Multi-party statistical query method based on differential privacy protection technology
A statistical query and differential privacy technology, applied in digital data protection, computing, computer security devices, etc., can solve the problems of complex design and difficult operation of secure multi-party computing protocols
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
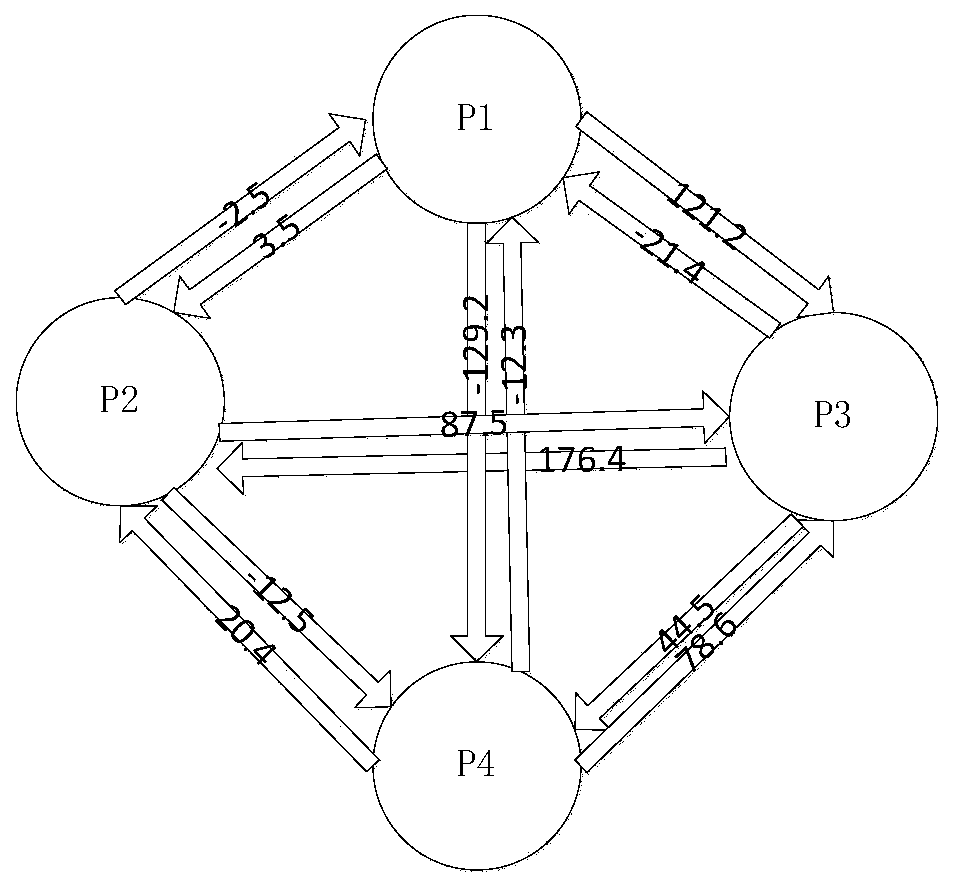
[0050] Suppose there are 4 parties involved, P 1 , P 2 , P 3 , P 4 ;
[0051] Step 1. Set P 1 , P 2 , P 3 , P 4 A number x for each of the four participants 1 = 3,x 2 = 4,x 3 =6,x 4 = 7, while assuming the selected ∈ = 0.01, u = 0;
[0052] Step 2: Set the participant P 1 , P 2 , P 3 , P 4 Each generate three satisfying Laplacian f(100,0) where b=100 is given by The obtained parameters are
[0053] x 1,2 =3.5,x 1,3 =121.2,x 1,4 =-129.2,x 2,1 =-2.5, x 2,3 =87.5,x 2,4 =-12.5, x 3,1 =-21.4,x 3,2 =176.4,x 3,4 =44.5,x 4,1 =-12.3, x 4,2 =20.4,x 4,3 =78.6;
[0054] Step three, such as figure 1 As shown, perform data exchange:
[0055] Each participant P i , Send the n-1 numbers generated by it to the remaining n-1 parties, and at the same time receive a number from the remaining n-1 parties; then update the value in your hand: subtract the n-1 numbers sent out digits, plus n-1 digits received, as follows:
[0056] P 1 to P 2 The number is 3.5, P ...
Embodiment 2
[0067] Suppose there are 4 parties involved, P 1 , P 2 , P 3 , P 4 ;
[0068] Step 1. Set P 1 , P 2 , P 3 , P 4 A number x for each of the four participants 1 = 3,x 2 = 4, x 3 =6,x 4 =7, the values of all parties are already integers, no conversion is allowed;
[0069] Step two, put x 1 , x 2 , x 3 , x 4 Convert to binary numbers: 11, 100, 110, 111;
[0070] Step three, for x 1 , x 2 , x 3 , x 4 The converted binary number is filled according to m equal to 3 digits: 011, 100, 110, 111;
[0071] Step 4: Compare sequentially from the high bit, j is equal to increasing from the 1st bit to the 3rd bit:
[0072] j=1 calls the first summation protocol, calculates that s is equal to 3, s is greater than or equal to 1, and outputs the value t 1 =1, at the same time, P 1 The binary 1 behind it is all set to 0;
[0073] j=2 calls the summation protocol, calculates that s is equal to 2, s is greater than or equal to 1, and outputs the value t 2 =1, at the same ...
Embodiment 3
[0077] Suppose there are 4 parties involved, P 1 , P 2 , P 3 , P 4 ;
[0078] Step 1. Set P 1 , P 2 , P 3 , P 4 A number x for each of the four participants 1 =1.1,x 2 =2.4,x 3 =2.6,x 4 =0.3, in order to eliminate decimal places, all parties are multiplied by 10 according to the number of decimal places, at this time the numbers of all parties become 11, 24, 26, 3;
[0079] Step two, put x 1 , x 2 , x 3 , x 4 Convert to binary numbers: 1011, 11000, 11010, 11;
[0080] Step three, for x 1 , x 2 , x 3 , x 4 The converted binary number is filled according to m equal to 3 digits: 01011, 11000, 11010, 00011;
[0081]Step 4: Compare sequentially from the high bit, j is equal to increasing from the 1st bit to the 5th bit
[0082] j=1 calls the summation protocol, calculates that s is equal to 2, s is greater than or equal to 1, and outputs the value t 1 = 1, while P 1 , P 4 Set all 1s behind it to 0;
[0083] j=2 calls the summation protocol, calculates that ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com