Thermal comfort modeling method based on changed adaptability factor and predicted average voting value
A modeling method and adaptive technology, applied in design optimization/simulation, computer-aided design, calculation, etc., can solve problems such as inability to accurately predict thermal comfort, inability to consider thermal adaptation dynamics, inability to fully explain thermal adaptation, etc., to achieve Accurately predict the effects of thermal comfort
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
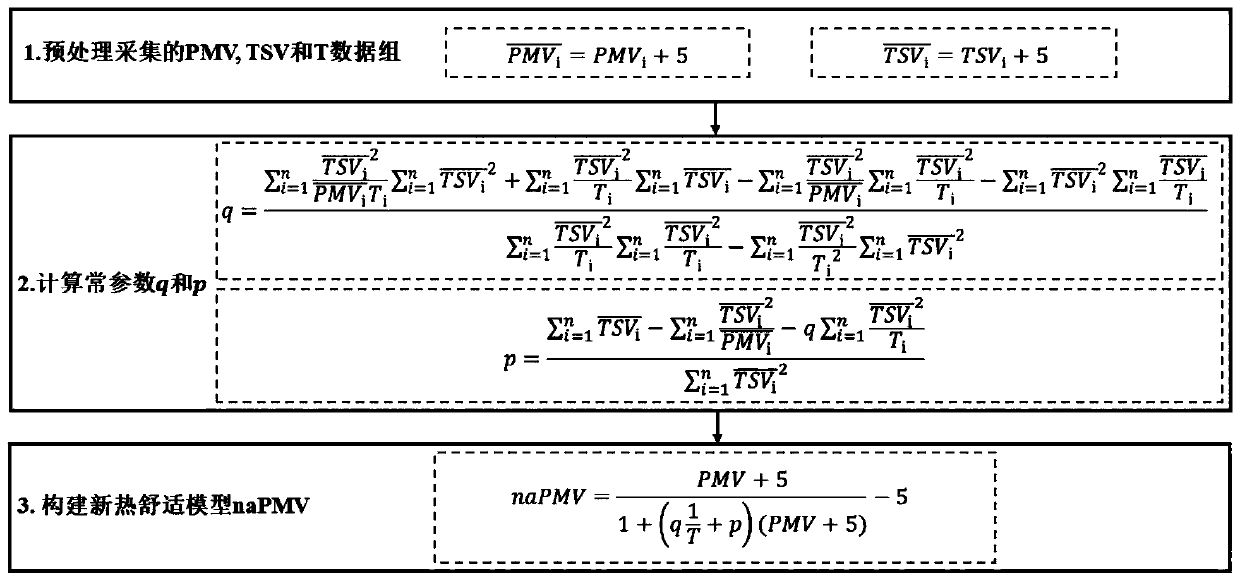
[0044] The present invention provides a novel thermal comfort model that can comprehensively account for thermal adaptation and thus more accurately predict thermal comfort. The method for building thermal comfort model of the present invention comprises three steps (as figure 1 shown): the first step is to preprocess the collected PMV, TSV and ambient temperature T data sets so that both PMV and TSV are greater than zero (such as formulas 12 and 13); the second step is to use the collected ambient temperature T and the pre-prepared dealt with Calculate the constant parameters q and p according to formulas 14 and 15 respectively; in the third step, use the obtained constant parameters q and p to construct the thermal comfort model naPMV according to formula 16.
[0045]
[0046]
[0047]
[0048]
[0049]
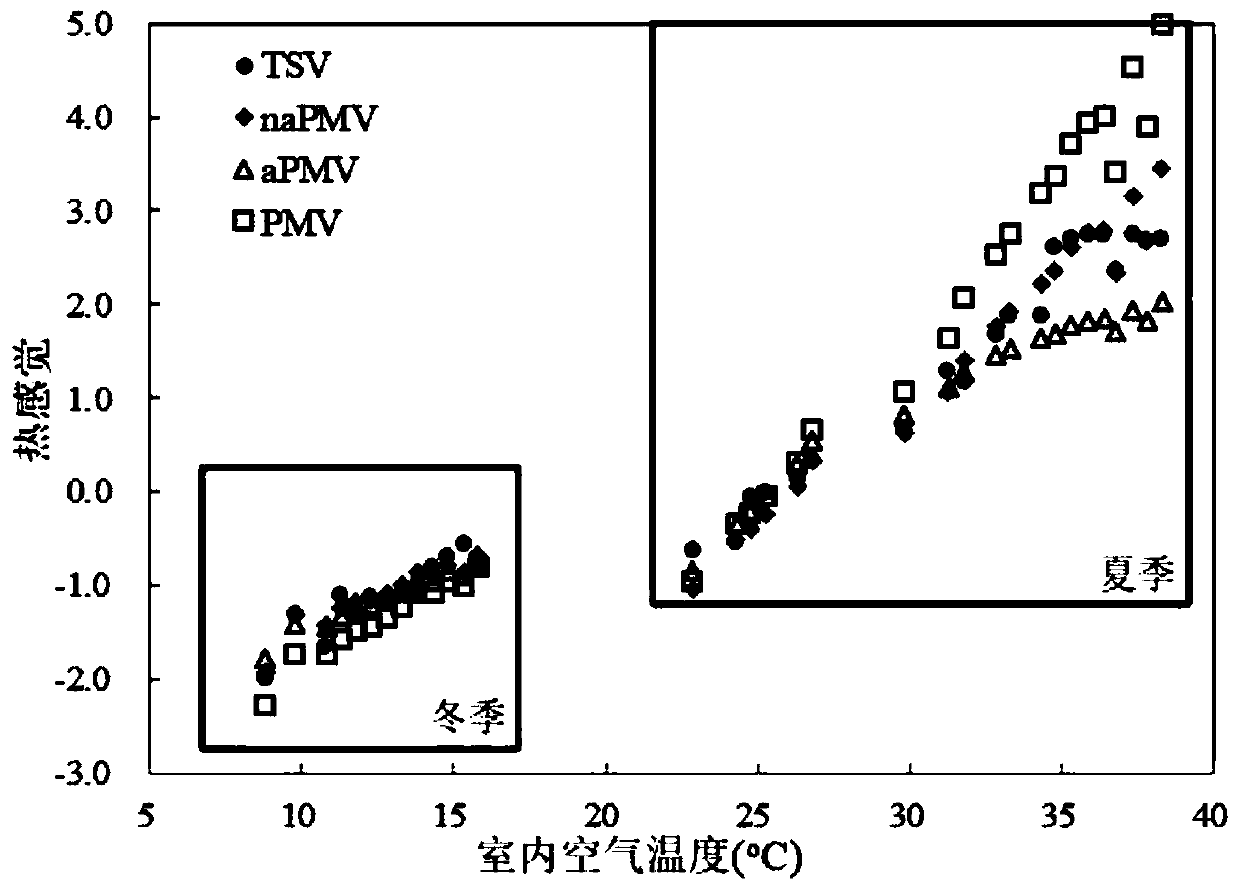
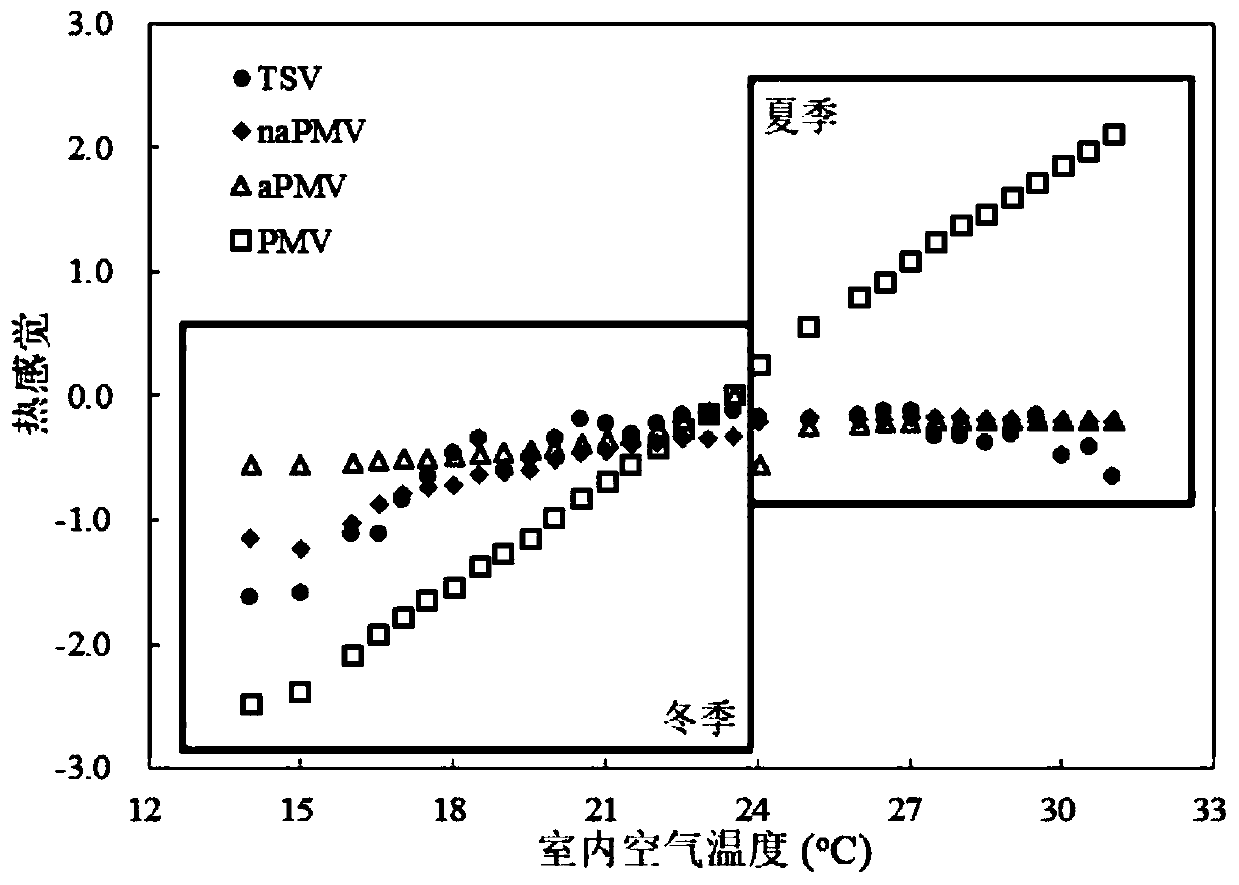
[0050] The advantages of the present invention are described below with two cases. The case will use the mean absolute error MAE and error standard deviatio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com