A radiofrequency tomography method based on zero-sparse data-driven weight model
A radio frequency tomography, data-driven technology, applied in the field of radio frequency, to achieve the effect of improving efficiency and improving effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
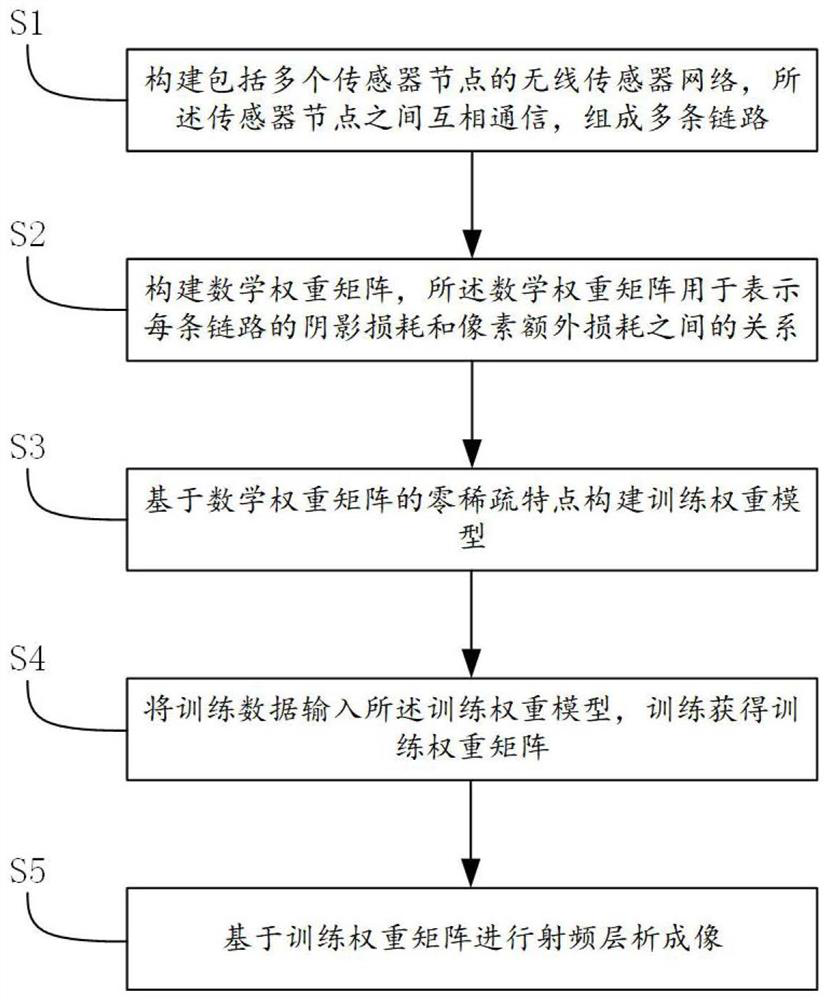
[0062] Please refer to figure 1 , the present embodiment provides a radio frequency tomography method based on a zero-sparse data-driven weight model, comprising the following steps:
[0063] S1. Construct a wireless sensor network including a plurality of sensor nodes, and the sensor nodes communicate with each other to form a plurality of links;
[0064] S2. Construct a mathematical weight matrix, the mathematical weight matrix is used to represent the relationship between the shadow loss and the pixel extra loss of each link;
[0065] S3. Construct a training weight model based on the zero-sparse characteristic of the mathematical weight matrix;
[0066] S4. Input the training data into the training weight model for training to obtain the training weight matrix;
[0067] S5. Perform radio frequency tomography based on the training weight matrix.
[0068] Wherein, the training weight matrix includes weight factors of each pixel corresponding to each link.
[0069] In t...
Embodiment 2
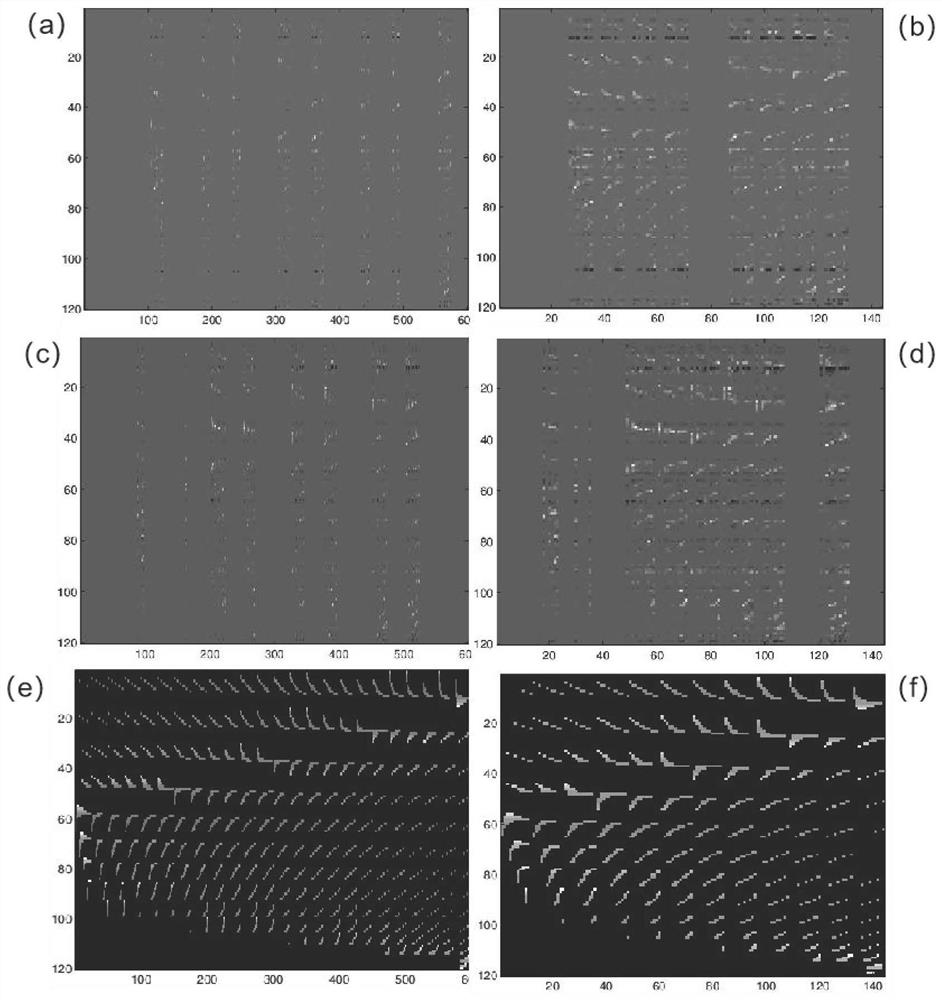
[0117] In the second embodiment, Scene 1 and Scene 2 are used as training data to train the training weight model, and the traditional ellipse weight model is used as a comparison example to explore the effect difference between the method of the present invention and the traditional method.
