Variable-conductance nano control method and system used for robot
A control method and control system technology, applied in the variable admittance control method and system field of robots, can solve the problems of inability to quickly and sensitively respond to operator intentions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
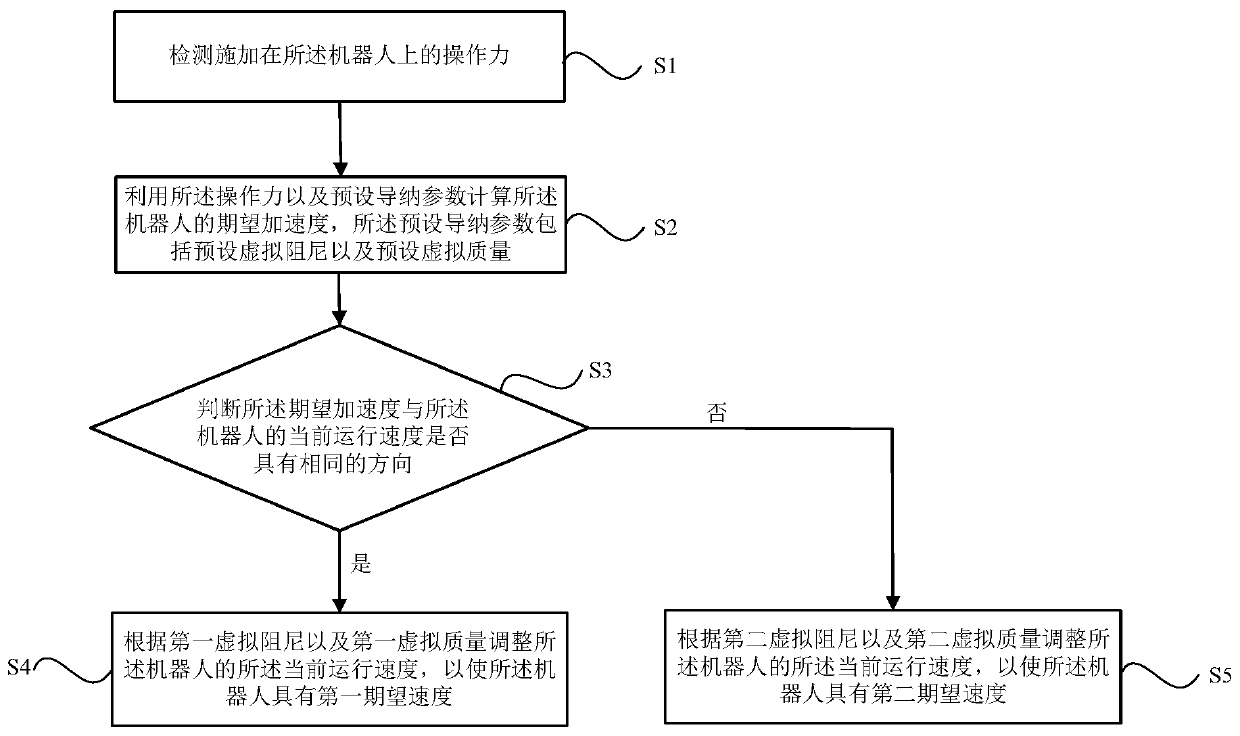
[0068] This embodiment provides a variable admittance control method for a robot, such as figure 1 As shown, the variable admittance control method may include the following steps:
[0069] Step S1: detecting the operating force applied to the robot;
[0070] Step S2: Calculate the expected acceleration of the robot by using the operating force and preset admittance parameters, the preset admittance parameters including preset virtual damping and preset virtual mass;
[0071] Step S3: judging whether the expected acceleration and the current running speed of the robot have the same direction;
[0072] If the judgment result is yes, execute step S4: adjust the current running speed of the robot according to the first virtual damping and the first virtual mass, so that the robot has a first desired speed, wherein the first virtual The damping is smaller than the preset virtual damping, and the first virtual mass is smaller than the preset virtual mass. At this time, since the...
