A method for regulating the maximum critical solubility temperature of zwitterionic polymers through terminal group modification
A zwitterionic polymer technology, which is applied in the field of regulating the maximum critical mutual solubility temperature of zwitterionic polymer propanesulfonate), can solve the problems of difficulty in improving UCST and single responsiveness of zwitterionic polymers, and achieves improving UCST and broadening applications. Foreground, simple effect of aggregation method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
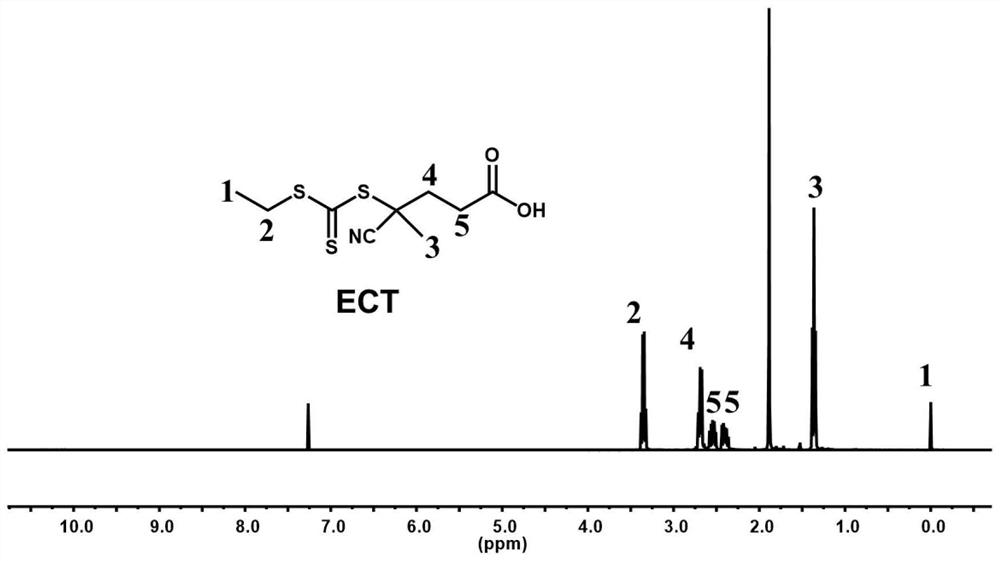
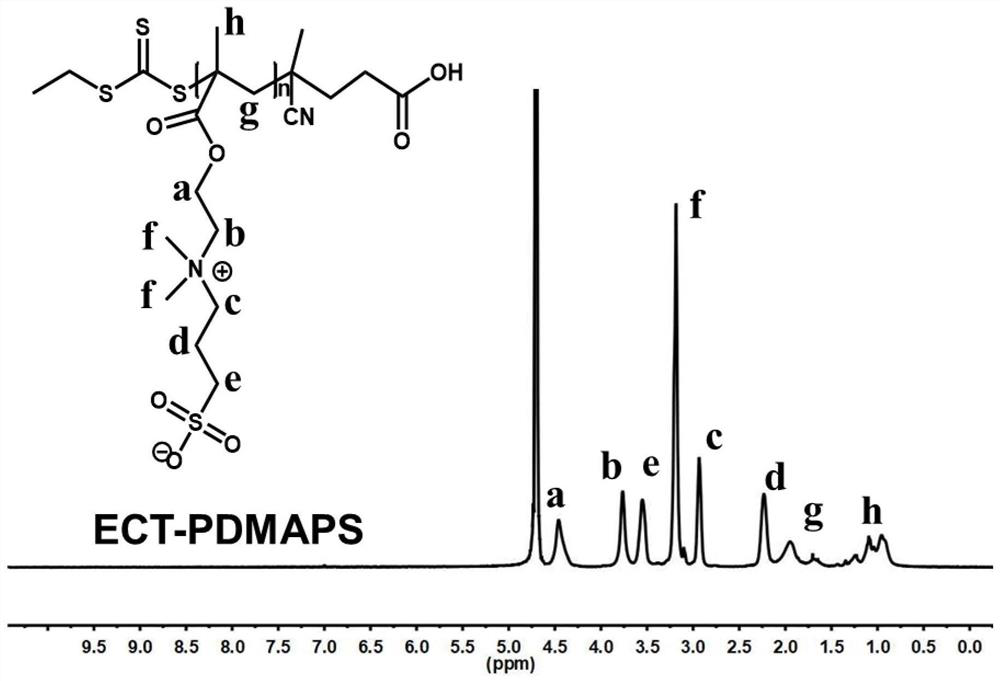
[0029] The design degree of polymerization is 80, and 20 mL of trifluoroethanol solvent and 3.0 g of zwitterionic monomer 3-(2-methacryloyloxyethyldimethylamino)propanesulfonate (DMAPS) are added to the round-bottomed flask, with There is a carboxyl trithioester RAFT reagent ECT (structural formula and nuclear magnetic resonance 1 H NMR spectrum see figure 1) 0.035g and initiator ACVA0.00753g, reacted at 70°C for 24h, and the product was dialyzed through a 3000MW molecular weight dialysis bag for 48h to obtain zwitterionic polymers (PDMAPS) with terminal carboxyl groups (structural formula and nuclear magnetic resonance 1 H NMR spectrum see figure 2 ). The resulting carboxyl-terminated zwitterionic linear polymer (ECT-PDMAPS 80 ) has multiple stimuli responsiveness. When pH=3, UCST can be increased to 13.5°C, and when pH=10, UCST can be decreased to 2.5°C, and the corresponding range of the whole pH can reach 11°C. The problem of the corresponding singleness of the zwitte...
Embodiment 2
[0031] The design degree of polymerization is 200, and 20 mL of trifluoroethanol solvent and 3.0 g of zwitterionic monomer 3-(2-methacryloyloxyethyldimethylamino)propanesulfonate (DMAPS) are added to the round-bottomed flask. There is a carboxyl trithioester RAFT reagent ECT (structural formula and nuclear