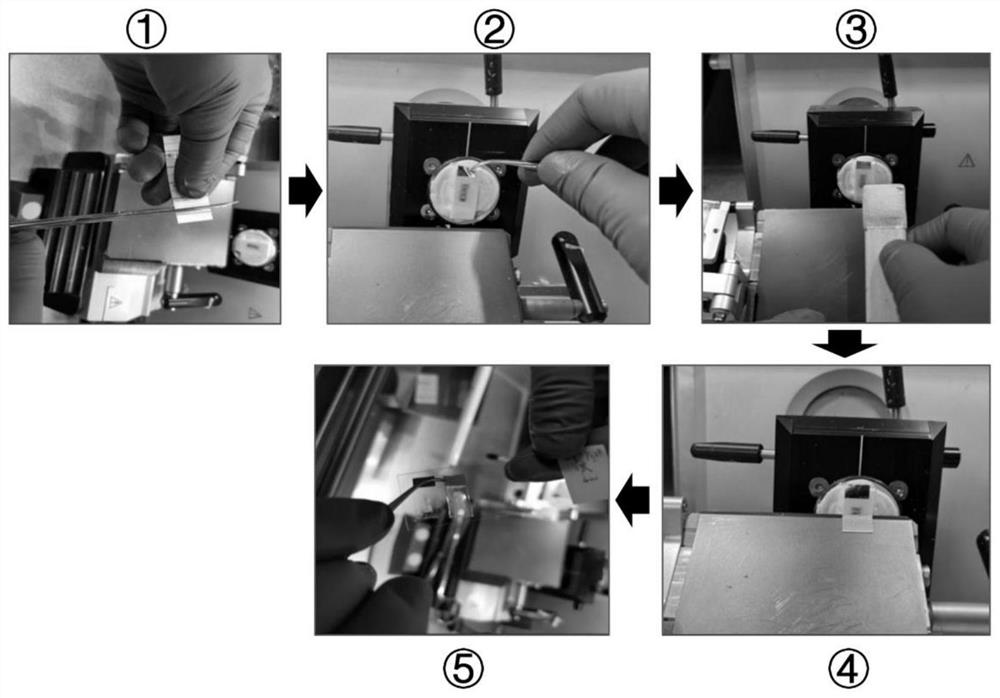
Slice preparation method of non-decalcified osteochondral tissue and osteochondral tissue cell tracing and RNAScope combined test method
A technique for tissue slices and cartilage tissue, which is applied in the joint testing of osteochondral tissue cell tracing and RNAscope, and the preparation of non-decalcified osteochondral tissue slices. Effects of fluorescence interference, avoiding damage and degradation, and saving decalcification time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
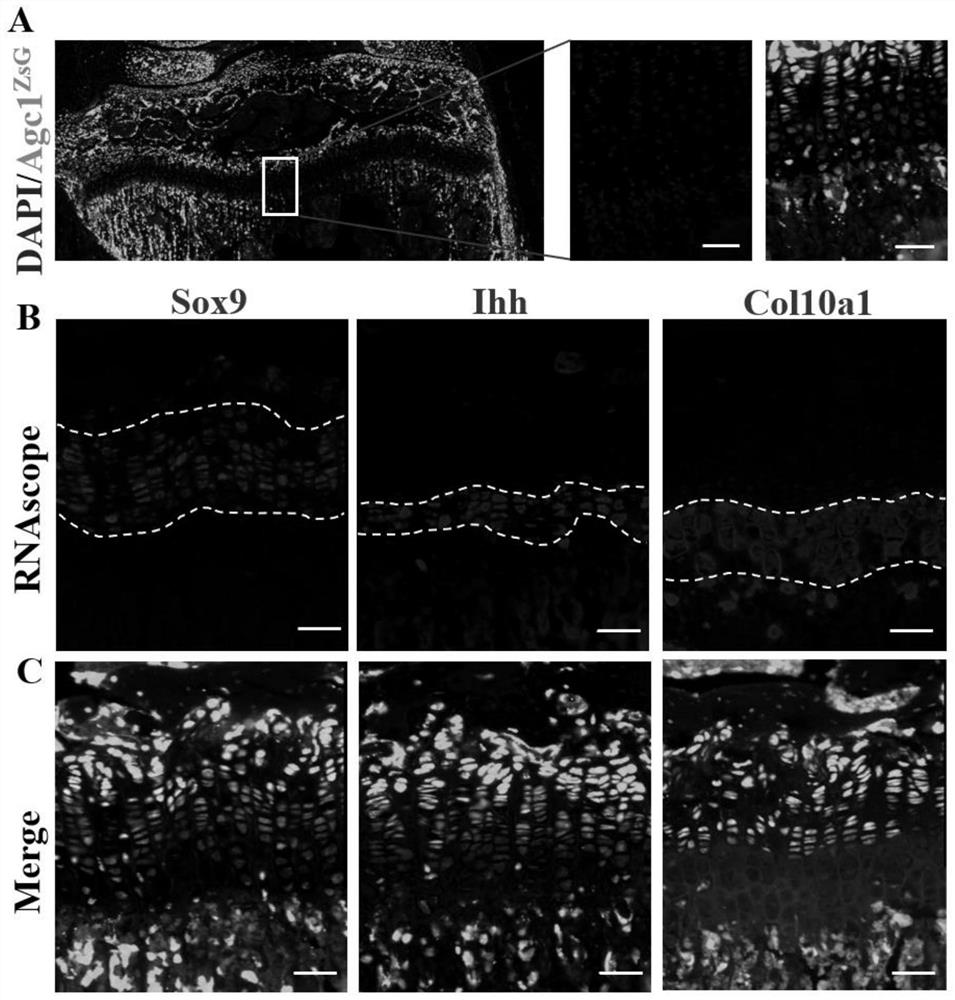
[0055] In this example, 6-week-old model mice were used, which were obtained by crossing Shp2fl / fl mice with Agc1-Cre / ER; Rosa26ZsG mice. The mouse genotype is, Tg(Agc1-CreER; Shp2 fl / + ;Rosa26 ZsG ), the mouse was intraperitoneally injected with tamoxifen within 2 weeks after birth to activate the expression of Cre recombinase, which can only be expressed under the action of Agc1 promoter, and the expression of Cre recombinase can activate the expression of fluorescent protein ZsG, In this way, the cells expressing Agc1 all have the expression of green fluorescent protein ZsG, so that Agc1 positive cells can be traced.
[0056] After preparing the osteochondral tissue slices pasted with Kawamoto membrane in the proximal tibia of the model mouse, RNAscope2.5HD Assay Red Kit produced by Advanced Cell Diagnostics was selected for the in situ hybridization experiment in this example. The process of the in situ hybridization hybridization experiment was performed according to th...
