Biodegradable tissue replacement implant and its use
An implant and tissue technology, applied in tissue regeneration, medical science, prosthesis, etc., can solve problems such as methods that have not yet provided functional verification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0261] Materials and methods
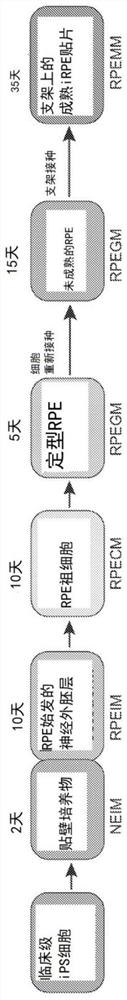
[0262] Research and Clinical Grade iPSC Derivation, Maintenance and RPE Differentiation: Reporter iPSC Lines Expressing GFP Under the Control of a Tyrosinase Enhancer and Constitutive RFP have been previously published (Maruotti et al., Proc Natl Acad Sci U SA112, 10950-10955(2015)), and for optimizing research-grade differentiation protocols. iPSCs were cultured on MEFs for 4 days before being used for differentiation. To prepare cell aggregates, iPSCs were treated with collagenase for 20 min. After aspirating collagenase, NEIM (DMEM / F12, KOSR, supplement N2, B27, LDN-193189 10uM, SB431452 10nM, CKI-7 hydrochloride 0.5uM and IGF-11ng / ml) was added to the wells (1ml / wells), and then scraped off the colonies with a cell scraper. Cell aggregates in NEIM medium at 10 cm 2 Grow in low-adsorption Corning dishes for 48 hours. After 48 h, the floating cell aggregates were collected and seeded on Coated plates were cultured in RPEIM (DMEM / F12, KO...
Embodiment 2
[0294] A clinical-grade three-phase protocol efficiently and reproducibly generates AMD-iRPE cells
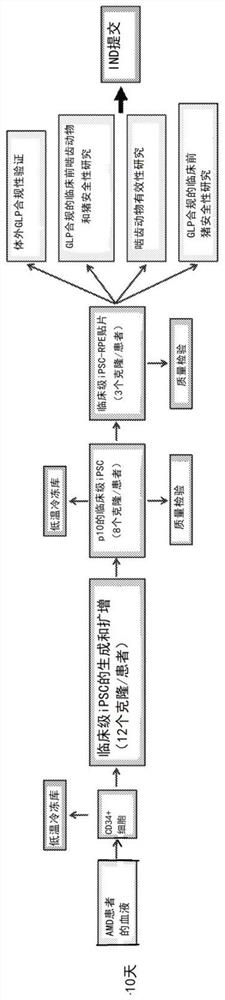
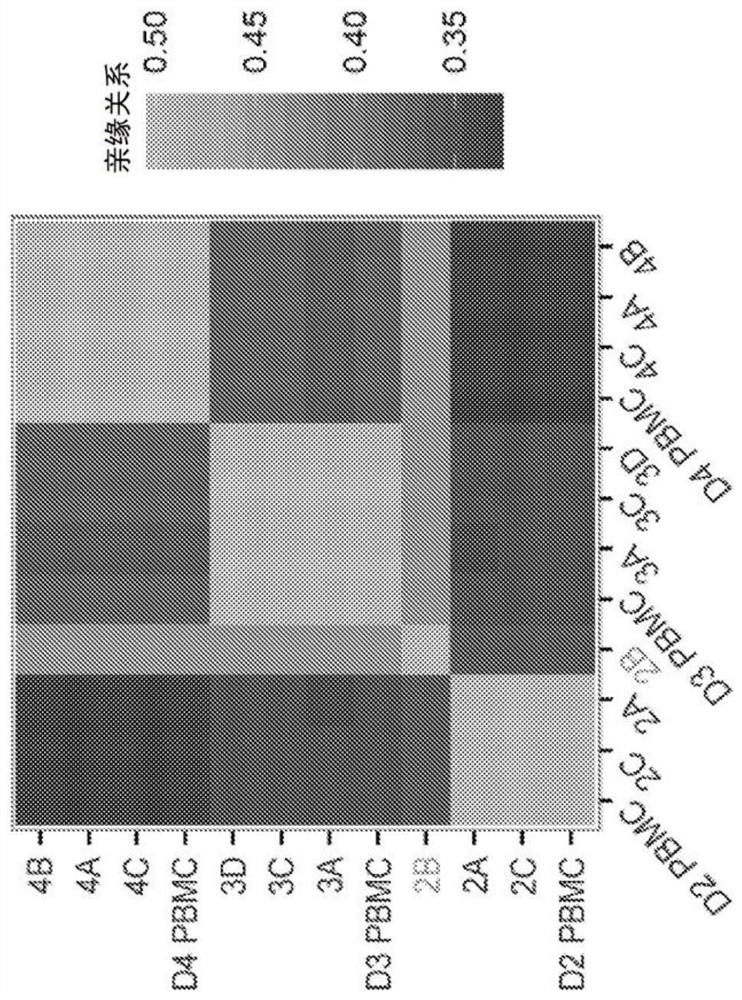
[0295] iPSCs derived from AMD patient skin fibroblasts acquired chromosomal copy number changes under clinical-grade conditions, likely during reprogramming (Mandai et al., N Engl J Med 376, 1038-1046 (2017)). However, when deriving iPSCs from older patients, skin fibroblasts are not considered an ideal starting source (Kang et al., Cell Stem Cell 18, 625-636 (2016)). Therefore, a production workflow for obtaining autologous iPSC-derived RPE patches from patient CD34+ peripheral blood cells was developed. Development of a pipeline diagram for the generation, functional validation and in vivo testing of clinical-grade AMD patient-specific iPSC-RPE patches ( Figure 1A , B). Due to their progenitor and proliferative properties, CD34+ cells isolated from peripheral blood of patients can provide a good source for iPSC generation. Using a clinical-grade additive genetic reprogram...
Embodiment 3
[0302] Biodegradable scaffold facilitates functional maturation of clinical-grade AMD-iRPE cells into monolayer tissue
[0303] It was hypothesized that a biodegradable scaffold would provide a suitable material for RPE cells to secrete extracellular matrix (ECM) to form polarized monolayers. As the scaffold degrades, the ECM and cells will form a native RPE-like tissue, which will increase the likelihood of long-term integration of the iRPE patch in the patient's eye. Scaffolds used in clinical-grade procedures were produced using poly-(lactic-co-glycolic acid) / PLGA (50:50 lactic / glycolic acid, IV midpoint 1.0 dl / g), The average fiber diameter was previously shown to be 350 nm to be optimal for RPE growth (Liu, et al., Biomaterials 35, 2837-2850 (2014); Stanzel et al., Stem Cell Reports 2, 64-77 (2014)). A single-layer heat-fused nanofibrous scaffold was chosen for iRPE patch production because its high Young's modulus correlates with ease of grafting ( Figure 2A , 2B). A...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com