Fusobacterium nucleatum subsp. animalis strain separated from human intestines and application of F. nucleatum subsp. animalis strain
A technology of Fusobacterium nucleatum and animals, applied in the direction of bacteria, microorganisms, microorganisms, etc., can solve the problems of inability to distinguish Fusobacterium nucleatum subspecies, lack of specificity, etc., and achieve the effect of promoting composition and source.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] This example provides a Fusobacterium nucleatum subsp. Wentenberg strain THCT6b3 isolated from the intestine.
[0031] The strain has been preserved, named Fusobacterium nucleatumsubsp.animalis, its preservation number is CCTCC NO: M 2019367, and the preservation date is May 17, 2019. The preservation unit is the China Center for Type Culture Collection.
[0032] The 16SrRNA gene sequence of the strain is specifically shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, which is 99.80% consistent with the 16SrRNA gene sequence (NCBI accession number NR_113378.1) of the F.nucleatum subsp.animalis strain JCM 11025, and has 99.80% consistency with the F.nucleatum subsp.nucleatum The 16S rRNA gene sequence of strain ATCC 25586 (NCBI accession number NR_114702.1) has 98.38% identity.
[0033] The whole genome sequencing of this strain shows that this strain contains a circular chromosome, which is 2268559bp, GC content 27.32%, containing 2115 protein coding genes, 63 non-coding genes (45 tRNA genes, 5 se...
Embodiment 2
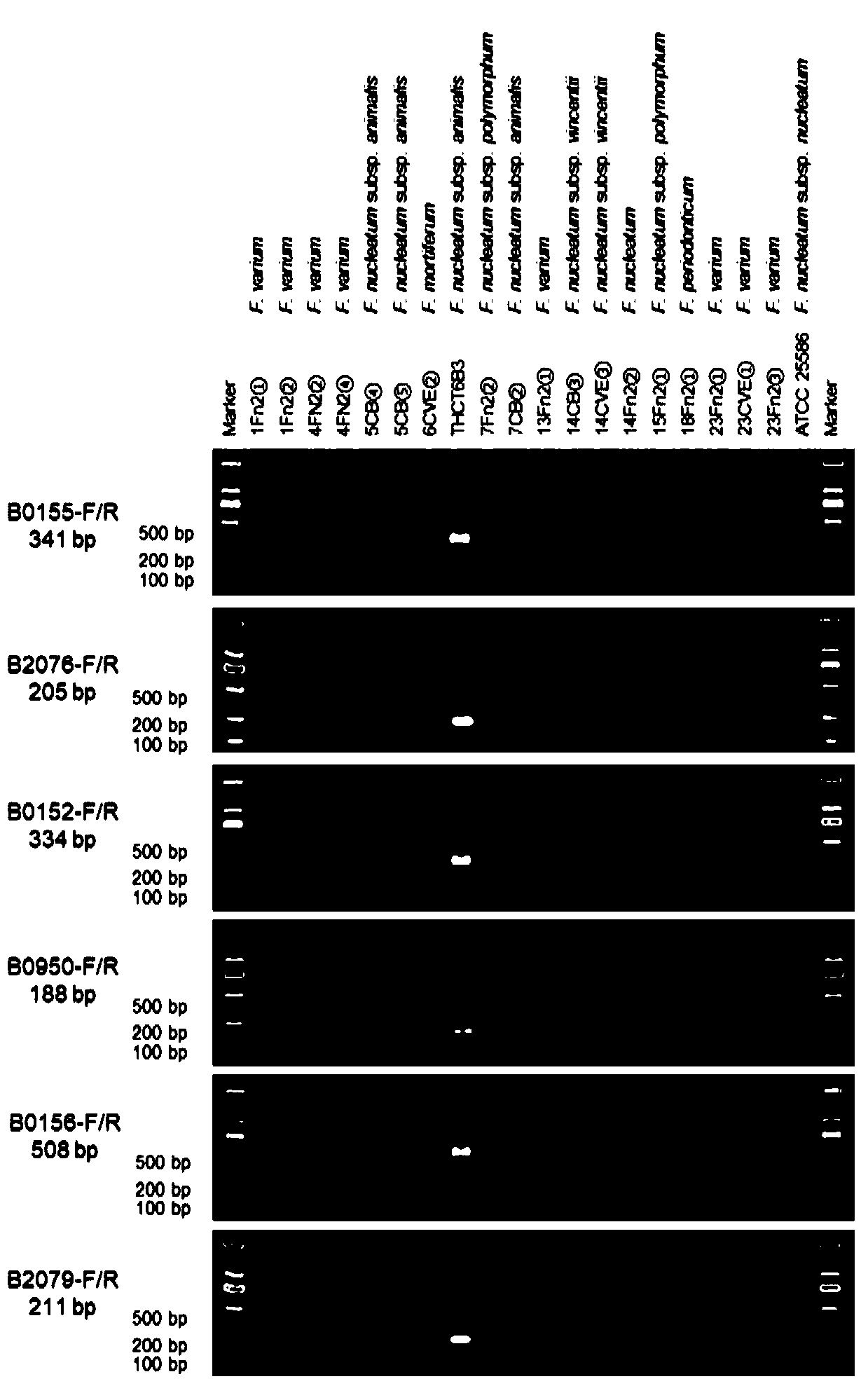
[0035] This example provides six segments for identifying the specific DNA sequences of the Fusobacterium nucleatum subsp. Wentleri strain THCT6b3 in Example 1.
