Main processor error detection using checker processors
A main processor, error detection technology, applied in the field of data processing, can solve problems such as increasing transient faults
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
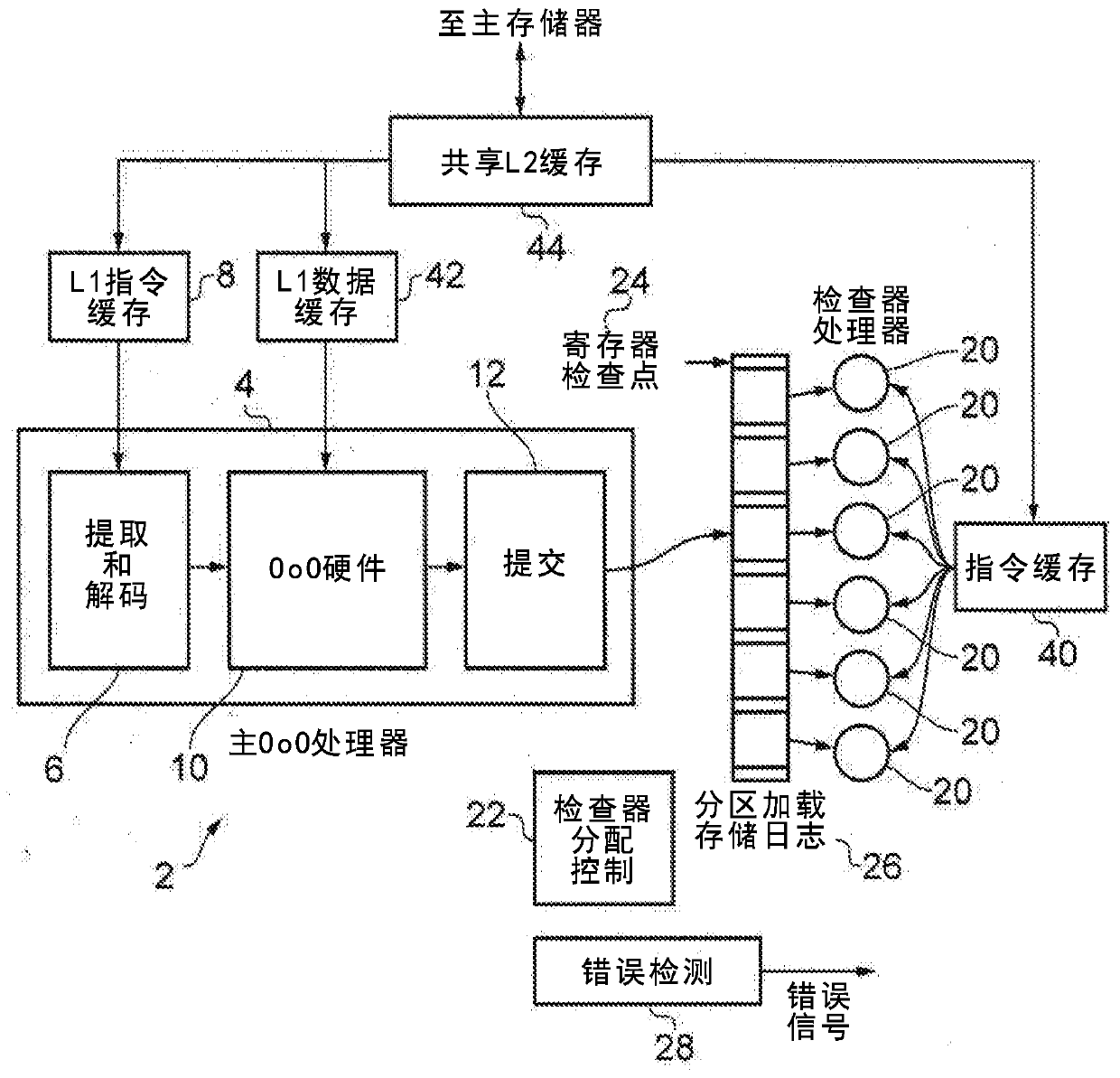
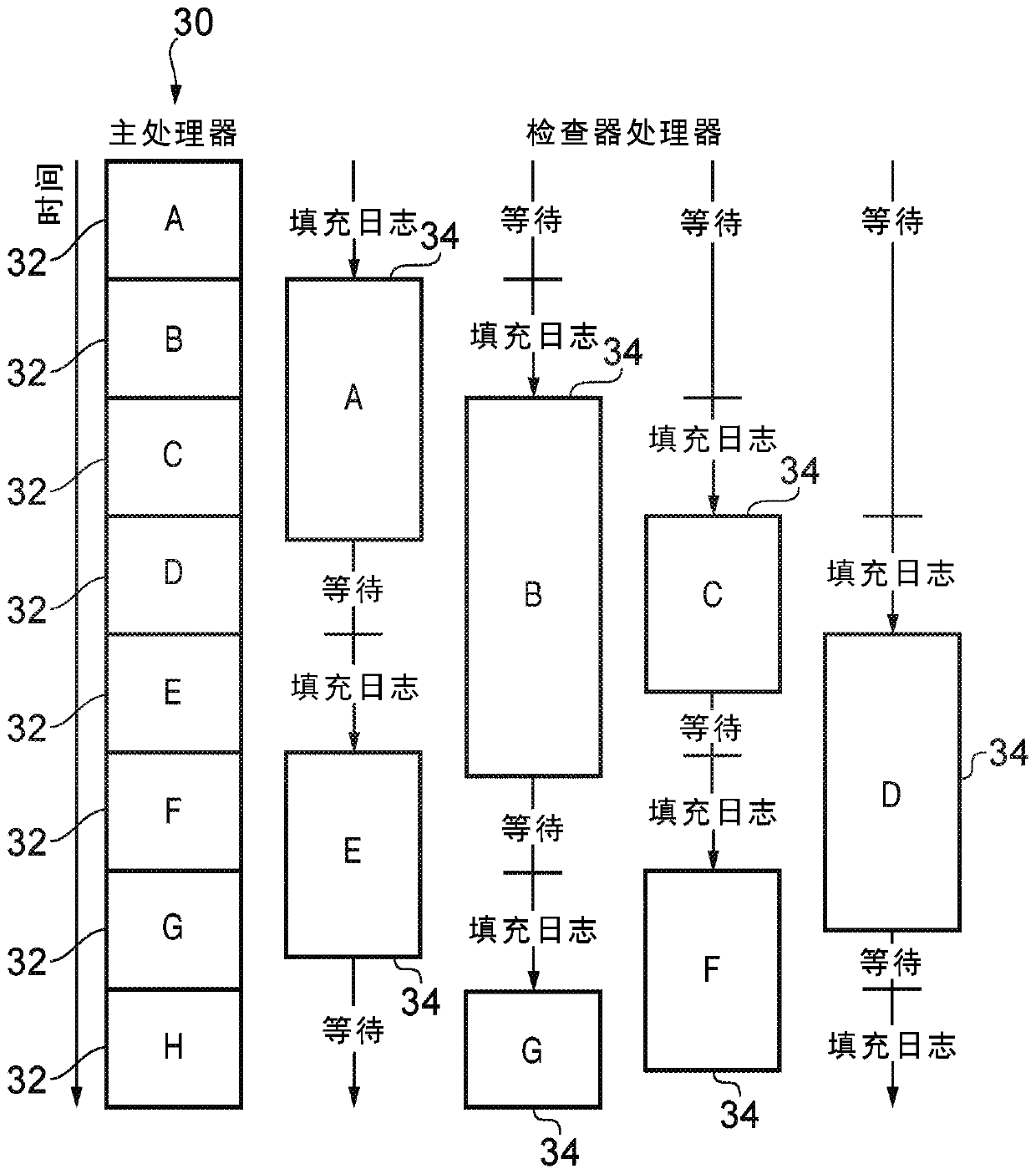
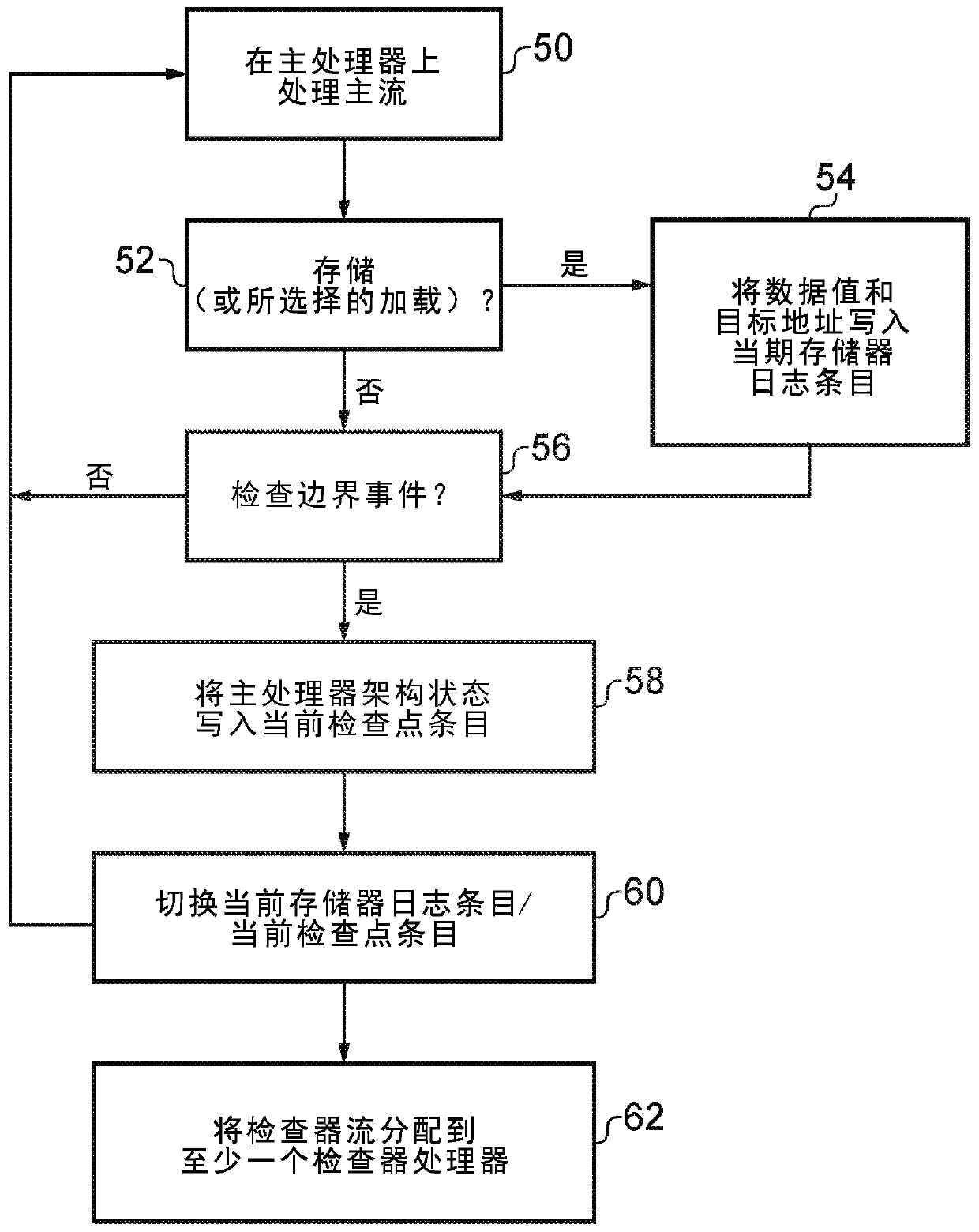
[0017] Implementing error detection can be challenging, especially with larger and more complex processors. One approach may use a dual-core lockstep technique, where two versions of the same processor are provided and the same instruction is executed in parallel on the same input, so that there can be a gap between the results of the two processors. An error was detected while diffing. However, this approach requires the second core to keep pace with the first core, so a full second core identical to the first core must be provided, doubling the area and power consumption of the processing system. This can be a significant cost, especially when the host processor is a relatively complex high-performance processor (eg, one that supports out-of-order execution). Furthermore, since many interfaces of the corresponding cores are compared to detect errors, a lot of extra wiring will be required. For more complex processors, due to the physical size of these processors and the re...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com