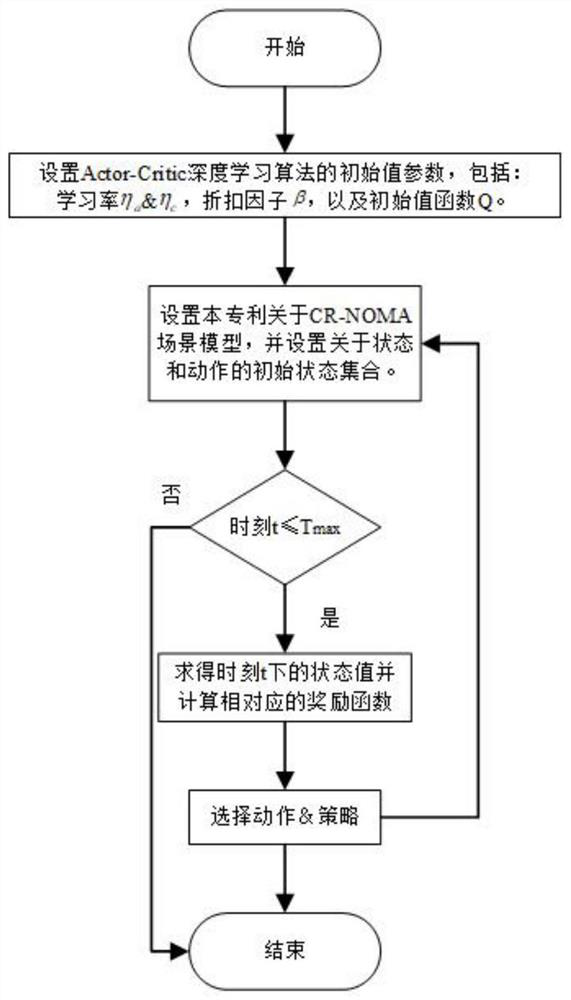
Algorithm for solving power distribution in cognitive radio based on reinforcement learning
A cognitive radio and reinforcement learning technology, applied in the field of power allocation strategy, can solve the problem of incomplete channel information and power allocation, and achieve the effect of effectively adjusting the transmission power
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
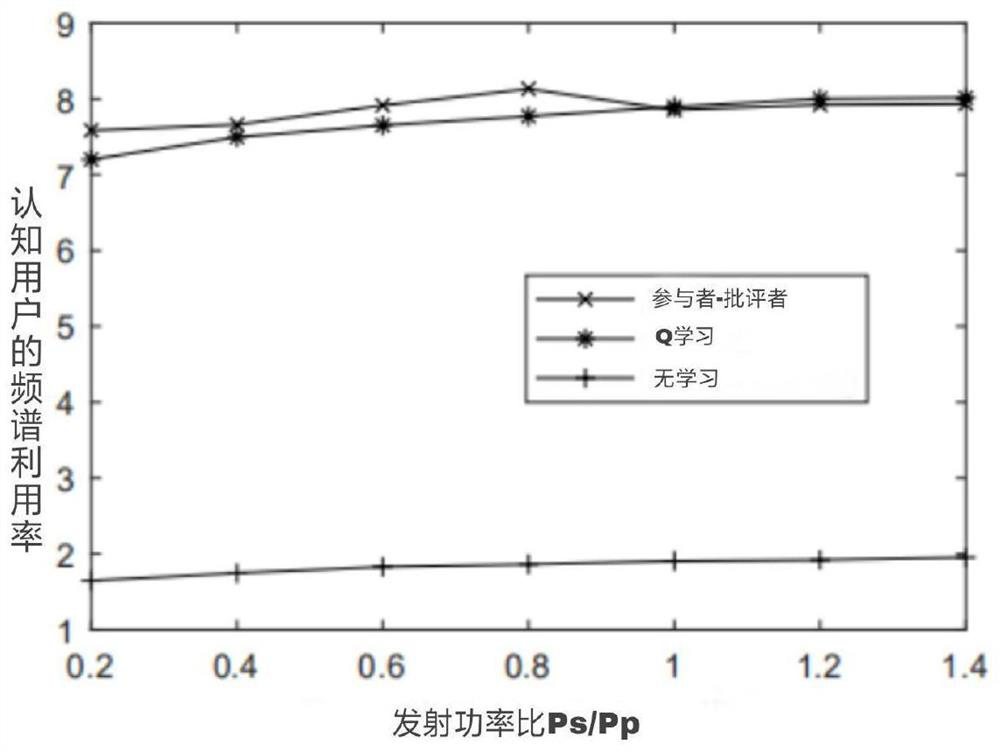
[0040] 1. Simulation conditions: 1) The number of CUs is K=6, 2) The transmission power of the PU is P PU = 15dB, 3) the discount factor is β = 0.9, 4) the learning rate of the participants is η a = 0.01, 5) The critic's learning rate is η c = 0.001.
