Rope-driven flexible claw and robot
A rope-driven flexible and flexible skeleton technology, applied in the field of robotics, can solve the problems of limited robot movement, unfavorable finishing and storage, and large space occupation, so as to improve the application range and product grabbing efficiency, avoid movement restrictions, The effect of reducing the occupied space
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
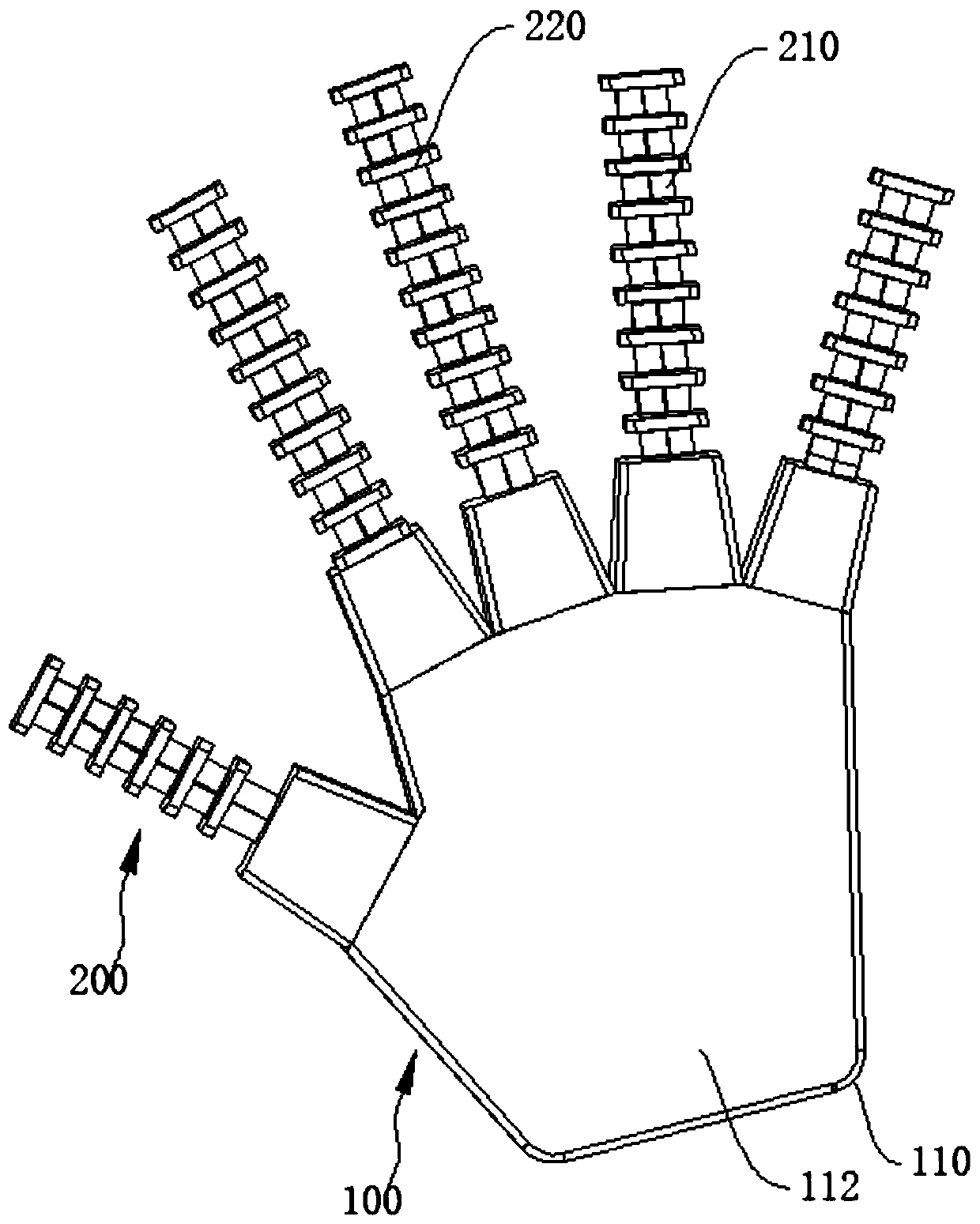
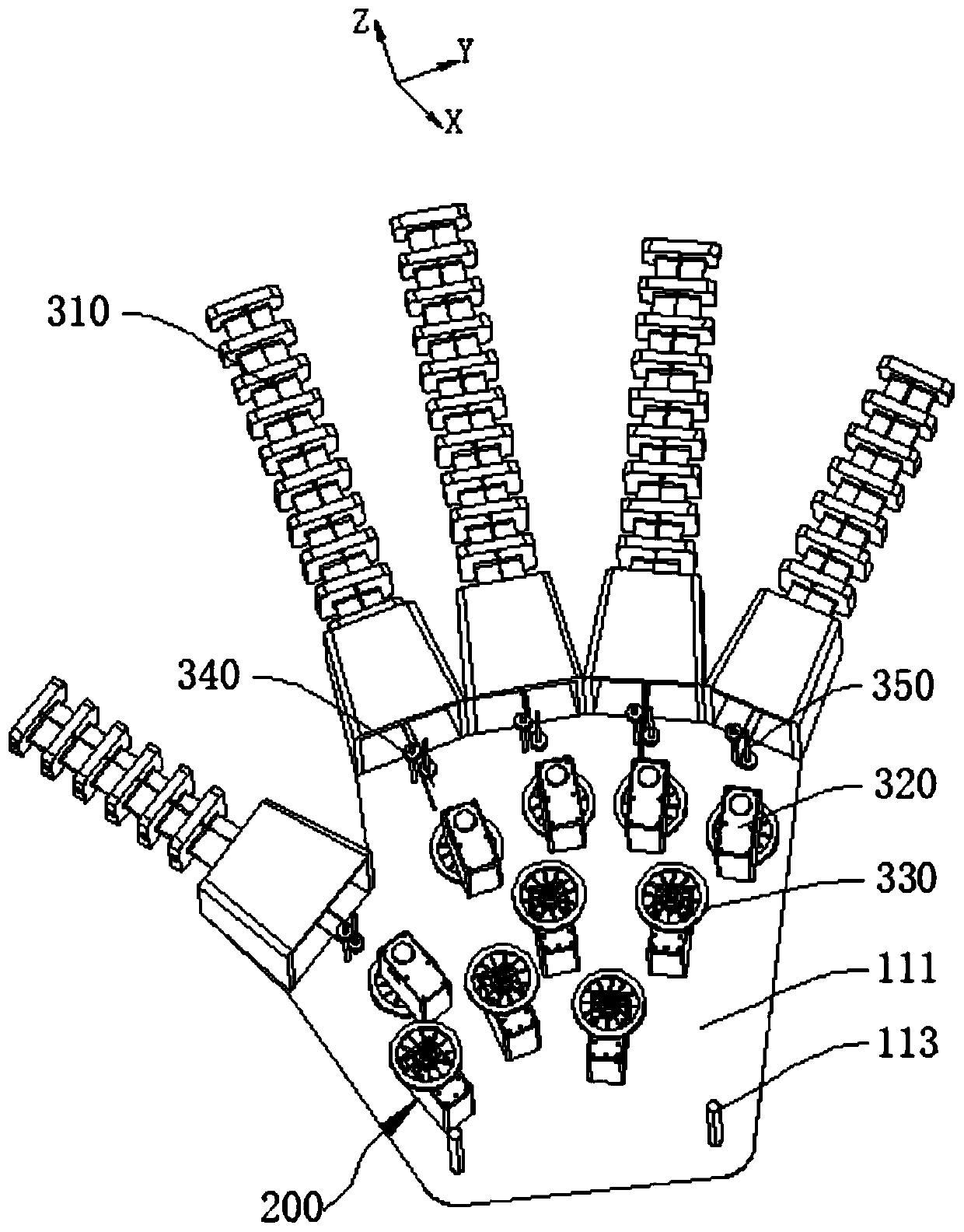
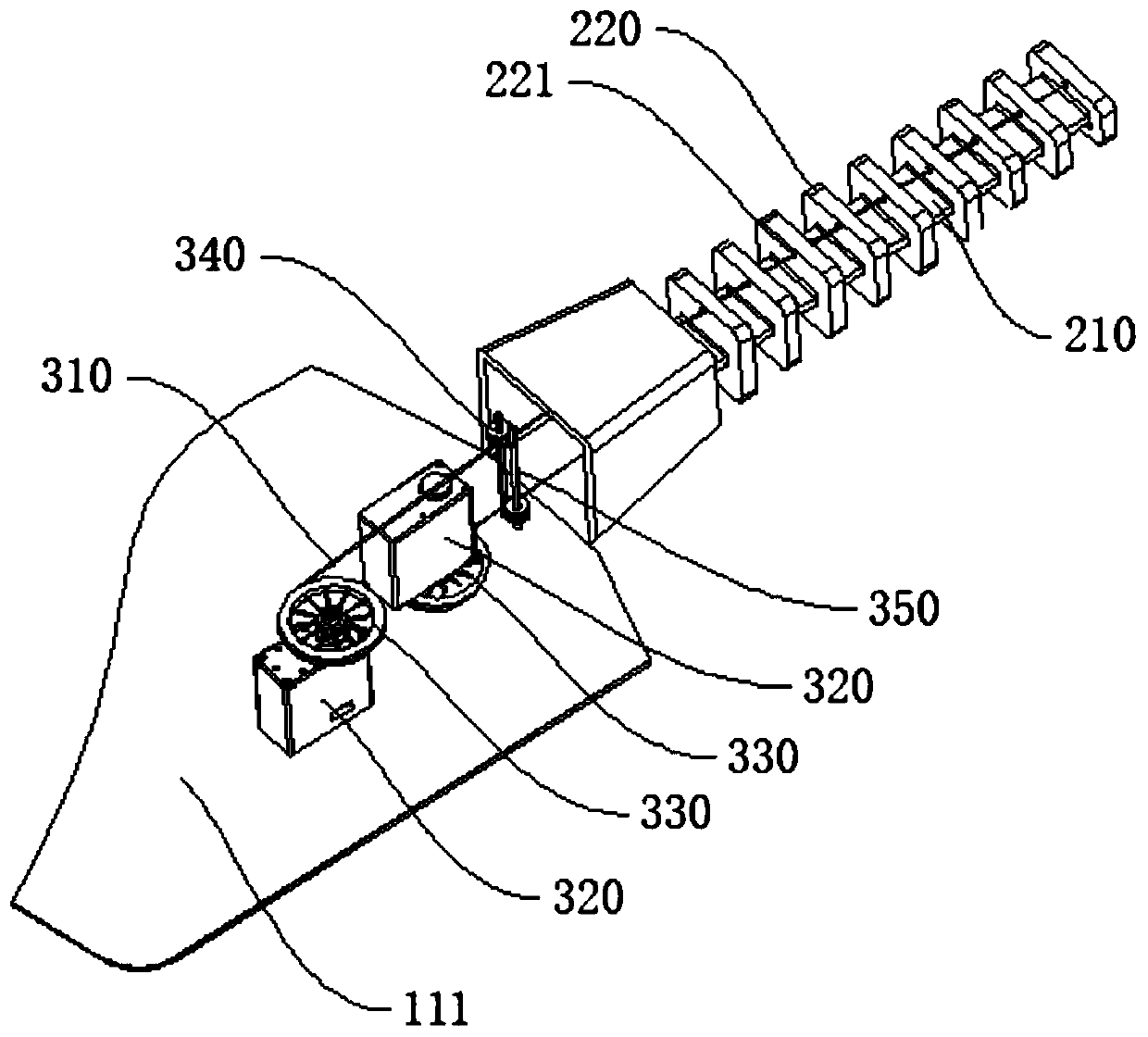
[0032] figure 1 is a schematic diagram of the overall structure of the rope-driven flexible claw, figure 2 It is a schematic diagram of the structure of the flexible claw of the rope drive after hiding part of the housing 110, image 3 is the structural diagram of the drive unit, and refer to Figure 1 to Figure 3 , the rope-driven flexible claw in this embodiment includes a fixed part 100, a finger part 200 and a driving part 300, the fixing part 100 includes a housing 110, the housing 110 provides an installation space