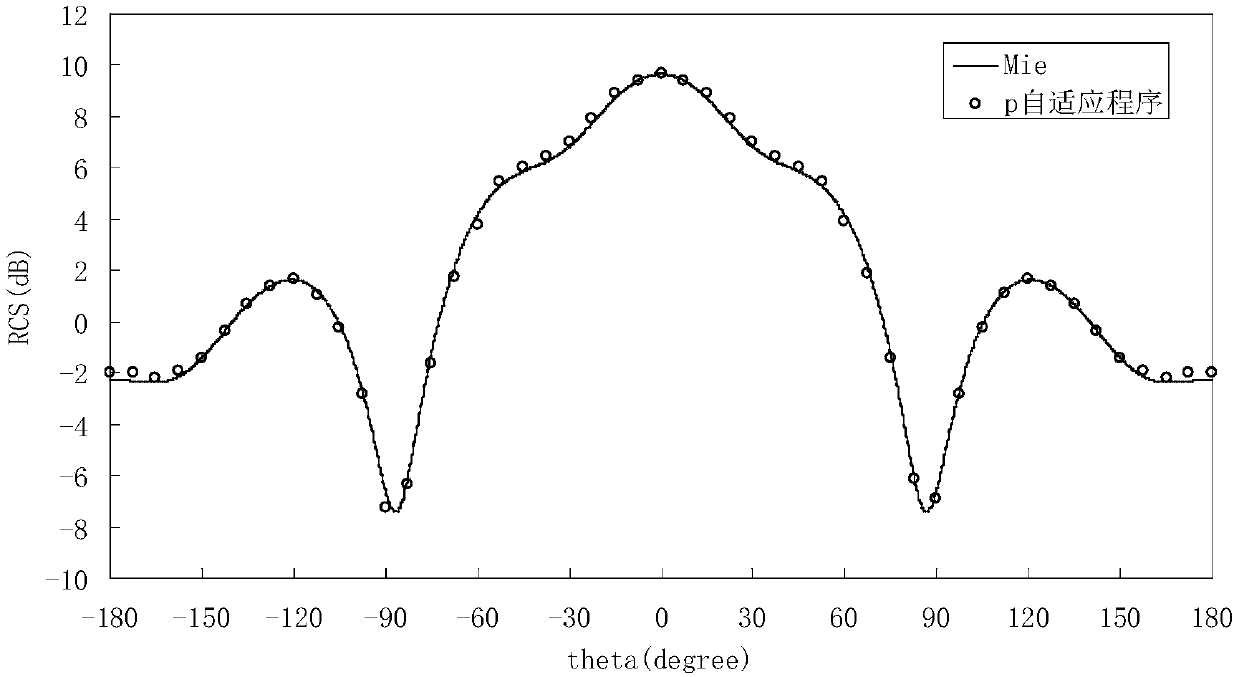
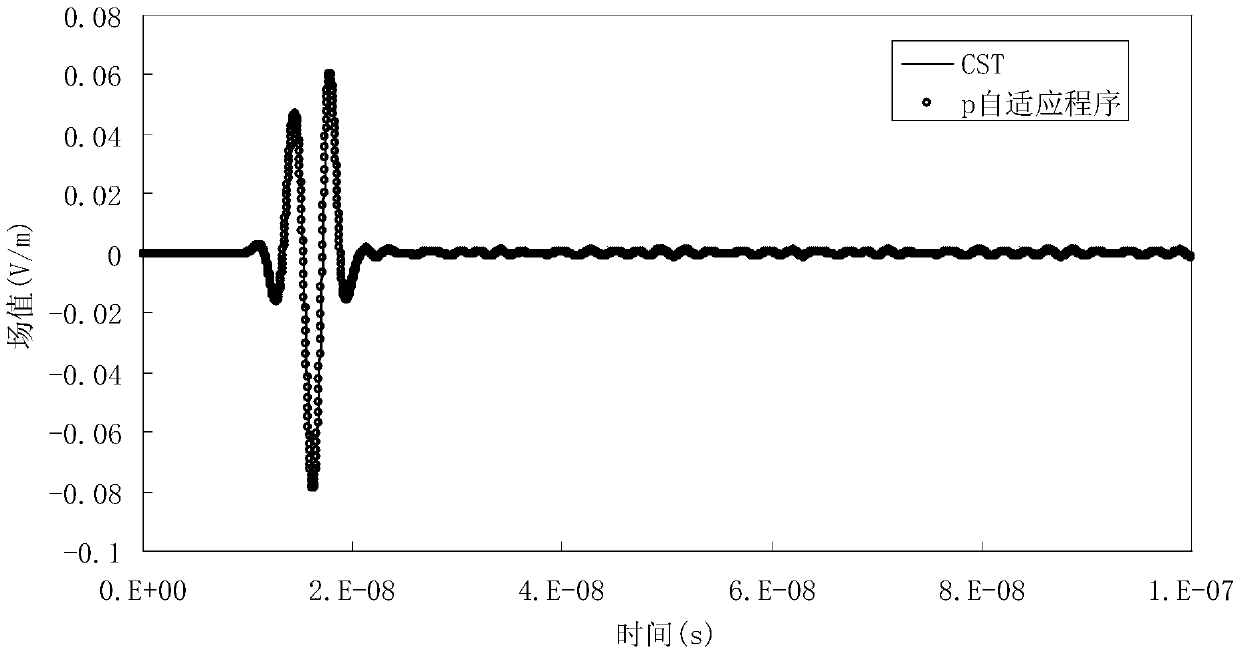
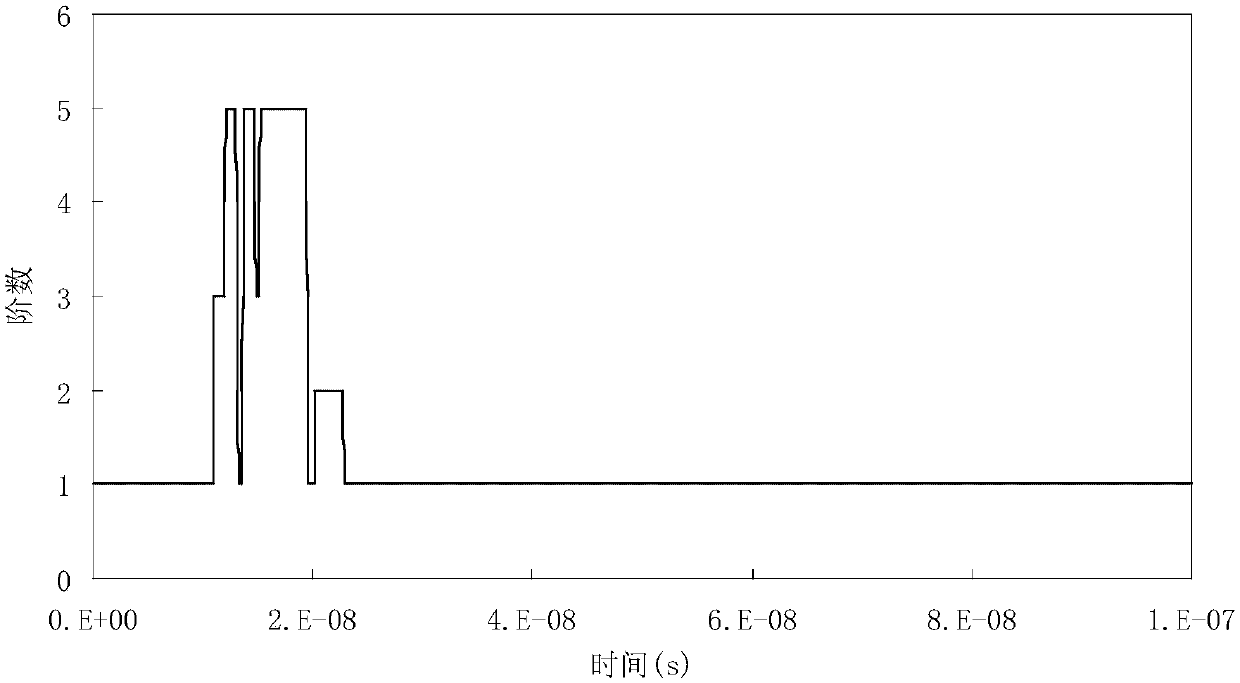
Dynamic p adaptive DG-FETD method based on laminated vector basis function
A technology of DG-FETD and vector basis functions, which is applied in special data processing applications, electrical digital data processing, instruments, etc., can solve the problem of long calculation time of high-order basis function methods, and achieve the effect of reducing calculation time and improving calculation efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0015] A dynamic p-adaptive discontinuous Galerkin time-domain finite element (DG-FETD) method based on stacked vector basis functions, the steps are as follows:
[0016] The first step is to establish the solution model, use the tetrahedral grid to discretize the model, and obtain the structural information of the model, including the node information and unit information of the tetrahedron; the node information includes the node number, node coordinates, and the unit information includes the unit number and The serial number of the node contained in the unit;
[0017] The second step is to set the simulation parameters and read the structural information of the model;
[0018] In the third step, according to the first-order Maxwell’s curl equation in which the electric field strength E and the magnetic field strength H are unknown quantities:
[0019]
[0020]
[0021] In the above formula, ε and μ represent the permittivity and permeability of the discrete unit, resp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com