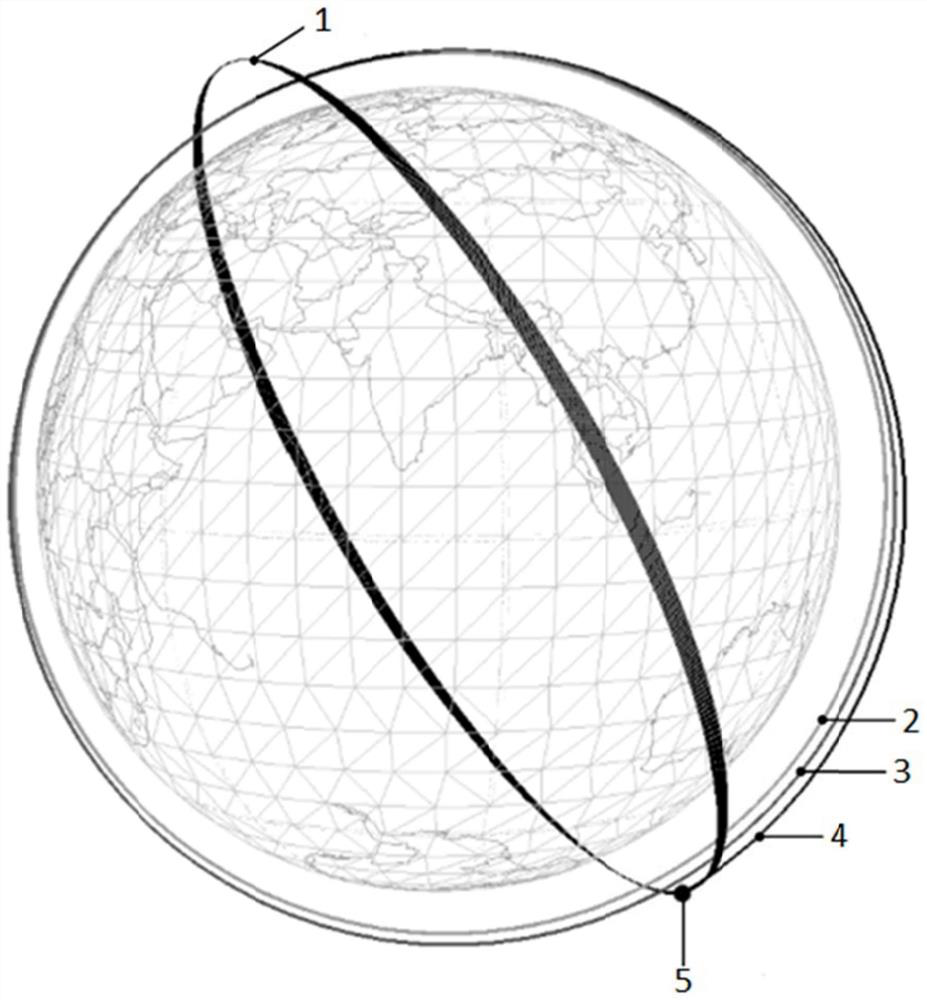
[0035] The rendezvous and approach method of this embodiment first obtains the position, velocity, atmospheric resistance, windward surface-to-mass ratio, light pressure coefficient, and light-pressure-to-surface-to-mass ratio of the maneuvering satellite and the target satellite according to the measured orbit, and accurately extrapolates through tools such as stk or matlab to obtain Parking track position speed (R P ,V P ), target orbital position velocity (R T ,V T ), the subscript P is the parking orbit, and T is the target orbit. When the mobile satellite and the target satellite orbit are in different planes, the calculation steps of the entire rendezvous are as follows:
[0036] (1) Solve the intersection vector and related parameters
[0037] The orbital specific angular momentum of the maneuvering satellite:
[0038] h P = R P ×V P (1)
[0039] Let the Z-axis vector of the coordinate system under the inertial coordinate system be: K=[0 0 1]'
[0040] Parking...
Embodiment 2
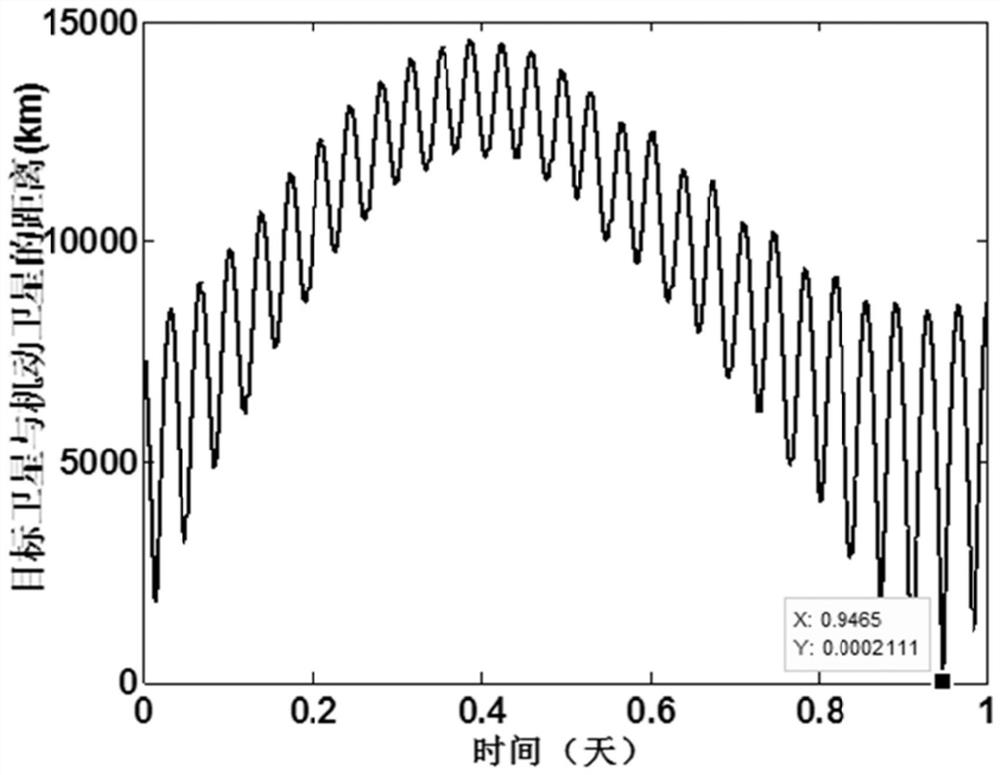
[0305]Embodiment one is the calculation steps of the different-orbit plane between the mobile satellite and the target satellite. This implementation is aimed at the same-orbit plane between the mobile satellite and the target satellite. Same, the details are as follows: when different orbital planes are used, only the intersection point with the smaller difference in geocentric distance of the intersecting lines can be used as the intersection point, but there is no such rule for the same orbital plane, because there is no intersection line vector on the same orbital plane, so the target The statistics of the number of satellite orbits are directly counted by the latitude argument, that is, when the latitude argument is covered once between 0 and 360 degrees, the number of circles is increased by one circle. When the target satellite takes the Kth orbit as a possible rendezvous circle, the Kth The target orbit is equally divided into 360 points as the possible rendezvous point...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com