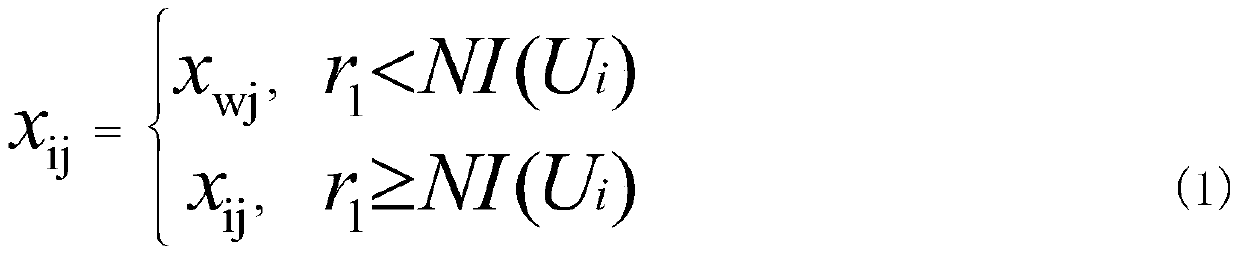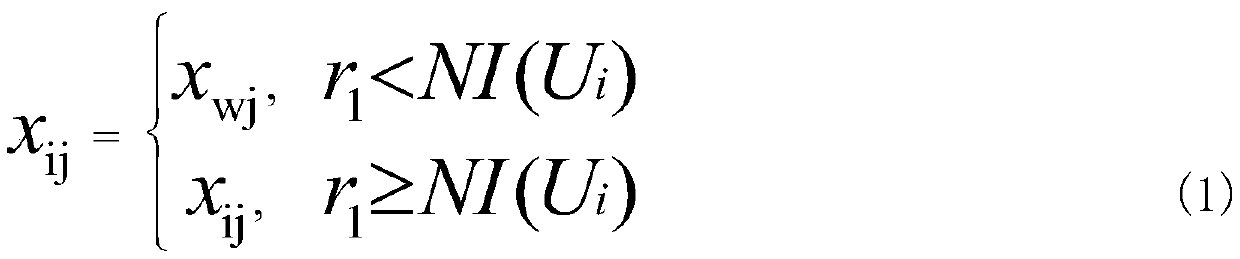DNA storage coding optimization method based on K-means clustering multivariate universe algorithm
A k-means clustering and optimization method technology, applied in DNA computer, computing, genetic model and other directions, can solve the problem of high cost of reading and writing DNA data, achieve fast iteration speed, improve average fitness, and speed up convergence.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
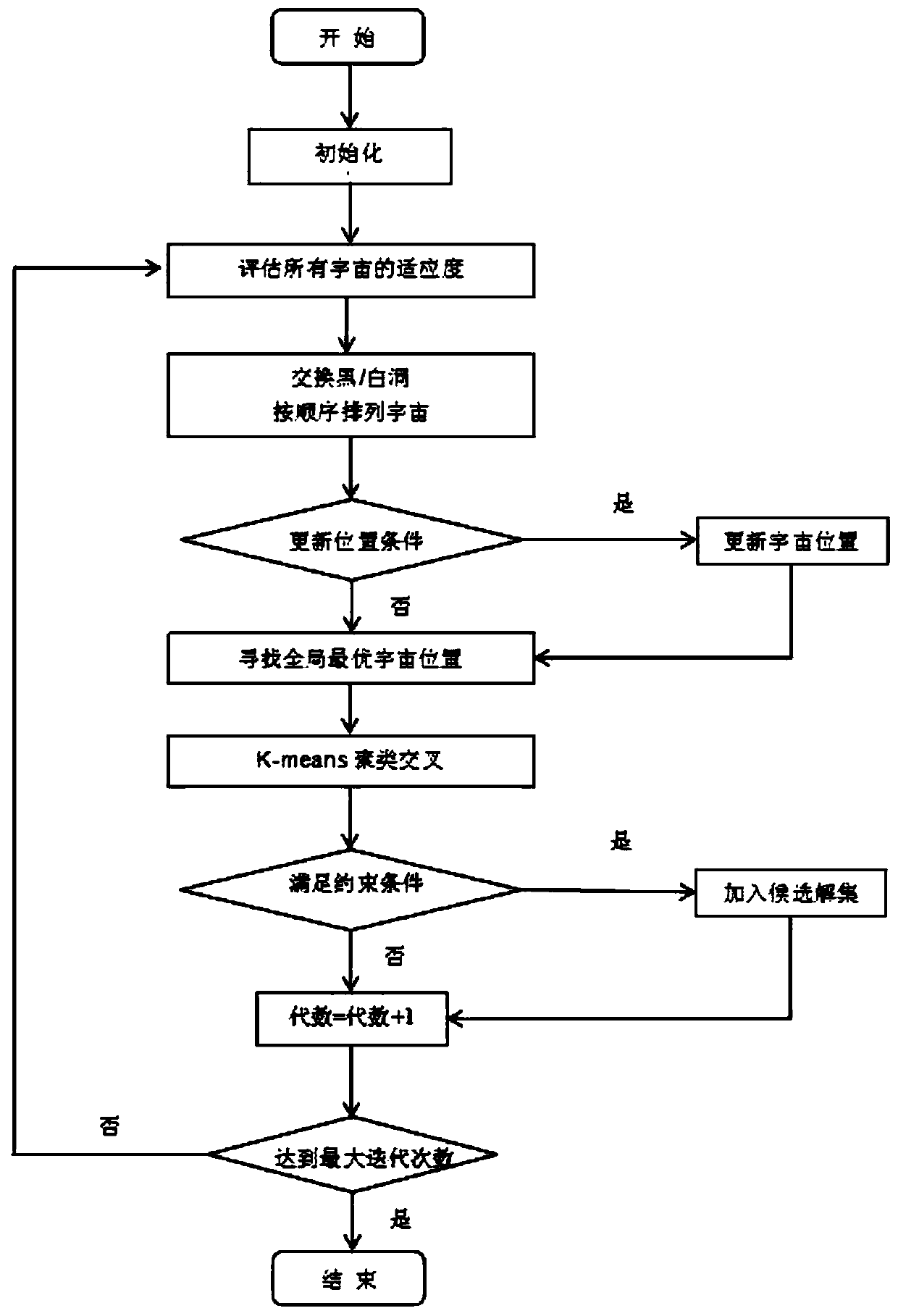
[0024] The embodiments of the present invention are implemented on the premise of the technical solutions of the present invention, and detailed implementation methods and specific operation processes are given, but the protection scope of the present invention is not limited to the following embodiments. In the example, the DNA coding length n is 6, the Hamming distance constraint is d≥4, and the full discontinuity constraint and GC content constraint are as described above.
[0025] Step 1: Initialize the population to generate 500 DNA coding sequences of length 6. Initialize the relevant parameters required by the algorithm. In the wormhole existence probability WEP, min takes 0.2, max takes 1, and p takes 6 in the travel distance rate TDR;
[0026] Step 2: Use the multiverse algorithm to search the initial population, first initialize the fitness of the universe population, and sort the fitness of the universe, select the universe with the best fitness and the worst fitnes...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com