Method for balancing node energy consumption of wireless sensor network based on Huffman tree
A sensor node and wireless sensor technology, applied in wireless communication, network topology, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of limited communication capability of sensor nodes, not fully utilized, and stop working, so as to reduce data forwarding tasks and optimize power consumption. Consume and reduce the effect of data forwarding
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0033] The specific implementation of the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments:
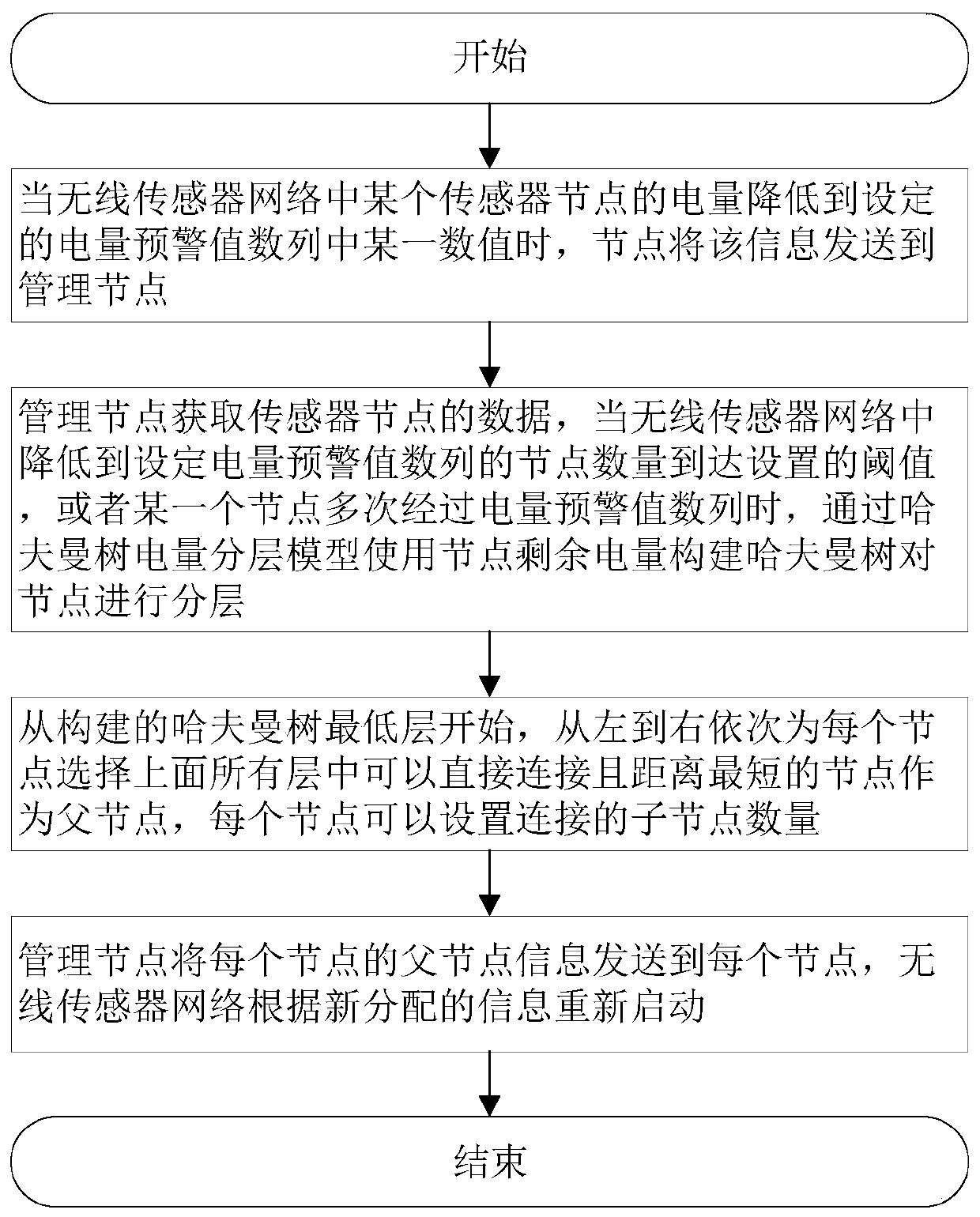
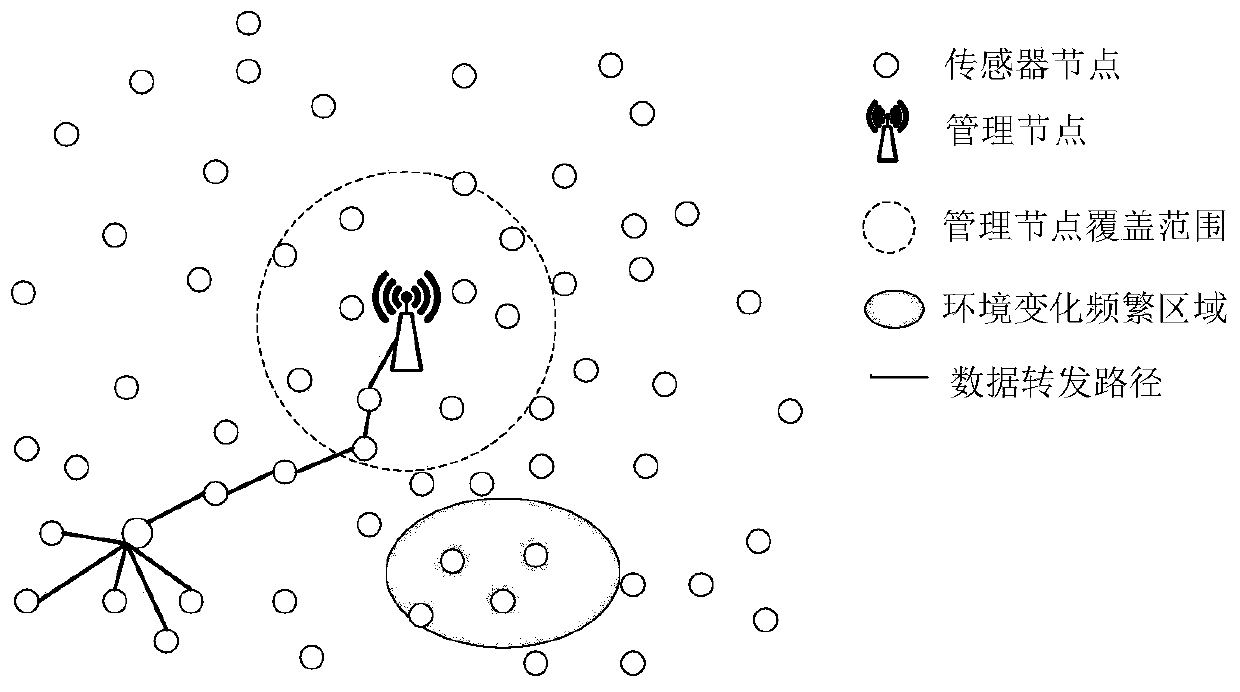
[0034] Such as figure 1 As shown, a method for balancing energy consumption of wireless sensor network nodes based on Huffman trees includes the following steps:
