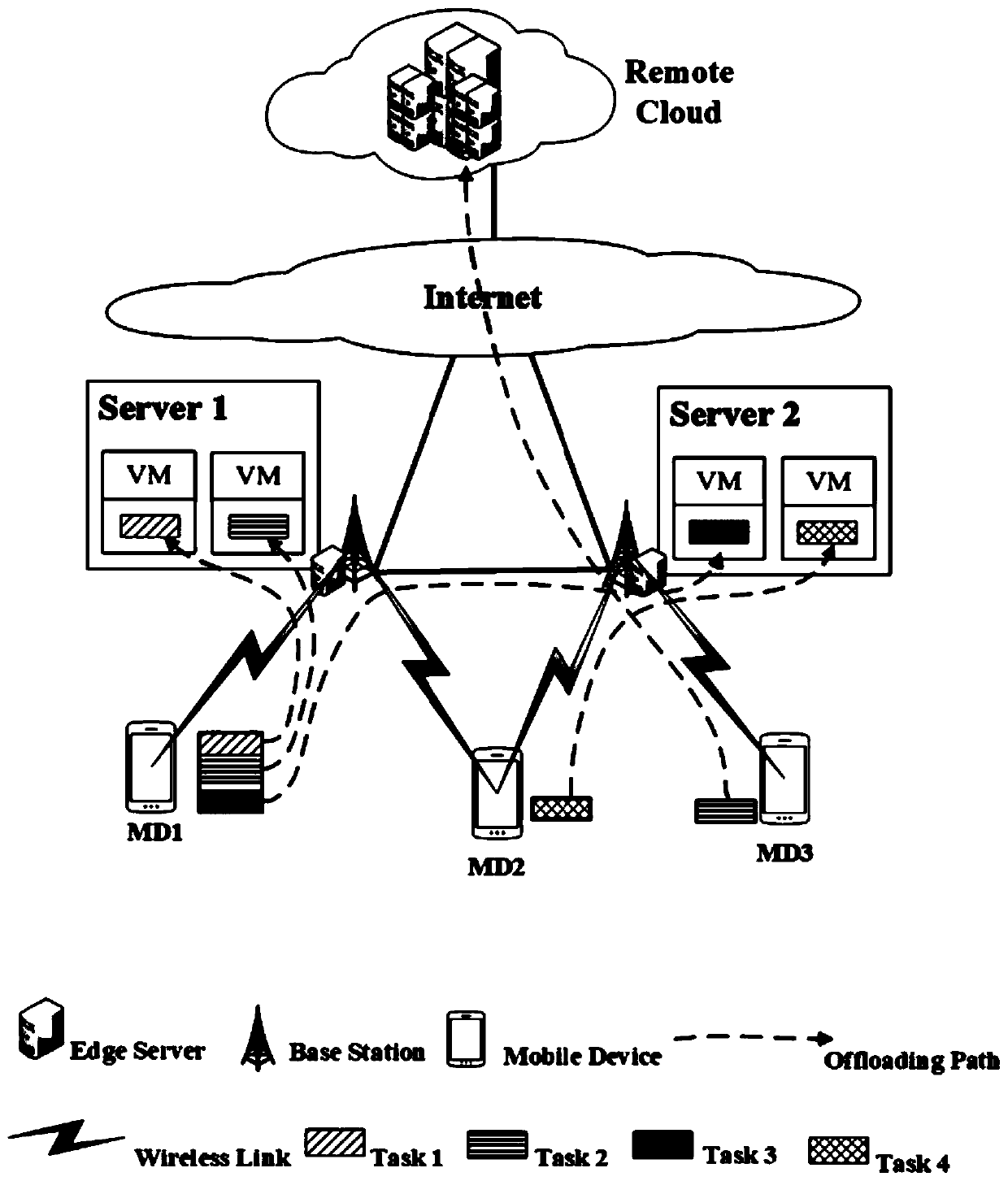
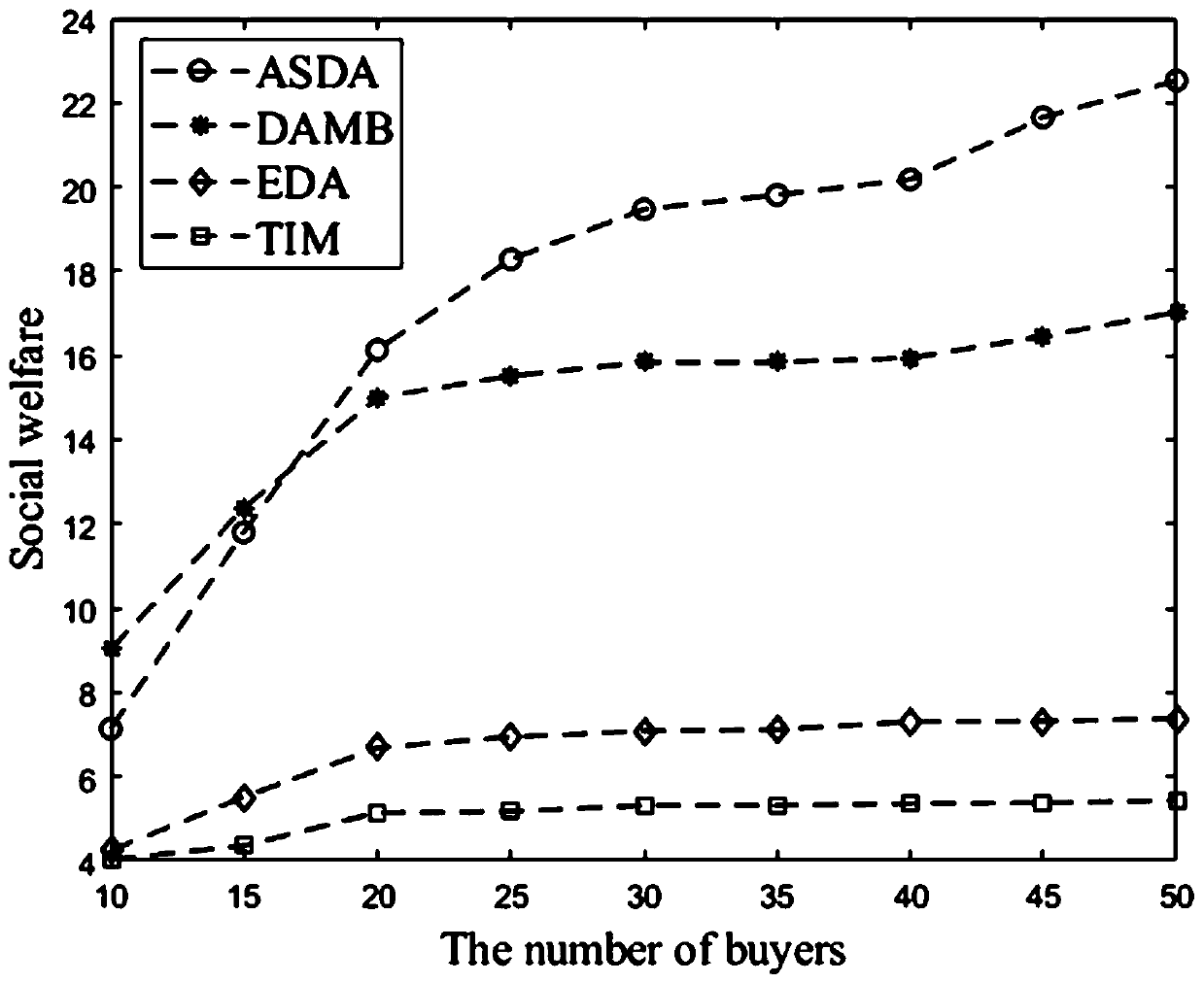
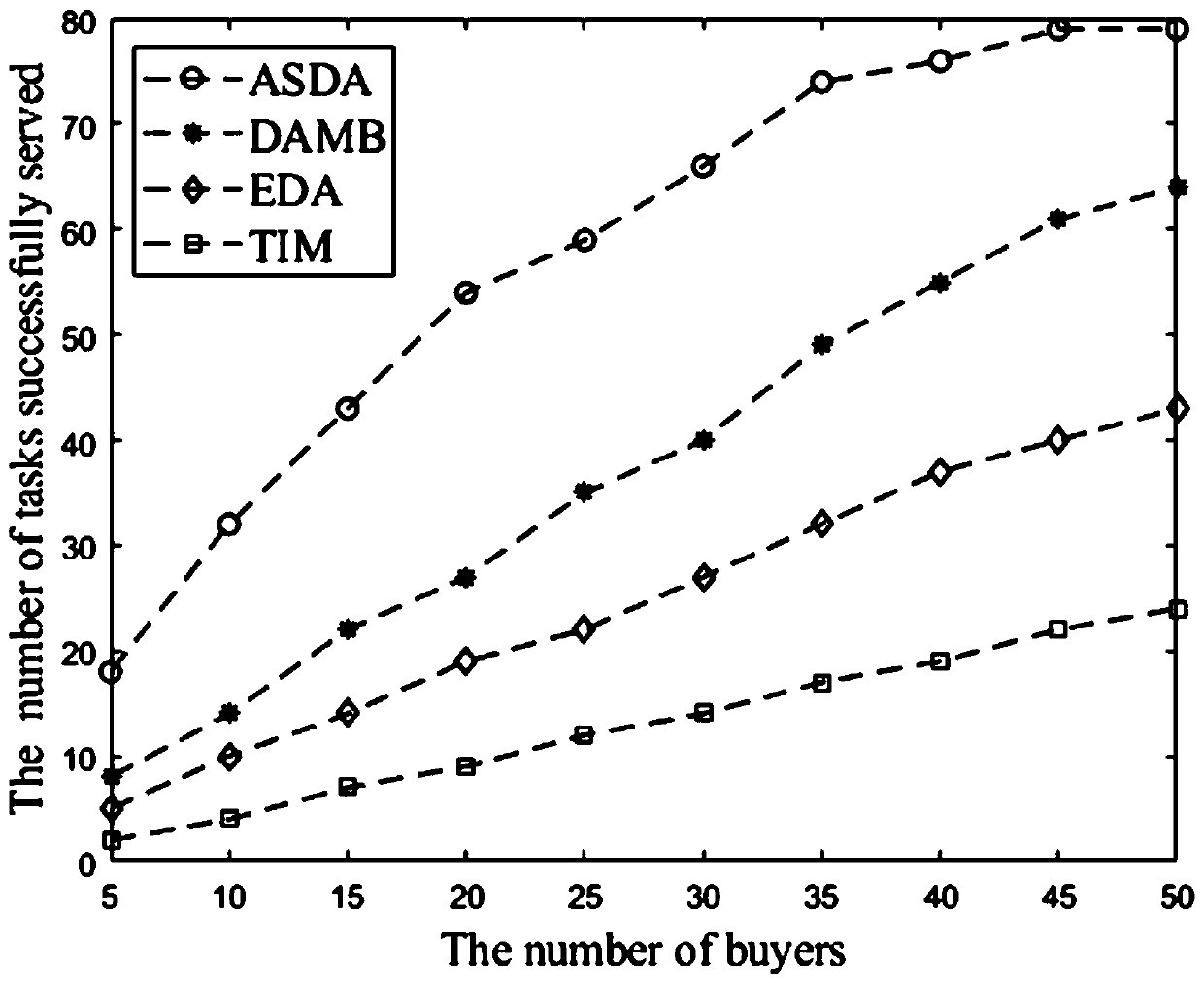
Multi-task cross-server resource allocation method based on bidirectional auction in MEC
A technology of server resources and allocation methods, applied in the field of mobile edge computing resource allocation, can solve problems such as inapplicability and low system efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0156] DAMB incentive mechanism:
[0157] (1) Sort the elements in A in ascending order:
[0158] A'=(a q1 =a 3 = 2, a q2 =a 1 = 3, a q3 =a 2 = 4, a q4 =a 5 = 5, a q5 =a 4 =6).
[0159] (2) Sort the elements in B in descending order:
[0160] b'=(b 2,3 =10,b 3,1 =10,b 1,3 =9,b 4,1 =8,b 1,2 =7,b 1,1 =7,b 2,1 =6,b 4,2 =6,b 3,3 =6,b 1,4 =6,b 4,4 =6,b 2,5 =5,b 4,5 =4).