Embodiment 2
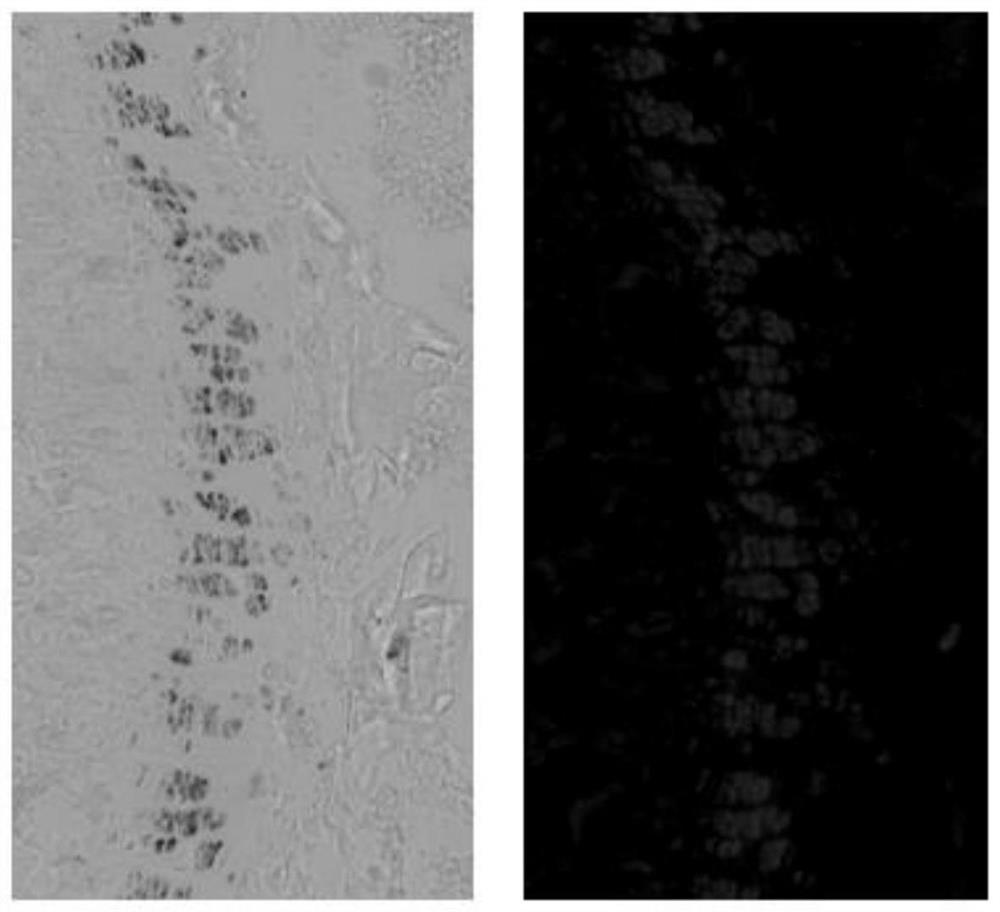
[0058] In this example, the cell tracking method and RNAscope were used to detect the knockout efficiency of the target gene at the mRNA level on the osteochondral tissue section. In this experiment, 10-week-old Tg(Agc1-CreER;Shp2 fl / + ;Rosa26 ZsG ) and Tg(Agc1-CreER; Shp2 fl / fl ;Rosa26 ZsG ) Proximal tibia of model mice. After the osteochondral tissue slices pasted with Kawamoto membrane were prepared, RNAscope 2.5HD Assay RedKit produced by Advanced Cell Diagnostics was used for in situ hybridization experiments. The process of the in situ hybridization hybridization experiment was performed according to the experimental manual of RNAscope 2.5HD Assay RedKit, and each time the osteochondral tissue slice was treated with the reagent, it only needed to cover the osteochondral tissue slice with the reagent. Test results such as Figure 4 shown. Counting the number of red dots among the 100 green cells in the middle region of the growth plate revealed a significant reducti...
Embodiment 3
[0060] In this example, the technical solution of the present invention is used to study the pathological changes of osteochondral bone. In this experiment, 10-week-old Tg(Ctsk-Cre;Shp2 fl / fl ;Rosa26 ZsG ) Proximal tibia of model mice. The chondroma on the articular cartilage of the proximal tibia after SHP2 was knocked out in Ctsk-positive cells in mice, the cells of the chondroma originated from Ctsk-positive cells. After the osteochondral tissue slices pasted with Kawamoto membrane were prepared, RNAscope 2.5HD Assay Red Kit produced by Advanced Cell Diagnostics was used for in situ hybridization experiment. The process of the in situ hybridization experiment was performed according to the experimental manual of the RNAscope 2.5HD Assay Red Kit, and each time the osteochondral tissue section was treated with the reagent, it was only necessary to cover the osteochondral tissue section with the reagent. Test results such as Figure 5 shown. In the figure, it can be obser...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com