Intelligent follow-up surveying method of radiation image report, system, equipment and storage medium
An imaging and reporting technology, applied in medical reports, medical images, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of radiological diagnosis and pathological diagnosis that consume a lot of manpower
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0064] An intelligent follow-up method for radiology imaging reports such as figure 1 As shown, the intelligent follow-up methods include:
[0065] S10. Obtain a pathology report of a patient; the pathology report includes the time of the pathology report and the identity information of the patient;
[0066] S20. Obtain all image reports of the patient within a preset time period before the pathology report time according to the identity information;
[0067] S30. Extract the pathological diagnosis attributes in the pathology report and the image diagnosis attributes in each image report respectively;
[0068] S40. Match each group of pathological diagnosis attributes with the image diagnosis attributes in each image report;
[0069] S50. If the matching is unsuccessful, determine that the image diagnosis in the image report with unsuccessful matching is wrong; if the matching is successful, determine that the image diagnosis in the image report with successful matching is c...
Embodiment 2
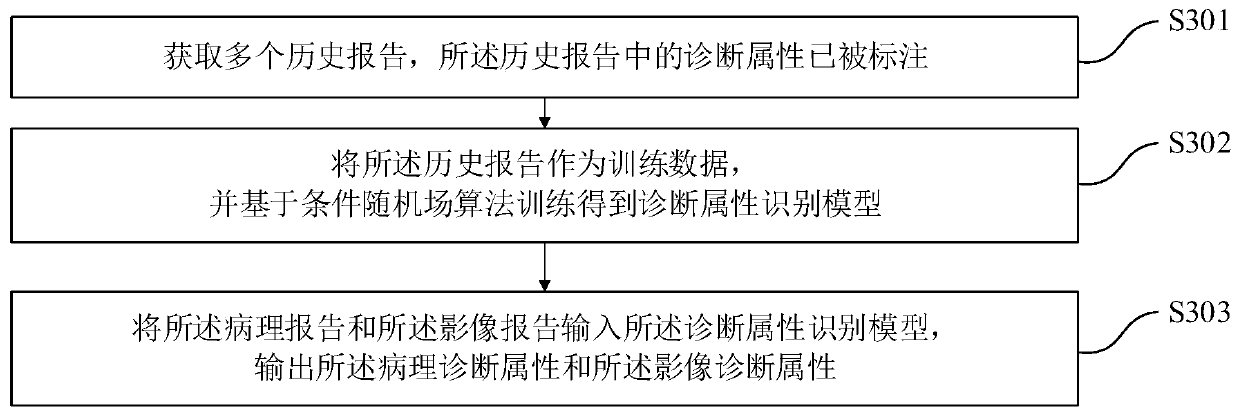
[0082] The intelligent follow-up method of the radiographic image report of the present embodiment is further improved on the basis of Embodiment 1, as figure 2 As shown, step S30 specifically includes:
[0083] S301. Obtain a plurality of historical reports, where diagnostic attributes in the historical reports have been marked;
[0084] S302. Using the historical report as training data, and training based on a conditional random field algorithm to obtain a diagnostic attribute recognition model;
[0085] S303. Input the pathology report and the image report into the diagnosis attribute recognition model, and output the pathology diagnosis attribute and the image diagnosis attribute.
[0086] In this embodiment, the historical report is marked by the medical consultant, and the diagnostic attributes (positioning, qualitative, and the attribute relationship between positioning and qualitative) in the report text are marked out, and then based on the conditional random field...
Embodiment 3
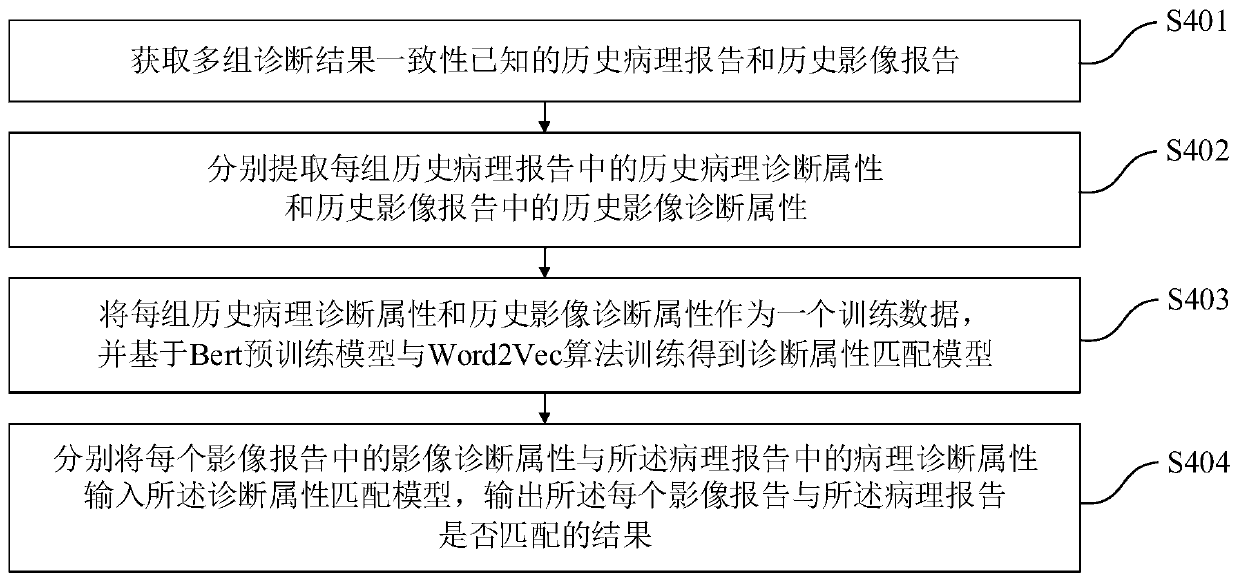
[0088] The intelligent follow-up method of the radiographic image report of the present embodiment is further improved on the basis of Embodiment 1, as image 3 As shown, step S40 specifically includes:
[0089] S401. Obtain historical pathology reports and historical image reports with known consistency of multiple groups of diagnostic results;
[0090] S402, respectively extracting the historical pathological diagnosis attributes in each group of historical pathology reports and the historical image diagnosis attributes in the historical image reports;
[0091] S403, using each group of historical pathological diagnosis attributes and historical image diagnosis attributes as a training data, and training a diagnostic attribute matching model based on the Bert pre-training model and the Word2Vec algorithm;
[0092] S404. Input the image diagnosis attribute in each image report and the pathology diagnosis attribute in the pathology report into the diagnosis attribute matching...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com