[0161] (3) A': Median:
[0162]
[0163] (4) Remove all less than Elements:
[0164] B c =(b2,3 =10,b 3,1 =10,b 1,3 =9,b 4,1 =8,b 1,2 =7,b 1,1 =7,b 2,1 =6,b 4,2 =6,b 3,3 =6,b 1,4 =6,b 4,4 =6,b 2,5 =5).
[0165] (5) Delete greater than or equal to in A' Elements:
[0166] A c =(a 3 = 2, a 1 =3).
[0167] (6) find B c The first element in is b 2,3 = 10, because a 3 ∈A c , the task of buyer 2 can be offloaded to seller 3. From Table 2, we know that the App deployment status of Seller 3 is R 3 =(1, 0, 1, 0), the task that buyer 2 needs to handle is R 2 =(1, 1, ...
Embodiment 2
[0178] ASDA Incentive Mechanism
[0179] (1) Sort the elements in A in ascending order:
[0180] A'=(a q1 =a 3 = 2, a q2 =a 1 = 3, a q3 =a 2 = 4, a q4 =a 5 = 5, a q5 =a 4 = 6);
[0181] (2) Start traversing from the first element of A', for a 3 =2 It is known from Table 2 that seller 3 has deployed App1 and App3. Suppose we randomly choose App1 to start the auction. All bids for seller 3App1 are extracted from B. Q from Table 2 1 and Q 2 It can be seen that only Buyer 1 and Buyer 2 need services, and we will form the extracted bids into a new vector Then buyer 2 is the winner, b 1,3 =9 is the highest bid for losing the bid. N ω ={2},M ω = {3}, φ(2) = 3, g 2,3 = 1, r 3,1 =0,q 2,1 =0. by Q 1 , Q 2 and Q 3 It can be seen that Buyer 1, Buyer 2, and Buyer 3 need App3, and we extract all bids for seller 3App3 from B Then buyer 2 is the winner, b 1,3 =9 is the highest bid for losing the bid. N ω ={2},M ω ={3},g 2,3 = 2, r 3,3 =0,q 2,3 =0.
[01...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com