Embodiment 2
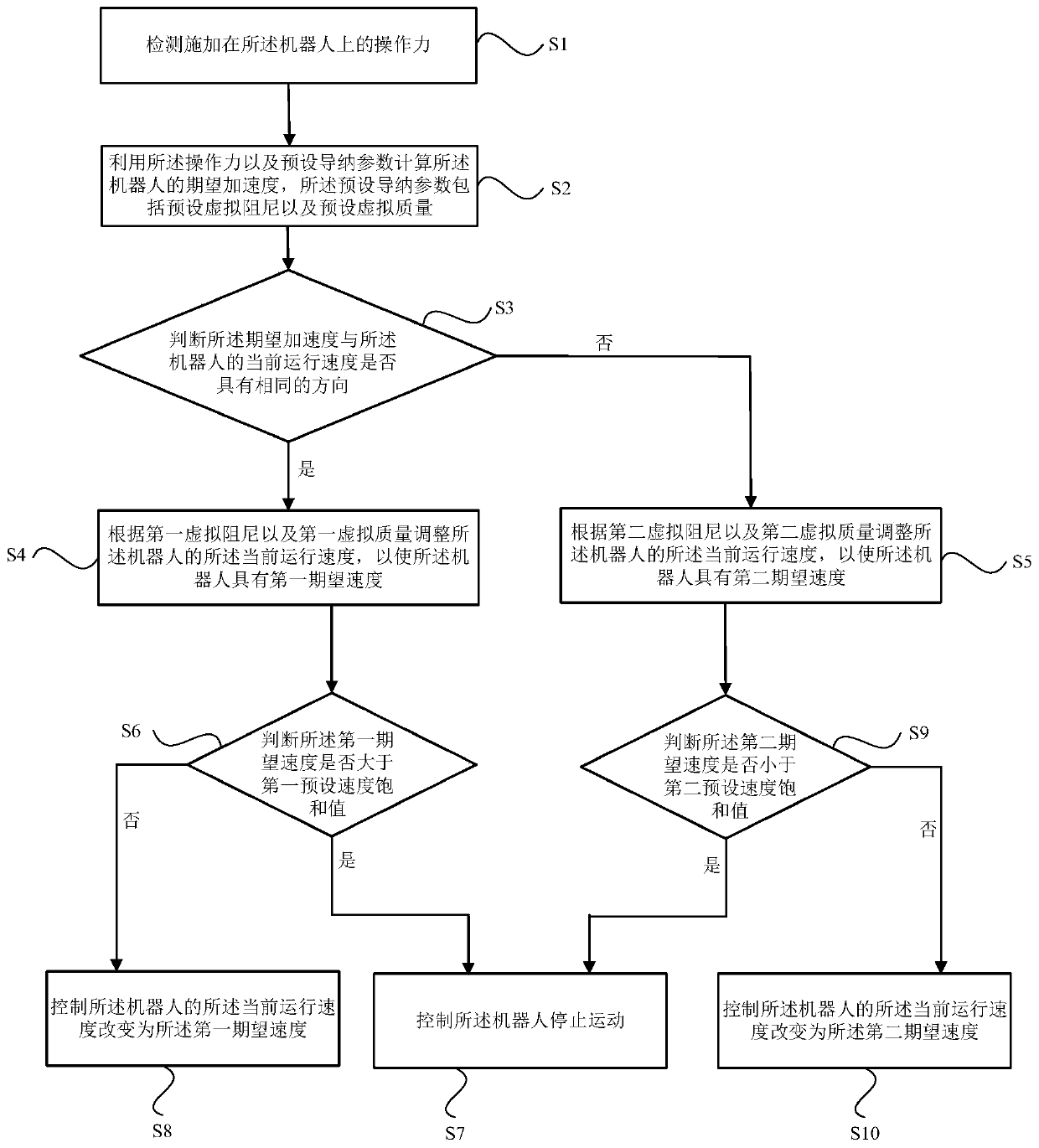
[0113] This embodiment provides a variable admittance control method for a robot, such as figure 2 As shown, this embodiment is a further improvement on the basis of Embodiment 1.