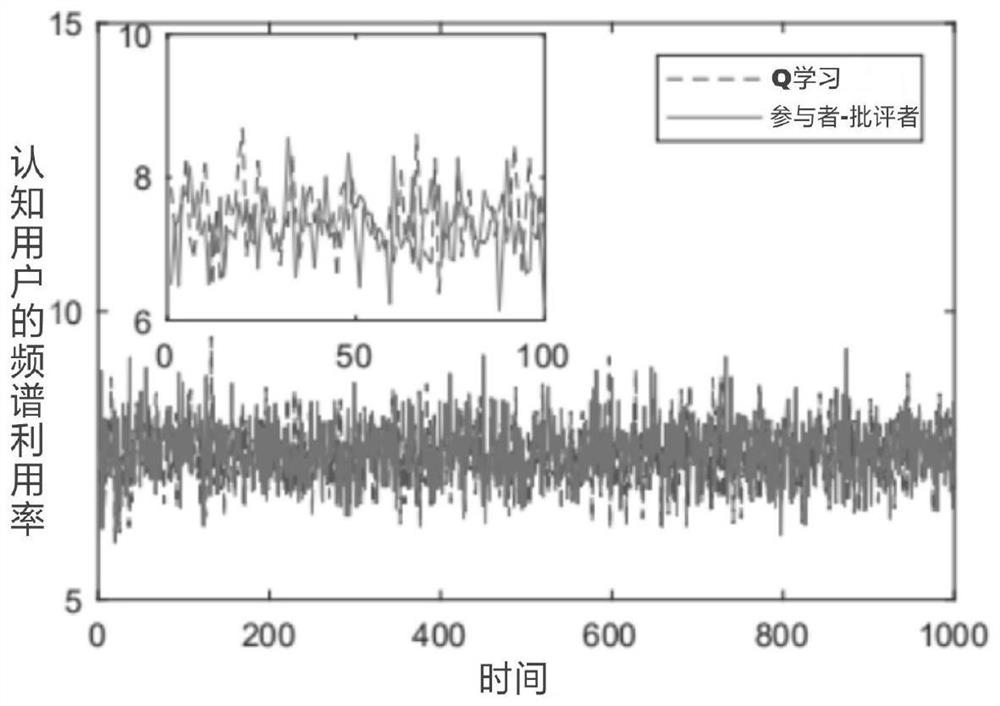
[0041] 2. Simulation content: simulate and compare the relationship between the spectral efficiency (Spectralefficiency, SE) performance of CUs and the time index under different learning algorithm scenarios. The results are as follows: figure 2 . figure 2 Among them, the vertical axis is "spectrum utilization rate of cognitive users"; the horizontal axis is "simulation iteration time".
[0042] Depend on figure 2 Simulation results show that by using Q-learning, continuous-valued states and actions must be quantized, and actual values are replaced by finite discrete-valued approximations. Contrary to our AC-RL algorithm, the Q-learning based power allocation algorithm needs to know the immediate CSI of CUs. Figure 2 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com