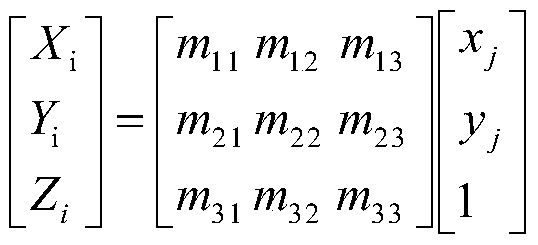Splicing method of pathological section scanning picture of microscope
A technology of pathological slices and microscopes, which is applied in the field of image processing, and can solve problems such as camera instability, small deviations, shakes, up, down, left, and right, computer inability to complete image stitching, and increased memory.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
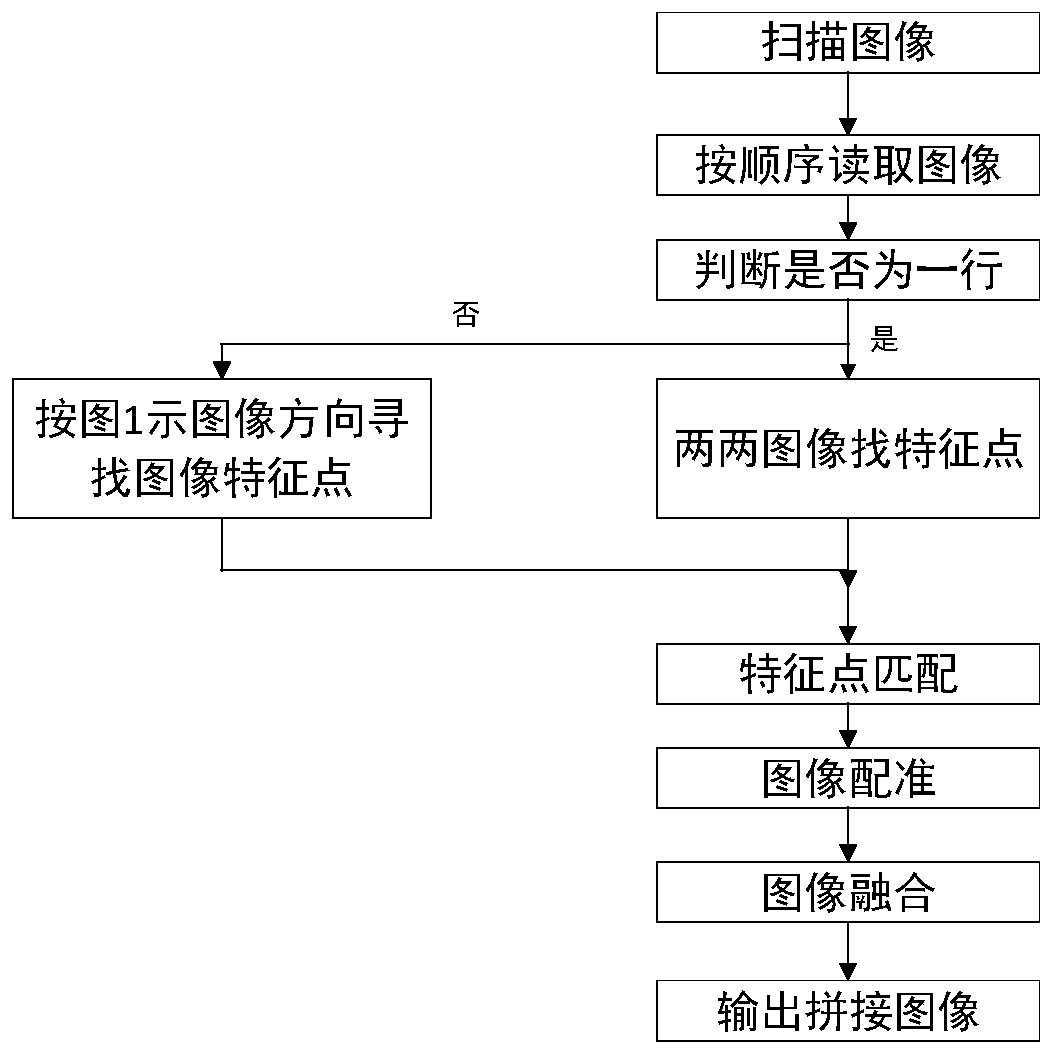
[0027] refer to figure 1 , which is the first embodiment provided in the present invention for a method for mosaicing scanned pictures of microscopic pathological sections. In this embodiment, the method for mosaicing scanned pictures of microscopic pathological sections includes the following steps:
[0028] S1, scan the image, and read the image in order, that is, read the image scanned by the high-power microscope, and place it in order.
[0029] S2, the high power microscope searches for feature points of the image.
