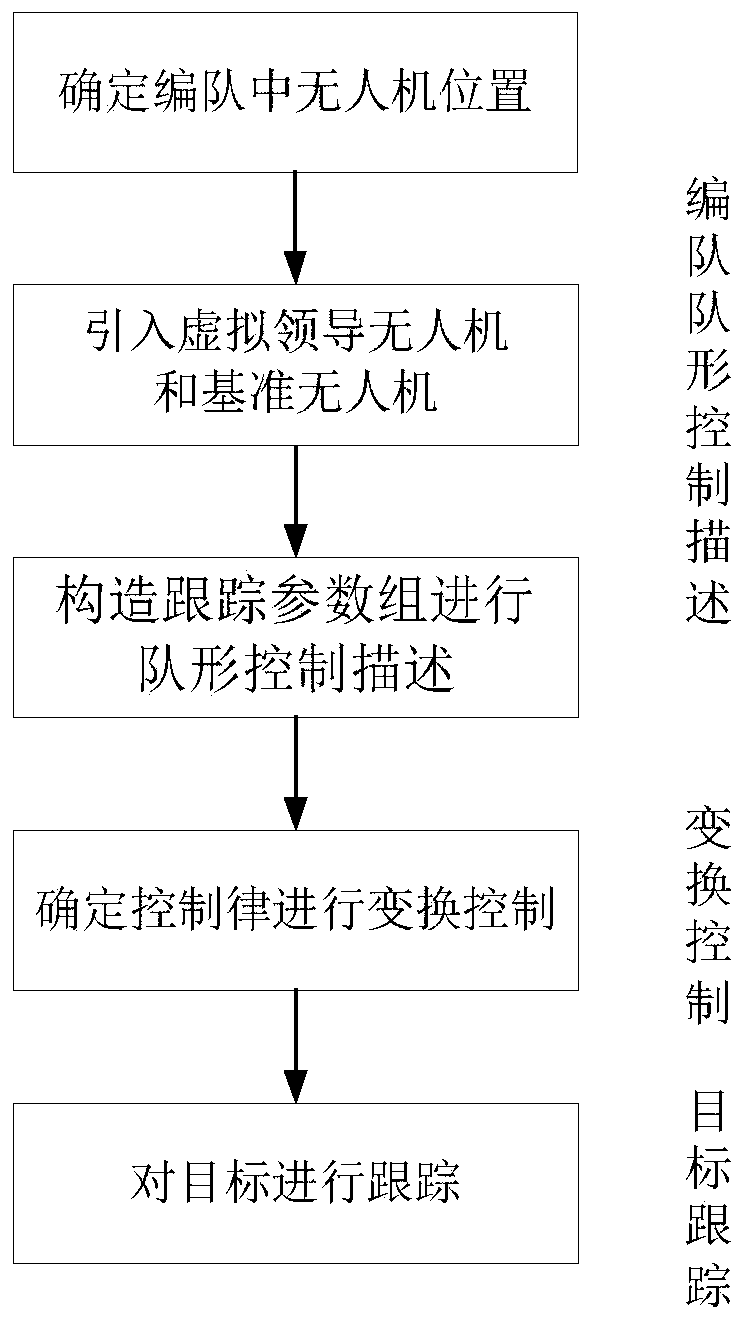
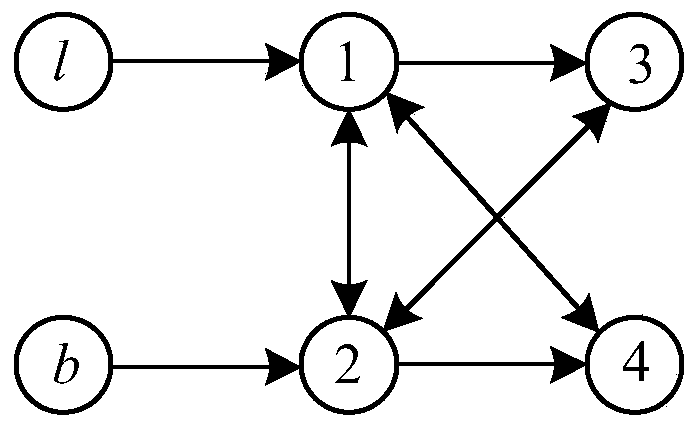
Multi-plane formation pattern control description, transformation control and target tracking method
A technology of transformation control and formation, which is applied in the field of target tracking and can solve problems such as formation invariance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0197] Let N=4, that is, using a formation composed of 4 UAVs as an example, respectively control the formation change and control the formation at two target speeds v t The formation target tracking problem in different situations is simulated and verified, and at the same time for different values of k 1 、k 2 Simulation verification of the influence of UAV formation performance, and with the literature "SUMMERS T H, AKELLA M R, MEARS M J. Coordinated standoff tracking of moving targets: Control laws and information architectures [J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2009,32(1):56-69." The proposed method is simulated and compared.