magnetic resonance 1 H NMR spectrum see figure 1 ) 0.014g and initiator ACVA0.003g, reacted at 70°C for 24h, and the product was dialyzed through a 3000MW molecular weight dialysis bag for 48h to obtain a zwitterionic polymer with terminal carboxyl groups (structural formula and nuclear magnetic resonance 1 H NMR spectrum see figure 2 ). The resulting carboxyl-terminated zwitterionic linear polymer (ECT-PDMAPS 200 ) has multiple stimuli responsiveness. When pH=3, UCST can be increased to 34°C, and when pH=10, UCST can be decreased to 23.5°C, and the corresponding range of the whole pH can reach 10.5°C. The problem of the corresponding singleness of the zwitterionic poly...
Embodiment 3
[0033] The design degree of polymerization is 300, and 20 mL of trifluoroethanol solvent and 3.0 g of zwitterionic monomer 3-(2-methacryloyloxyethyldimethylamino)propanesulfonate (DMAPS) are added to the round-bottomed flask. There is a carboxyl trithioester RAFT reagent ECT (structural formula and nuclear magnetic resonance 1 H NMR spectrum see figure 1 ) 0.0036g and initiator ACVA0.00072g, reacted at 70°C for 24h, and the product was dialyzed through a 3000MW molecular weight dialysis bag for 48h to obtain a zwitterionic polymer with terminal carboxyl groups (structural formula and nuclear magnetic resonance 1 H NMR spectrum see figure 2 ). The resulting carboxyl-terminated zwitterionic linear polymer (ECT-PDMAPS 300 ) has multiple stimuli responsiveness. When pH=3, UCST can be increased to 44°C, and when pH=10, UCST can be reduced to 35°C, and the corresponding range of the whole pH can reach 9°C. The problem of the corresponding singleness of the zwitterionic polymer ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| phase transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| degree of polymerization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| degree of polymerization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com