Solid waste incineration condition recognition method based on multi-scale color moment characteristics and random forest
A random forest and working condition recognition technology, which is applied in character and pattern recognition, computer components, complex mathematical operations, etc., can solve the problems of uneven brightness changes, redundant features, and unclear images of burning flame images
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
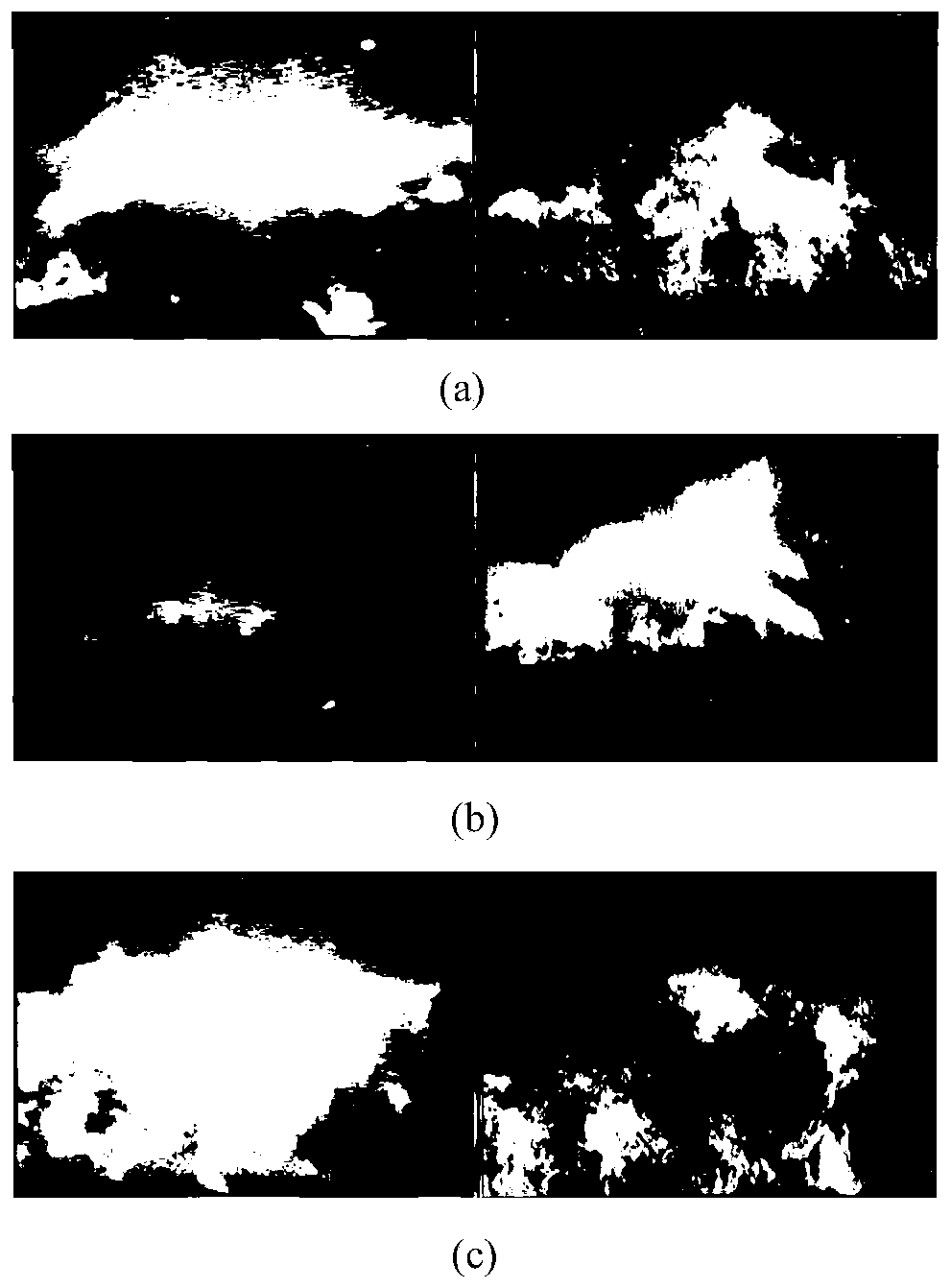
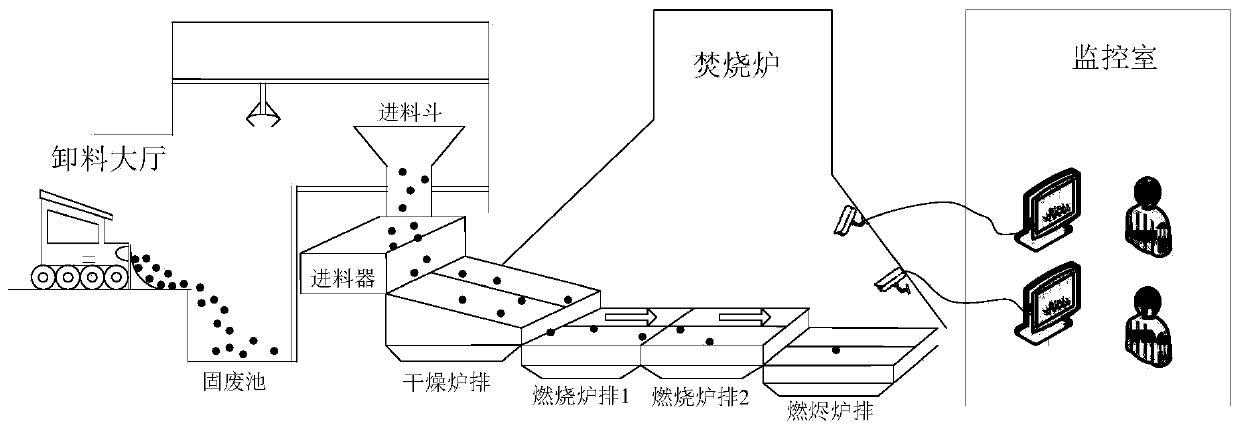
[0078] The experimental data in this paper refers to a MSWI solid waste incineration plant in Beijing. The incineration video is captured at a sampling rate of one minute. The size of the collected original incineration picture data set is N=270, and the pixel ratio of the flame picture is 1436*507. Combined with the experience of on-site experts, mark the pictures as: working condition 1, working condition 2 and working condition 3.