for the driving part 300, and the driving part 300 is the finger part 200. Bending provides power support; specifically, there are no less than two fingers 200 and are installed on the edge of the fixed part 100, the fingers 200 include a flexible skeleton 210 and a plurality of joint units 220, and the joint units 220 are arranged at intervals on the flexible skeleton 210 , the section of the joint unit 220 gradually decreases along the direction away from...
no. 2 example
[0045] refer to Figure 5 The difference between this embodiment and the first embodiment is that the flexible skeleton 210 in this embodiment adopts a variable cross-section configuration, the cross section of the flexible skeleton 210 gradually decreases along the direction away from the fixed part 100, and the joint unit 220 adopts a constant cross-section structure. type, the cross-sectional shapes of different joint units 220 are the same. Therefore, when the driving rope 310 is pulled or released, the driving force required for bending the finger 200 is relatively small, and under the condition that the driving force applied by the driving part 300 is the same, the finger 200 in this embodiment has better load capacity.
no. 3 example
[0047] refer to Image 6 , this embodiment combines the features of the finger portion 200 in the first embodiment and the second embodiment, that is, both the flexible skeleton 210 and the joint unit 220 adopt a variable cross-section configuration, and the cross-sections of the flexible skeleton 210 and the joint unit 220 are along the back. The direction of the fixed portion 100 gradually decreases, thereby improving the load capacity of the finger portion 200 on the premise of overcoming the limitation of the movement of the finger portion 200 and reducing the space required for placing the flexible claw.
[0048] The present invention also provides a robot, which includes the above-mentioned rope-driven flexible gripper, uses the above-mentioned rope-driven flexible gripper to cooperatively grasp objects, and is applicable to product grasping in different situations.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com