External illuminator radar-based blade state monitoring method for wind turbines
An external radiation source radar, wind turbine technology, applied in the direction of using re-radiation, radio wave measurement system, radio wave reflection/re-radiation, etc., can solve the problem of time-consuming and laborious sensor installation and replacement, high wind turbine height, and sensor monitoring range limited issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
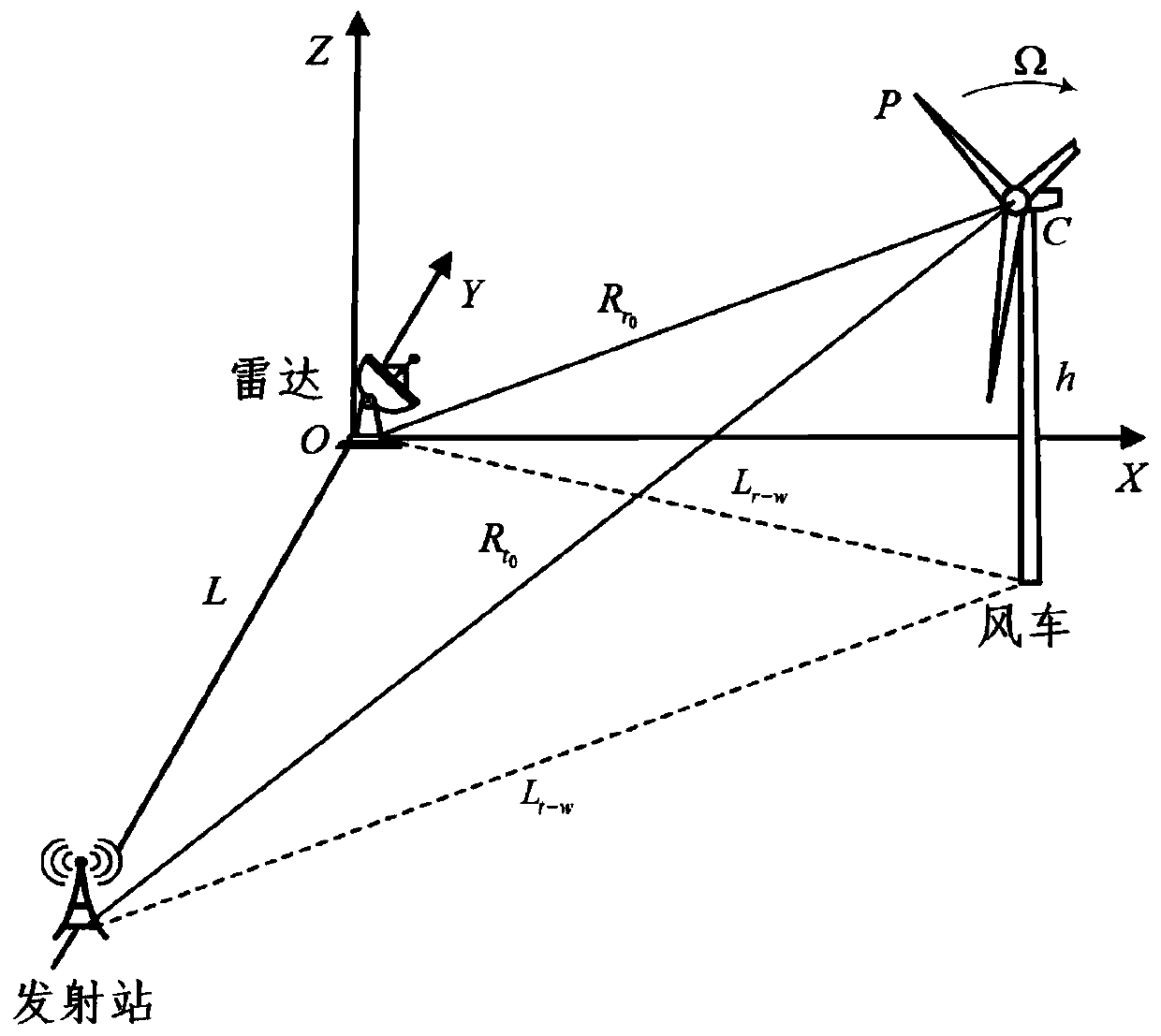
[0072] This example is a simulation example. An external radiation source radar system is used to monitor the status of two wind turbine blades. The center frequency of the irradiation source signal used in the simulation process is 722MHz, and the coherent