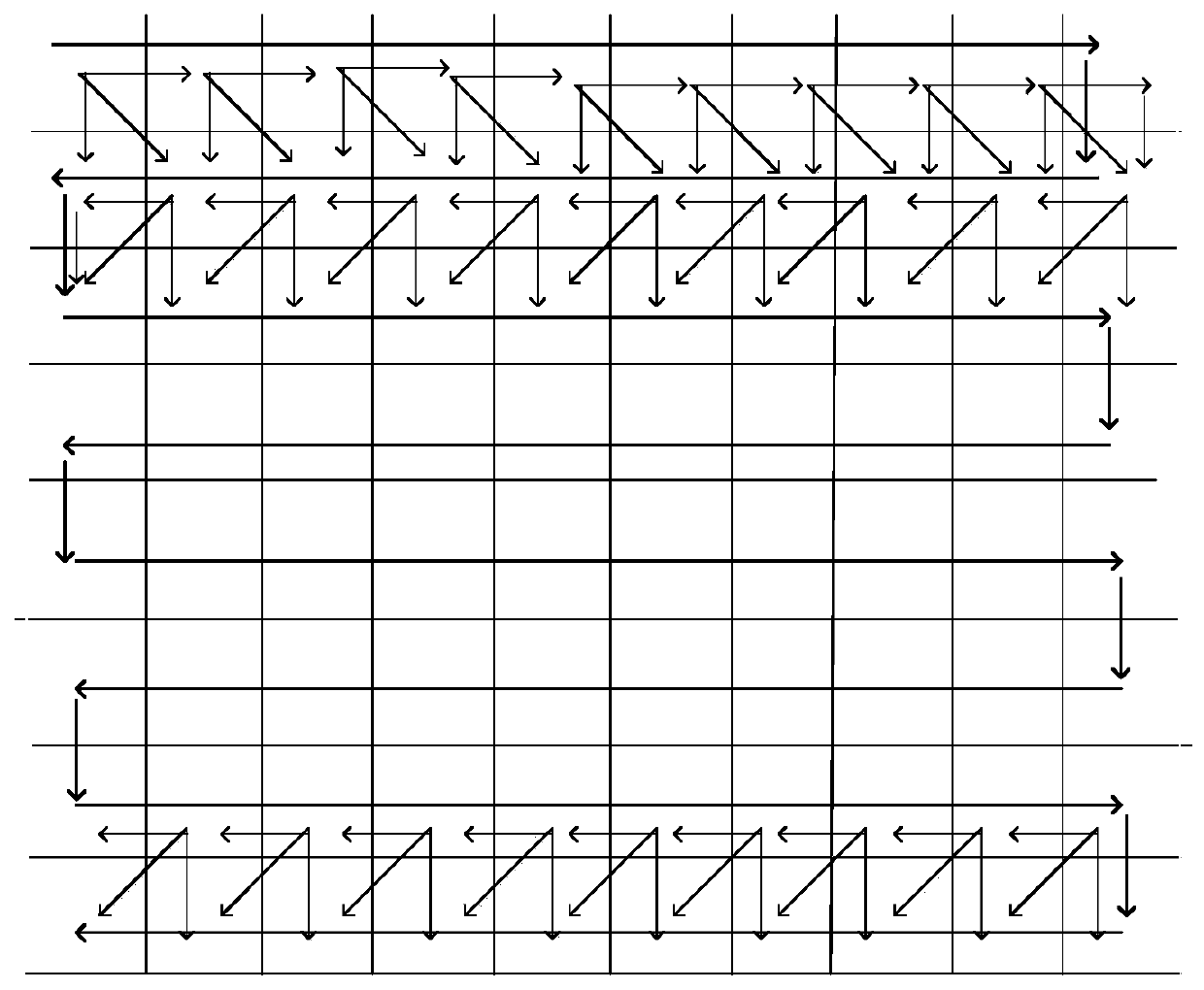
[0030] It should be noted that before looking for image feature points, it is necessary to judge whether the images are in the same line. If they are in the same line, find feature points between two images. If they are not in the same line, follow the figure 2 Find the feature points of the image in the direction indicated in .
[0031] S3, performing feature point matching on the scanned image and the image;
[0032] S4, performing image registration ac...
Embodiment 2
[0079] refer to figure 1 , which is the second embodiment provided in the method for mosaicing scanned pictures of microscopic pathological slices provided by the present invention. This embodiment is different from the first embodiment in that: in the embodiment, due to the large number of images, it is possible to It takes up a lot of memory. It is recommended to add the following two steps before starting to read the scanned image of the high-power microscope:
[0080] (1) First check your computer configuration, calculate the largest pixel m that can be spliced and rendered by the computer, calculate the best number N of pictures that can be spliced and rendered at one time, and then divide the images to be spliced into S equal parts according to the actual situation ;
[0081] (2) Stitch and render each equal portion of the images separately according to the above steps, release the memory by deleting the spliced images, and then splice each equal portion of the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com