[0114] Specifically, the variable admittance control method may also include the following steps:
[0115] Step S6: judging whether the first desired speed is greater than a first preset speed saturation value;
[0116] If the judgment result is yes, execute step S7: control the robot to stop moving;
[0117] If the judgment result is no, then perform step S8: control the current running speed of the robot to change to the first desired speed.
[0118] Further, the variable admittance control method may also include the following steps:
[0119] Step S9: judging whether the second expected speed is less than a second preset speed saturation value;
[0120] If the judgment result is yes, execute step S7: control the robot to stop moving;
[0121] If the judgment result is no, execute step S10:...
Embodiment 3
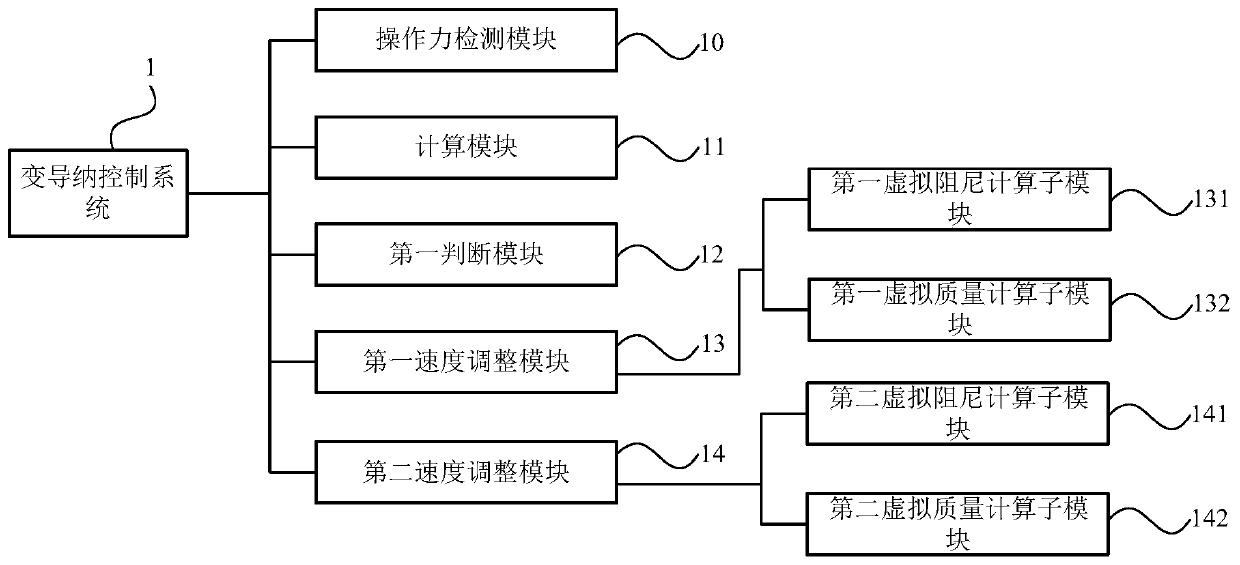
[0126] This embodiment provides a variable admittance control system for a robot, such as image 3 As shown, the variable admittance control system 1 may include:
[0127] An operating force detection module 10, configured to detect the operating force applied to the robot;
[0128] The calculation module 11 is used to calculate the expected acceleration of the robot by using the operating force and preset admittance parameters, and the preset admittance parameters include preset virtual damping and preset virtual mass;
[0129] A first judging module 12, configured to judge whether the expected acceleration and the current running speed of the robot have the same direction;
[0130] If the judgment result is yes, then call the first speed adjustment module 13, the first speed adjustment module is used to adjust the current running speed of the robot according to the first virtual damping and the first virtual mass, so that the robot It has a first desired speed, wherein the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com