[0118] The ellipse model used for comparison with the present embodiment is as follows:
[0119]
[0120] Among them, φ ij Indicates the shadow fading weight of pixel j with respect to link i, d tx(i),j and d rx(i),j Respectively represent the distance between pixel j and the transmitting node and receiving node of link i, d represents the distance between receiving and transmitting nodes.
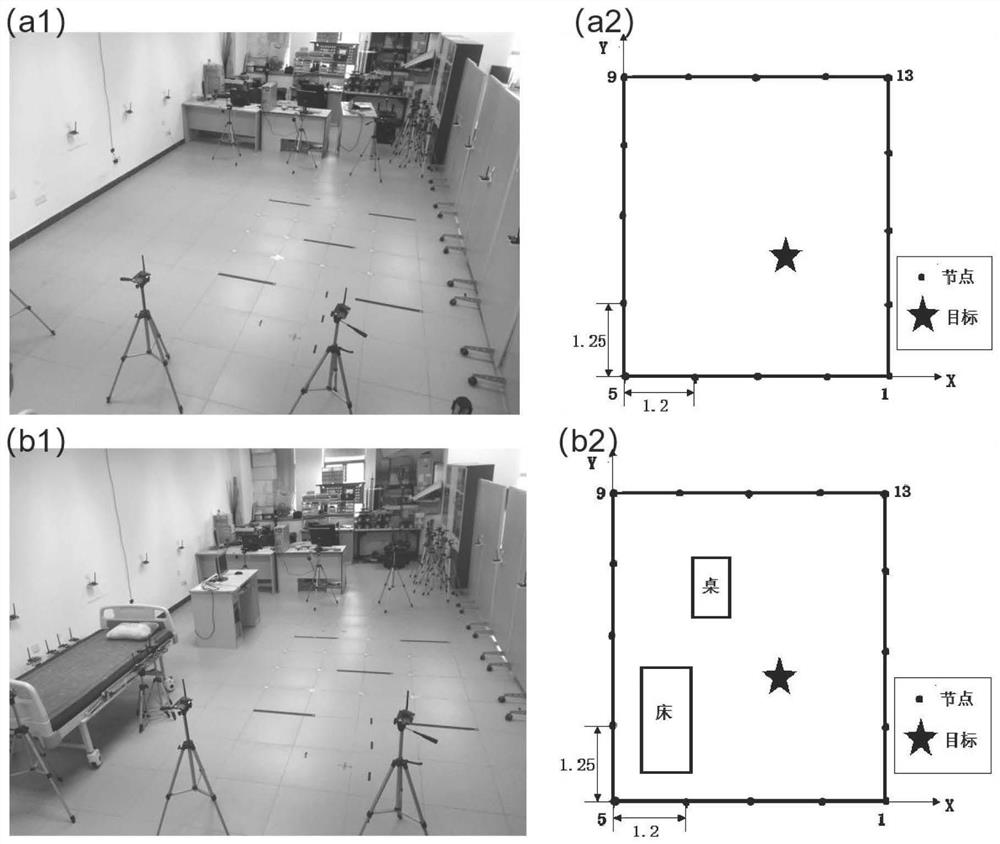
[0121] Scene 1 described in this embodiment is an obstacle-free perception area. Such as the real picture of scene 1 ( figure 2 (a1)) and topological graph ( figure 1 As shown in (a2)), there are no obstacles in the scene, but there are walls on the left and right sides of the scene, and des...
Embodiment 3
[0127] In this embodiment, a hands-free positioning experiment is carried out to test the actual positioning effect of the training weight model provided by the present invention.
[0128] In this embodiment, scene 1 and scene 2 are respectively used as training data to input the training weight model, and the training weight matrix based on scene 1 and the training weight matrix based on scene 2 are obtained, and the weight matrices obtained from different scene data are reconstructed respectively. Hands-free target and compare with the localization results of the ellipse weight model. In this embodiment, the Bayesian target estimation algorithm is used for sparse image reconstruction, and the parameter settings in the reconstruction algorithm are the same. In this embodiment, the pixel width is set to 0.2m and 0.4m respectively, which is mainly based on the fact that the width of the human body is generally between 0.2m-0.4m, if the pixel width is set to be greater than 0.4m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com