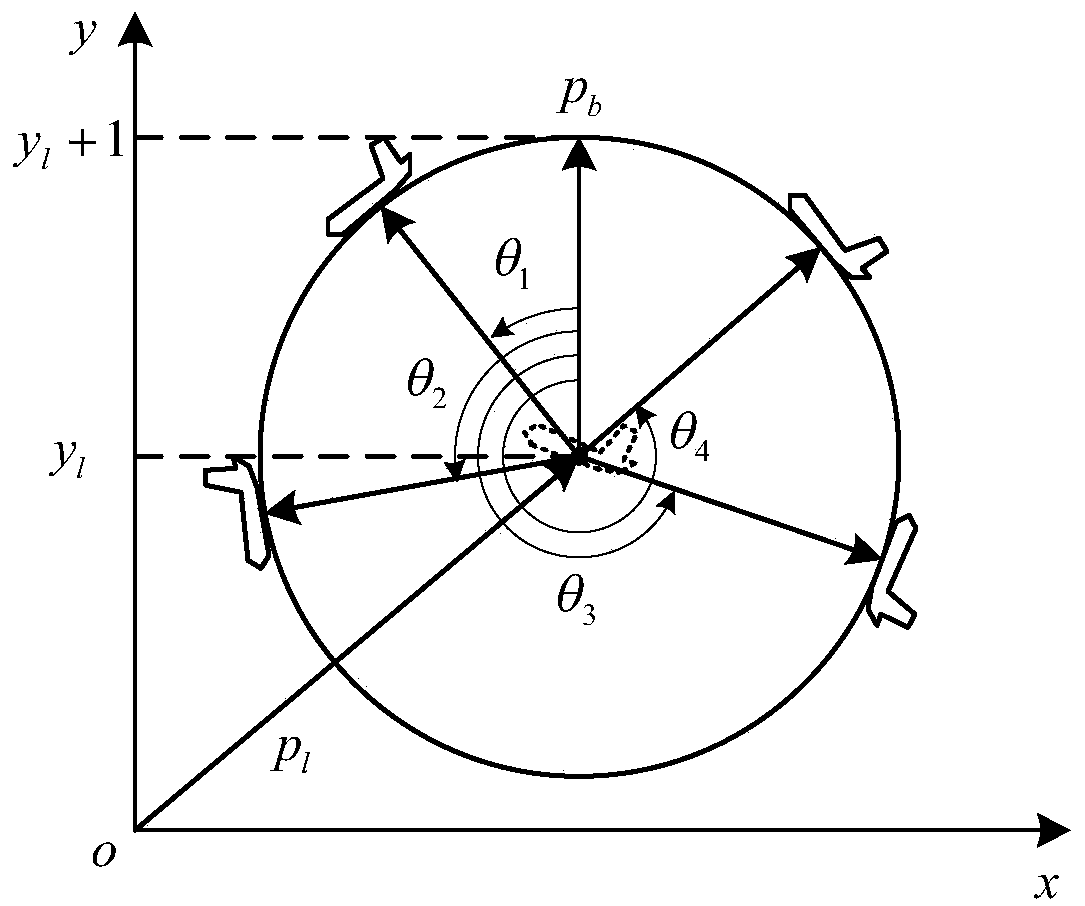
[0198] At the beginning of the simulation, the initial states of the UAV and the target are set. Set the minimum flying speed of the UAV to 6m / s, and let the initial positions of the four UAVs be (-500m,0), (0,500m), (0,-500m) and (500m,0); the initial speed v i is [20,0] T m / s; UAV l The initial position of is the center point ...
Embodiment 2
[0204] When tracking against a target v t min case, let r i =200, i∈Θ. Other simulation parameters are the same as in Embodiment 1.
[0205] Set target speed v t is [4,4] T m / s, the minimum rotational angular velocity ω can be obtained from (42) i = 1 / 100 rad / s. Figure 7 It shows that four UAVs start from their respective positions, form a circular formation during the process of tracking the target, and then maintain the formation flight state to track the target. After the UAV formation tracks the target, due to the target speed v t Fixed-wing UAV minimum flight speed v not reached min , so the UAV formation maintains a fixed distance Standoff tracking around the target. Figure 8 Error e before and after generation for the UAV formation i =p i -p l -C i p b It can be seen from the figure that the formation error tends to 0 at about 10.8s, which is the expected formation state between UAVs; at 19.7s, the error curve has a slight jitter, but at 24.4s the error te...
Embodiment 3
[0207] When tracking against a target v t ≥v min In the case of , set the target speed v t is [10,10] T m / s. Other simulation parameters are the same as in Embodiment 1.
[0208] Figure 9 It shows the trajectories of four UAVs tracking the target in a formation state. Due to the target speed v t Greater than the fixed-wing UAV minimum flight speed v min , so the UAV formation does not need to hover around the target, but only needs to keep the phase around the target to track the target. Figure 10 is the error e of the UAV formation i image, same as v t min Consistent, at 10.8s, the expected formation formation was formed between UAVs, and the formation error tended to 0; at 48.3s, the error curve showed a slight jitter, but at 52.4s, the error tended to 0 again, which was also due to the UAV’s caused by speed adjustment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com