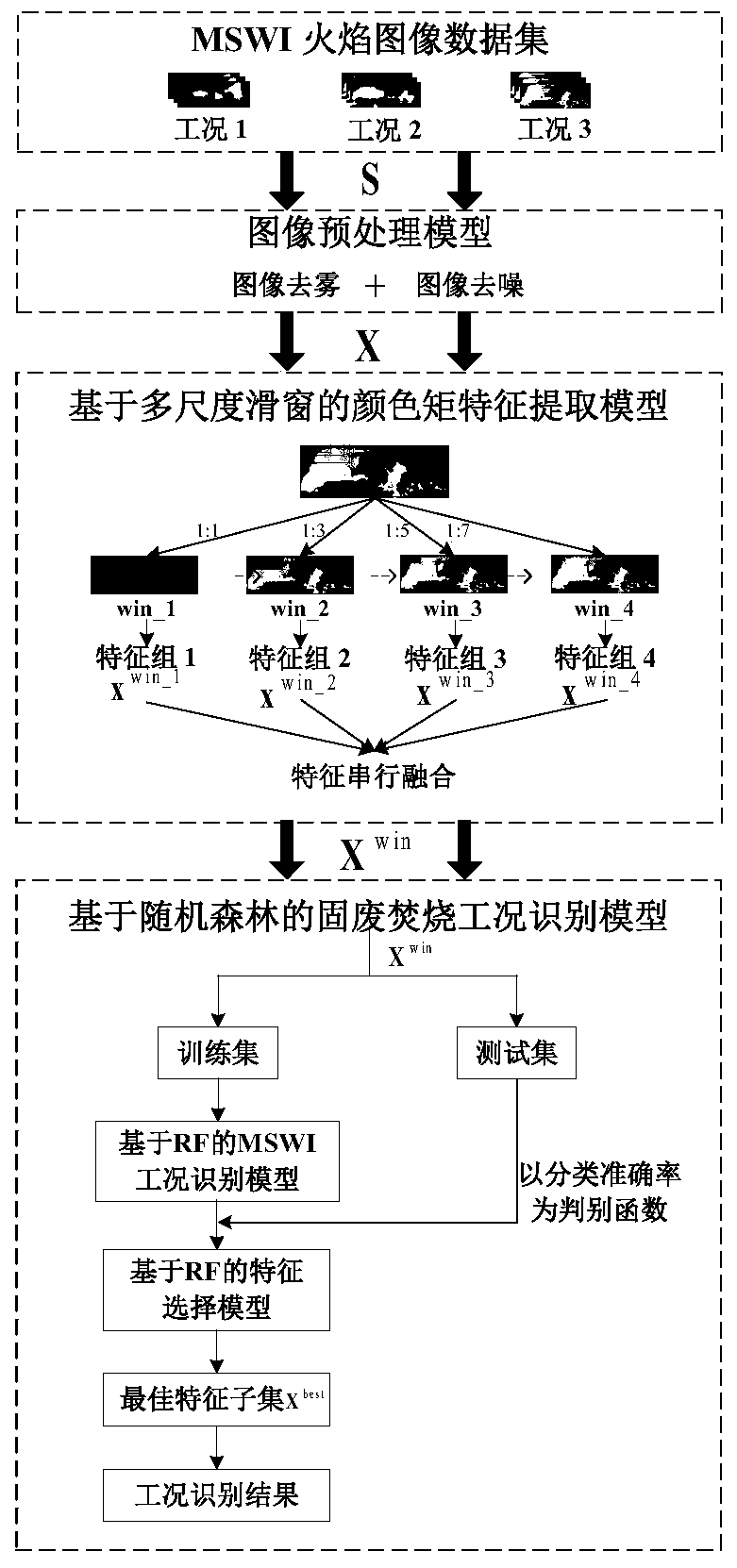
[0079] Apply the dark channel prior dehazing algorithm, set Ω=9*9, threshold r 0 =0.1, λ=0.95; then use a size of 5*5
[0080] The template of the image is used to denoise the image; finally, the flame image is converted from the RGB space to the HSV color space. The result is as follows:
[0081] After the incineration picture is dehazed, the smoke and dust in the picture are significantly less, and the image shows clear brightness changes and color distribution; after denoising, the edge of the image is smooth, and the random noise is signif...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com