Multicast service management method and device
A technology of multicast service and management method, applied in the field of multicast service management method and equipment, capable of solving problems such as impact on network resources
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
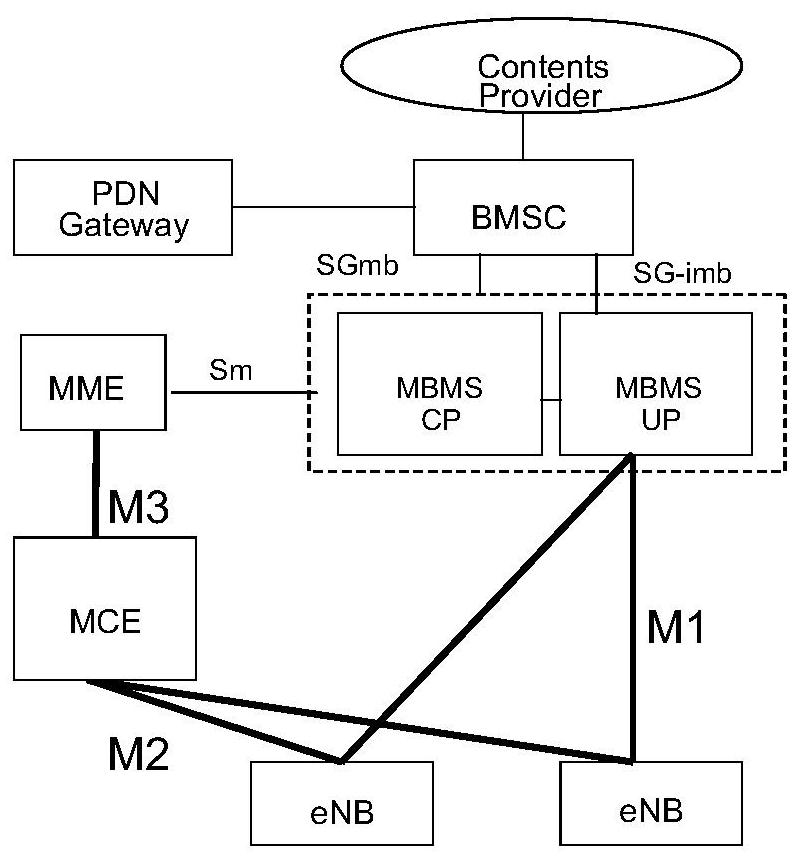
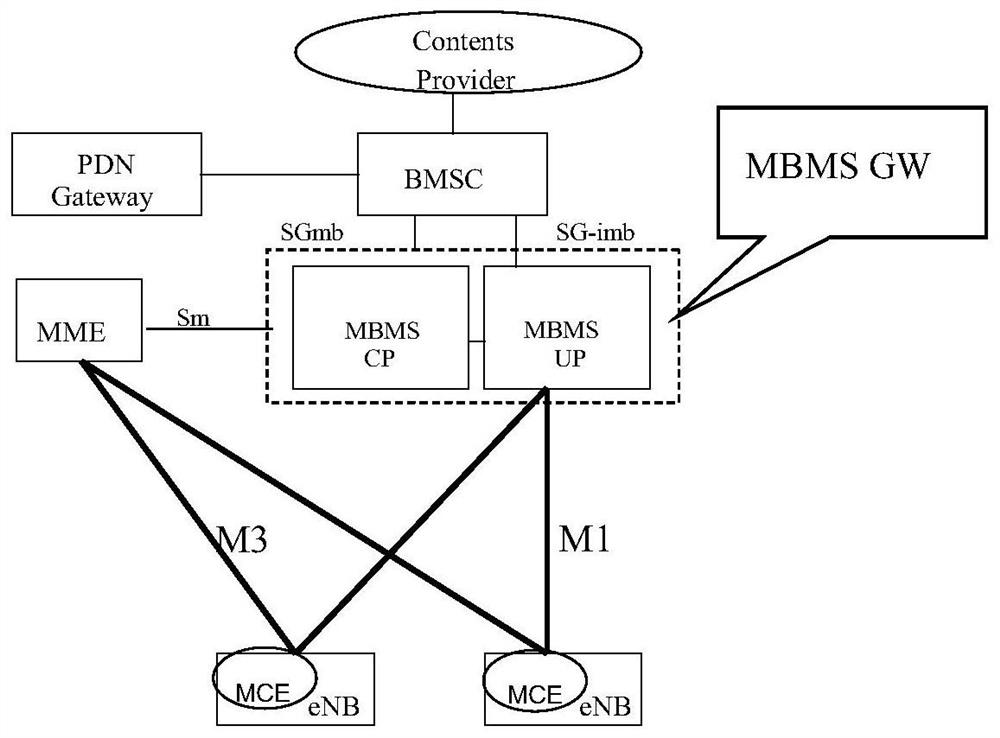
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0360] Embodiment 1: Based on a network architecture similar to EPS eMBMS
[0361] see Figure 6 ,exist Figure 6 In the network architecture shown:
[0362] (1) Multicast (Multimedia Broadcast, MB)-access and mobility management function (Acess and Mobility Management Function, AMF) is responsible for MB-session management function (Session Management Function, SMF) and next generation (next generation, NG)-wireless access Forwarding of session management messages between radio access networks (RANs);
[0363] (2) MB-SMF is a dedicated SMF for MBMS, corresponding to the MBMS-gateway (Gateway, GW) control plane, responsible for: MBMS bearer session creation / modification / release, Internet Protocol (Internet Protocol, IP) multicast address allocation, etc.
[0364] (3) MB-UPF is a dedicated MBMS user plane function (User plane function, UPF), corresponding to the MBMS-GW user plane, responsible for: sending MBMS user plane data to the Evolved UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Net...
Embodiment 2
[0413] Embodiment 2: MBMS network architecture based on 5G core network (5GC)
[0414] see Figure 11 ,exist Figure 11 In the network architecture shown:
[0415] (1) When the application function (Application function, AF) requires the 5GC to establish a group session (groupsession), the NEF selects the group (Group)-SMF, hereinafter referred to as (G-SMF).
[0416] (2) The AF is responsible for the service announcement: inform the UE of the necessary information of the multicast service (such as TMGI and service start time) through the application layer message.
[0417] (3) G-SMF selects a specific AMF to support message interaction between G-SMF and RAN;
[0418] (4) The G-SMF selects a UPF and informs the AF of the relevant information of the UPF.
[0419] see Figure 12 ,Specific steps are as follows:
[0420] Step 1: The UE measures and determines the target cell list, and reports the multicast related information to the AF through an application layer message. ...
Embodiment 3
[0437] Embodiment 3: Receive multicast data through EPS, send / receive unicast data through 5GS, see Figure 13 .
[0438] In the E-UTRAN network, the UE is in a receive-only mode (Receive-only mode, ROM), that is, it can directly receive the MBMS multicast service without registering to the Evolved Packet System (Evolved Packet System, EPS) network.
[0439] UE knows the MBMS service service area. If the UE finds that there is no E-UTRAN within the coverage of multiple target gNBs to support the UE's multicast reception preference, it will trigger the App server to establish a multicast session with some eNBs. The App server will feed back the establishment status to the UE through an application layer message.
[0440] When reporting the measurement results, the UE only reports the measurement results of the target gNB that can ensure E-UTRAN multicast reception to the source gNB.
[0441] During handover, the source gNB will comprehensively consider the MBMS support of th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com