Low-driving-potential aluminum alloy sacrificial anode for seawater and preparation method thereof
A sacrificial anode and low drive technology, which is applied in the field of corrosion protection of hydrogen embrittlement sensitive material structures, can solve the problems of poor activation performance of aluminum alloy sacrificial anodes, failure to achieve protection effect, uneven distribution, etc., to reduce casting defects , long service life, uniform dissolution improvement effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
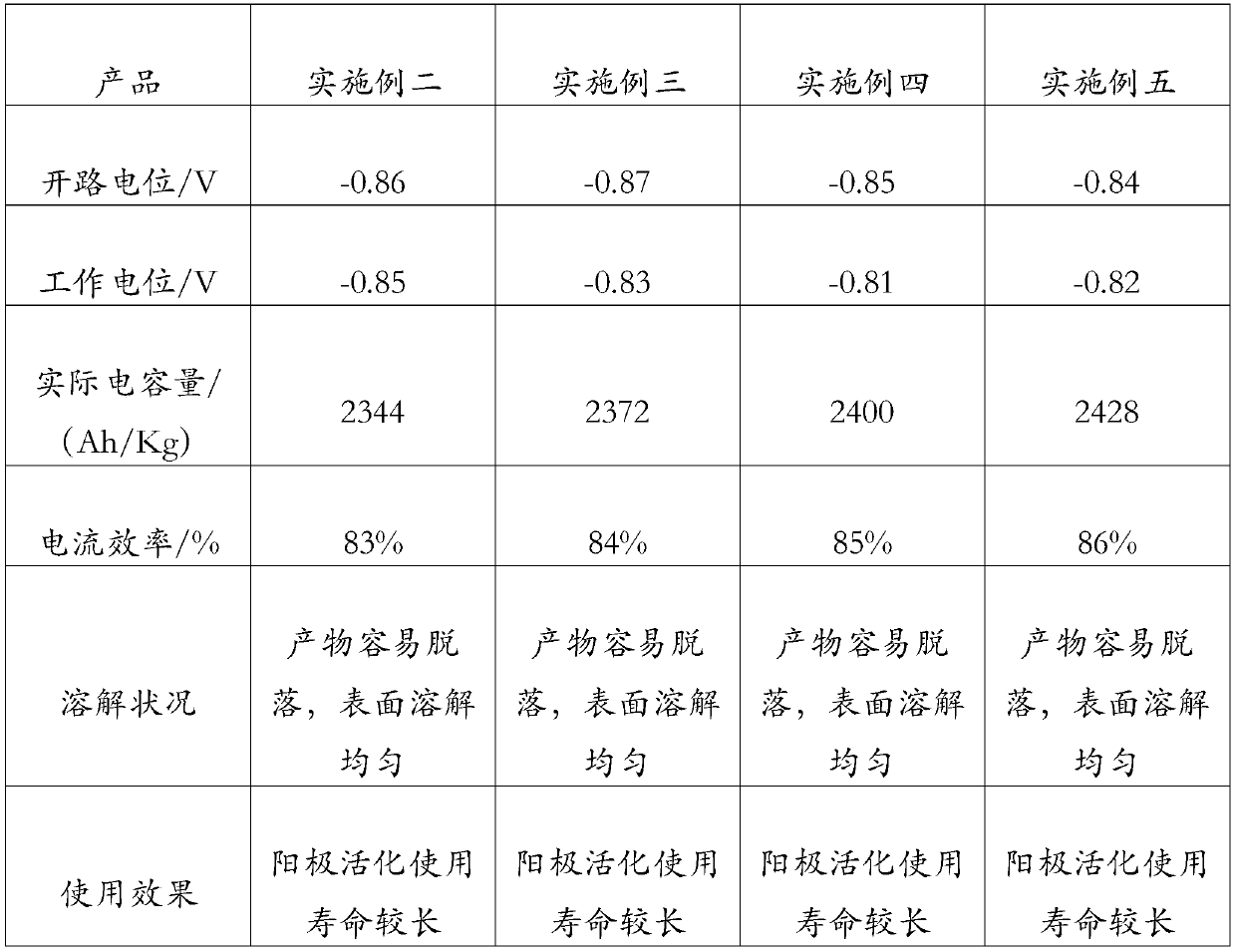
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] A low driving potential aluminum alloy sacrificial anode suitable for seawater, comprising the following raw materials in weight percentage: 85% of aluminum, 2% of zinc, 1% of bismuth, 0.05% of manganese, and 0.02% of gallium.
[0023] The preparation method of the low driving potential aluminum alloy sacrificial anode suitable for seawater comprises the following steps:
[0024] (1) Under the protection of dynamic inert gas, aluminum is added into the smelting furnace, heated and melted to obtain molten aluminum;
[0025] (2) preheat manganese, bismuth, zinc, gallium, remove contained moisture, then drop manganese, bismuth, zinc into aluminum liquid, stir and add gallium after fully dissolving, continue to stir and keep warm for a period of time;
[0026] (3) Casting with a cast steel mold, and quenching the casted product by spraying water to obtain the low driving potential aluminum alloy sacrificial anode suitable for seawater.
Embodiment 2
[0028] A low driving potential aluminum alloy sacrificial anode suitable for seawater, comprising the following raw materials in weight percentage: 85% of aluminum, 2% of zinc, 1% of bismuth, 0.05% of manganese, and 0.02% of gallium.
[0029] The preparation method of the low driving potential aluminum alloy sacrificial anode suitable for seawater comprises the following steps:
[0030] (1) Under the protection of dynamic inert gas nitrogen, aluminum is added into the smelting furnace, heated and melted at a temperature of 730°C to obtain molten aluminum;
[0031] (2) Preheat manganese, bismuth, zinc, and gallium at a temperature of 100°C for 8 minutes to remove the contained water, then put manganese, bismuth, and zinc into the aluminum liquid, stir them with permanent magnetic stirring, and then add gallium , continue to stir and keep warm for 10 minutes;
[0032] (3) Preheat the cast steel mold at a temperature of 300°C for 15 minutes, then cast it with a cast steel mold a...
Embodiment 3
[0034] A low driving potential aluminum alloy sacrificial anode suitable for seawater, comprising the following raw materials in weight percentage: 86% of aluminum, 3% of zinc, 1% of bismuth, 0.06% of manganese, and 0.02% of gallium.
[0035] The preparation method of the low driving potential aluminum alloy sacrificial anode suitable for seawater comprises the following steps:
[0036] (1) Under the protection of dynamic inert gas nitrogen, aluminum is added into the smelting furnace, heated and melted at a temperature of 750°C to obtain molten aluminum;
[0037] (2) Preheat manganese, bismuth, zinc, and gallium at a temperature of 120°C for 9 minutes to remove the contained water, then put manganese, bismuth, and zinc into the aluminum liquid, stir them with permanent magnetic stirring, and then add gallium , continue to stir and keep warm for 12 minutes;
[0038] (3) Preheat the cast steel mold at a temperature of 320°C for 18 minutes, then cast it with a cast steel mold a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com