[0036] Through comparative genomics analysis, the six segments are used to identify the specific DNA sequences of the strain: THCT6b3_specific_region_1~THCT6b3_specific_region_6, the nucleotide sequences of which are shown in SEQ ID NO:8~SEQ ID NO:19 respectively.
[0037] The sequences of the amplification primers designed on the basis of the six specific DNA sequences used to identify the strain are shown in SEQ ID NO: 8 to SEQ ID NO: 19, respectively as follows (both 5' to 3') :
[0038]
[0039] The above six pairs of primers can be used for the specific recognition of THCT6b3 by amplifying the corresponding DNA fragments. Six pairs of primers can be applied to common PCR and real-time quantitative PCR. The above six sequences and corresponding primer pairs can be used alone or in combination.
Embodiment 3
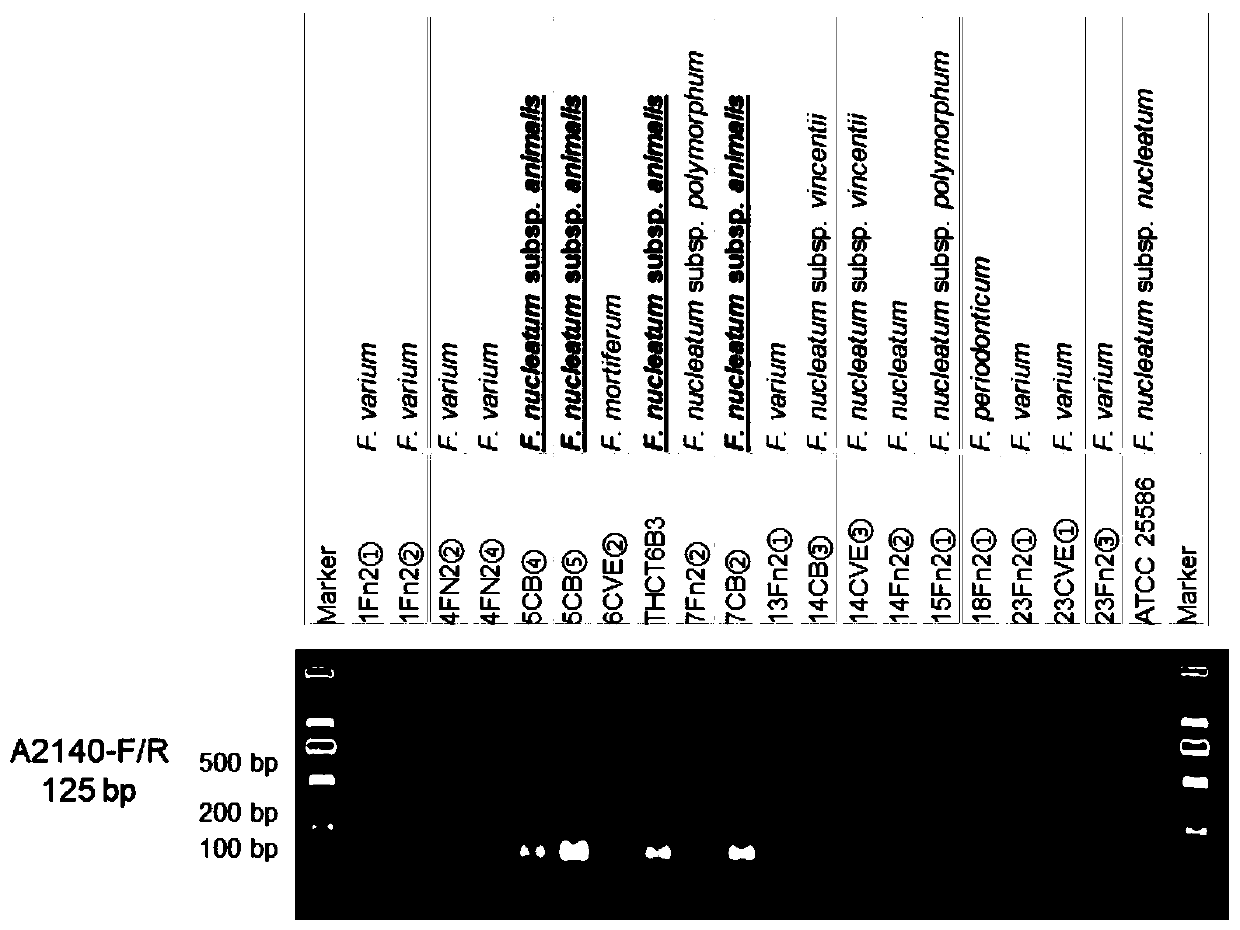
[0041] This example provides specific DNA sequences that can be used to identify Fusobacterium nucleatum subspecies.
[0042] The specific method for obtaining the above-mentioned specific DNA sequence for identifying the subspecies of Fusobacterium nucleatum is: download the Fusobacterium nucleatum genome from NCBI, and combine the THCT6b3 genome; classify the subspecies according to the ANIb value; Through BLASTn analysis in the genome, find the regions that are conserved in all strains; perform BLASTn analysis on these conserved regions and the genomes of other subspecies, and keep the regions that do not exist in the genomes of other subspecies; thus obtain subspecies-specific DNA sequences.
[0043] Three specific DNA sequences: animalis_specific_region_1~animalis_specific_region_3, respectively shown in SEQ ID NO:20~SEQ ID NO:22. The subspecies-specific DNA sequence includes the sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:20~SEQ ID NO:22 or the sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:20~SEQ ID NO:2...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com