accumulation time is set to 6s during the processing process. Other detailed simulation parameters As shown in the table below:
[0073] Table 1 The parameters of the embodiment simulation
[0074]
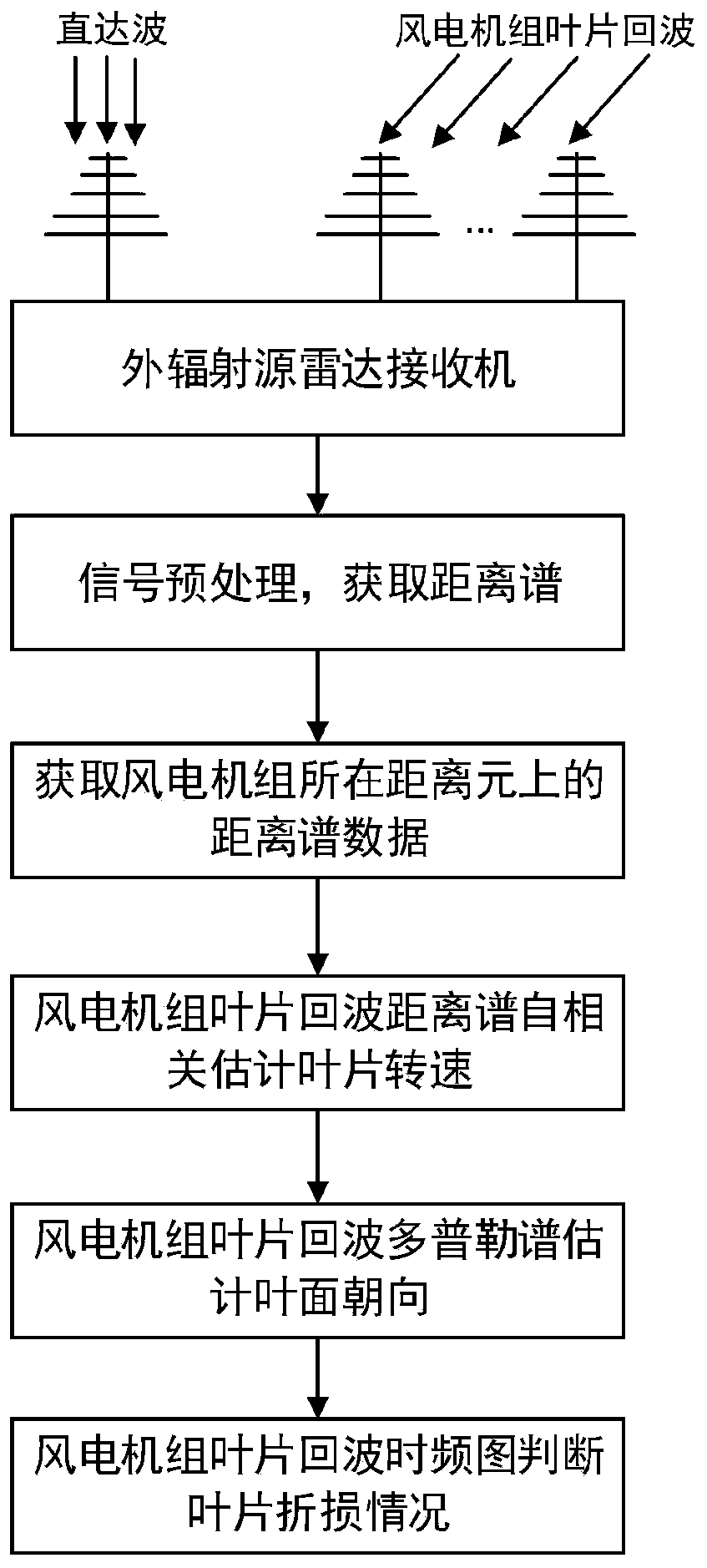
[0075] Utilize the present invention to monitor the status of wind turbine blades, the basic signal processing flow is as follows figure 2 As shown, it specifically includes the following steps:
[0076] Step 1: Point the reference antenna of the external radiation source radar system to the transmitting station to receive the direct wave signal, point its monitoring antenna to the wind turbine to receive the radar echo signal, and pre-empt the direct wave signal and the radar echo signal. Process and obtain distance spec...
