RANSAC (Random Sample Consensus) improvement method suitable for simultaneous localization and mapping
A map construction and model technology, applied in the fields of computer vision, image processing and positioning and navigation, can solve the problems of high time cost, inability to achieve real-time SLAM, unavoidable cumulative error, etc., to achieve the effect of improving accuracy and robustness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
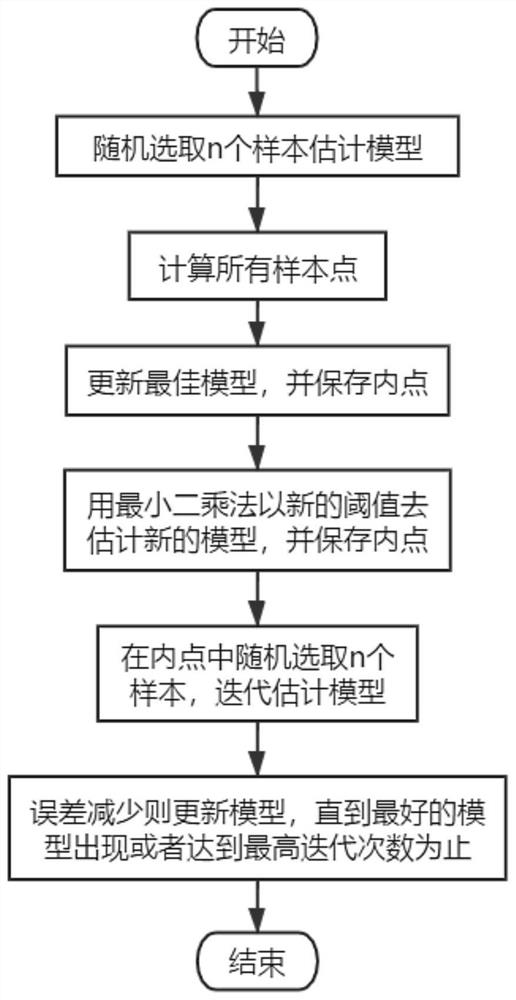
[0050] refer to figure 1 , is the first embodiment of the present invention, and this embodiment provides a kind of RANSAC improved method that is suitable for real-time positioning and map construction, comprises:
[0051] RANSAC (Random Sample Consensus) is an algorithm that calculates the mathematical model parameters of the data based on a set of sample data sets containing abnormal data, and obtains effective sample data.
[0052] S1: Randomly select n sample estimation models, use the sample estimation models to calculate all points, and obtain the number of internal points.
[0053] It should be noted that the sample estimation model can be a one-dimensional primary model, two-variable primary model or one-dimensional quadratic model, etc. The sample estimation model in this embodiment is:
[0054] y=ax+b
[0055] Substitute all the points into the sample estimation model, and the points conforming to the sample estimation model are considered as inliers, otherwise th...
Embodiment 2
[0078] In order to verify and illustrate the technical effect adopted in this method, this embodiment conducts experiments in various situations, utilizing the TUM of the indoor hand-held camera to collect the data set, the data set KITTI of the outdoor expressway and urban traffic, and the micro air vehicle (MAV) The collected data set EuRoC is used for comparative experiments.
[0079] The parameters are set as follows: the value of f is 0.99, the maximum number of iterations is 300, the number of randomly selected samples is 4, the probability d of selecting an inlier from the data set each time is 0.5, and the threshold for judging the maximum error is 5.991σ 2 , wherein, σ=0.3; the number of samples randomly selected during iteration is: min(14, I / 2), where I is the number of interior points in the previous round, and the multiple of threshold value change is 0.7.
[0080] (1) From a qualitative point of view, figure 2 and image 3 shows the matching of the two frames ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com