[0035] Step 1: When the power of a sensor node in the wireless sensor network drops to a certain value in the set power warning value series, the sensor node sends the information to the management node;
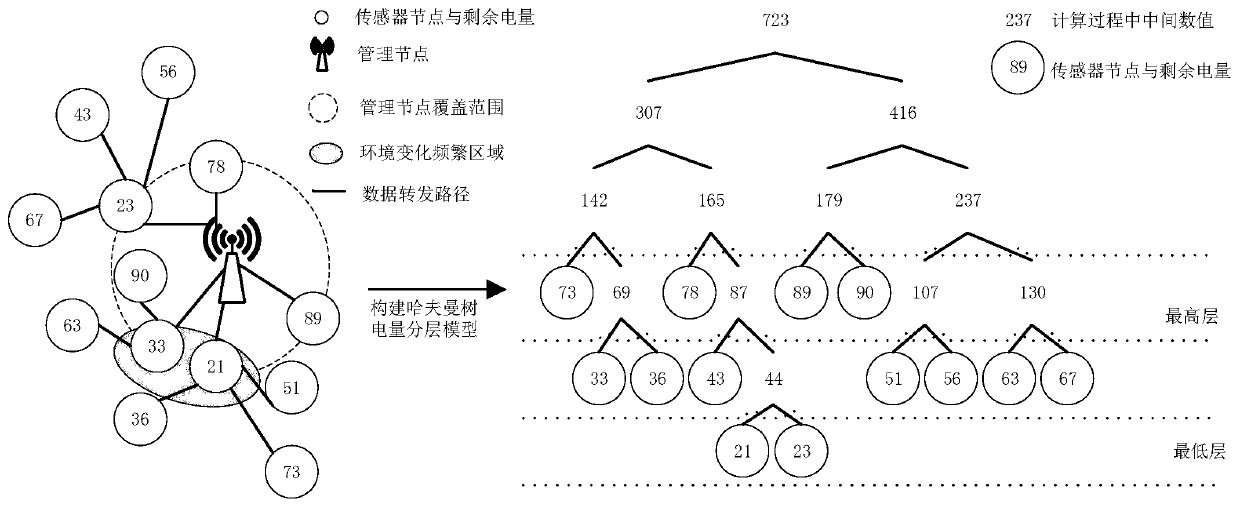
[0036] Step 2: The management node obtains the data of the sensor nodes. When the number of sensor nodes in the wireless sensor network reduced to the set power warning value sequence reaches the set threshold, or a certain sensor node passes through the power warning value sequence multiple times, pass the Huff Mann tree power hierarchical model uses the remaining power of sensor nodes to construct a Huffman tree to layer sensor nodes;
[0037] Step 3: Start...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com