Hyperspectral remote sensing image segmentation method based on K-means clustering
A k-means clustering and hyperspectral remote sensing technology, applied in the fields of instruments, character and pattern recognition, computer parts, etc., can solve the problems of inaccurate segmentation of hyperspectral remote sensing images and insufficient use of a large amount of information in hyperspectral remote sensing images. , to achieve accurate segmentation results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
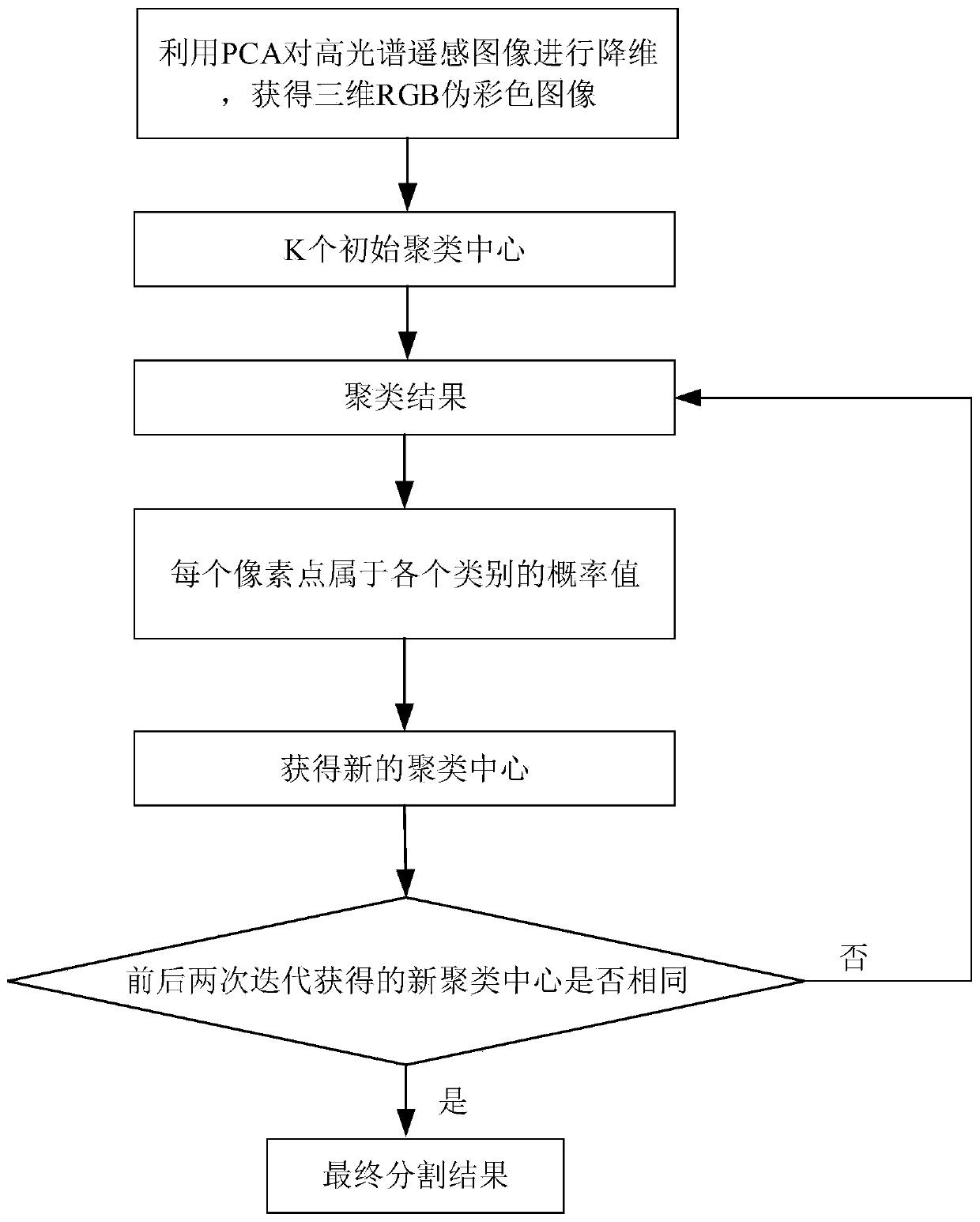
[0023] Specific implementation mode one: as figure 2 Shown: a kind of hyperspectral remote sensing image segmentation method based on K-means clustering described in the present embodiment, this method comprises the following steps:
[0024] Step 1, using principal component analysis (Principal Component Analysis, PCA) to reduce the dimensionality of the hyperspectral remote sensing image to obtain a three-dimensional RGB pseudo-color image, the dimension of the hyperspectral remote sensing image is d;
[0025] Use the K-means method (K value needs to be specified in advance) to cluster and segment the obtained 3D RGB pseudo-color image, and obtain K cluster centers of the cluster segmentation results; use the obtained K cluster centers as hyperspectral remote sensing images The initial cluster centers of each dimension of ;
[0026] Step 2, using the initial clustering center to cluster each pixel in each dimension in the hyperspectral remote sensing image, and obtain the c...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0034] Specific implementation mode two: the difference between this implementation mode and specific implementation mode one is: the specific process of said step two is:
[0035] Use the initial clustering center to cluster each pixel in each dimension in the hyperspectral remote sensing image, that is, assign each pixel in each dimension to the nearest clustering center according to the Euclidean distance , to obtain the clustering result.
[0036] For the i'th pixel in the hyperspectral remote sensing image, assign the spectral value of the i'th pixel to the initial clustering center closest to the i'th pixel. Similarly, for the hyperspectral remote sensing image For each pixel in , perform the same operation until all clustering is completed.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0037] Specific implementation mode three: the difference between this implementation mode and specific implementation mode two is: the specific process of the step three is:
[0038] The d-dimensional label vector X of the i-th pixel in the hyperspectral remote sensing image i The expression is:
[0039] x i ={c 1 ,c 2 ,...,c d},i=1,2,...,m×n
[0040] Among them: m×n represents the total number of pixels in the hyperspectral remote sensing image, c 1 Represents the category label of the i-th pixel in the hyperspectral remote sensing image in the first dimension, c 2 Represents the category label of the i-th pixel in the hyperspectral remote sensing image in the second dimension, c d Represents the category label of the i-th pixel in the hyperspectral remote sensing image in the d-th dimension, c j The value of is [1,K], and c j The value of is a positive integer, j=1,2,...,d;
[0041] Scan each pixel in turn, and read in the category label data of each pixel;
[00...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com