Embodiment 2
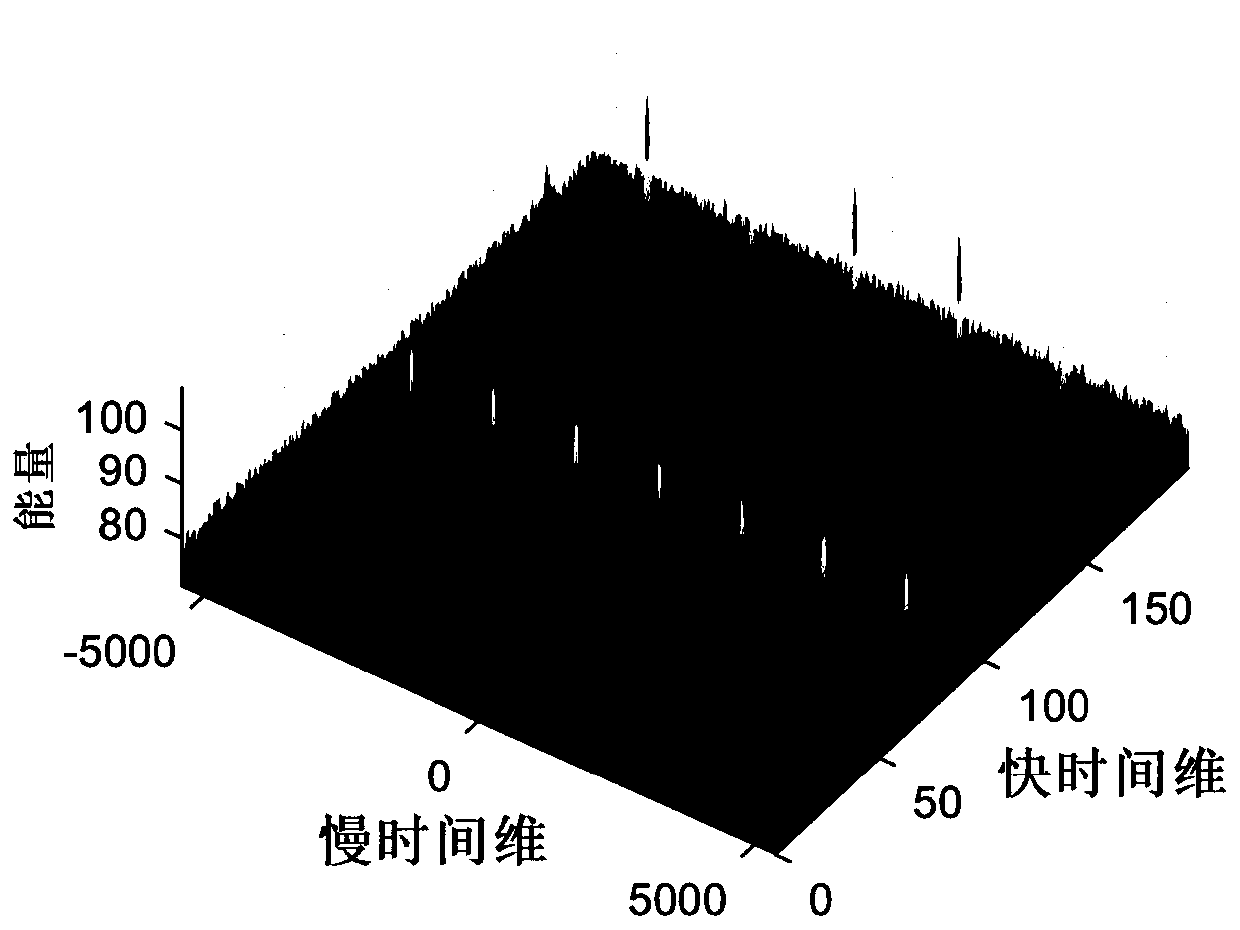
[0115] This embodiment verifies the effectiveness of the present invention through field experiments. The external radiation source radar system used in this embodiment uses the terrestrial digital multimedia broadcasting signal (DTMB) as the source of opportunity radiation, the signal center frequency is 722MHz, and the bandwidth is 7.56MHz. The wind turbines used are located in Luoyang, Henan, and there are 10 wind turbines within the radar detection range. Figure 7 is the range-Doppler spectrum of the radar echo. From the figure, we can clearly see the Doppler dimension expansion caused by the micro-Doppler effect of the echo of each wind turbine blade. It shows that the wide-area monitoring of wind turbine blade status by external radiation source radar has great potential. Not generally, this embodiment takes blade condition monitoring of one of the wind turbines as an example to illustrate the specific implementation process of the present invention. The following tab...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com