Method for extracting catechin and epicatechin by using camellia plant peels
A technology of epicatechin and catechin, which is applied in the field of extracting catechin and epicatechin, and can solve problems such as numerous steps, high prices for consumers, and pushing up catechins
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] a. Selection of raw materials:
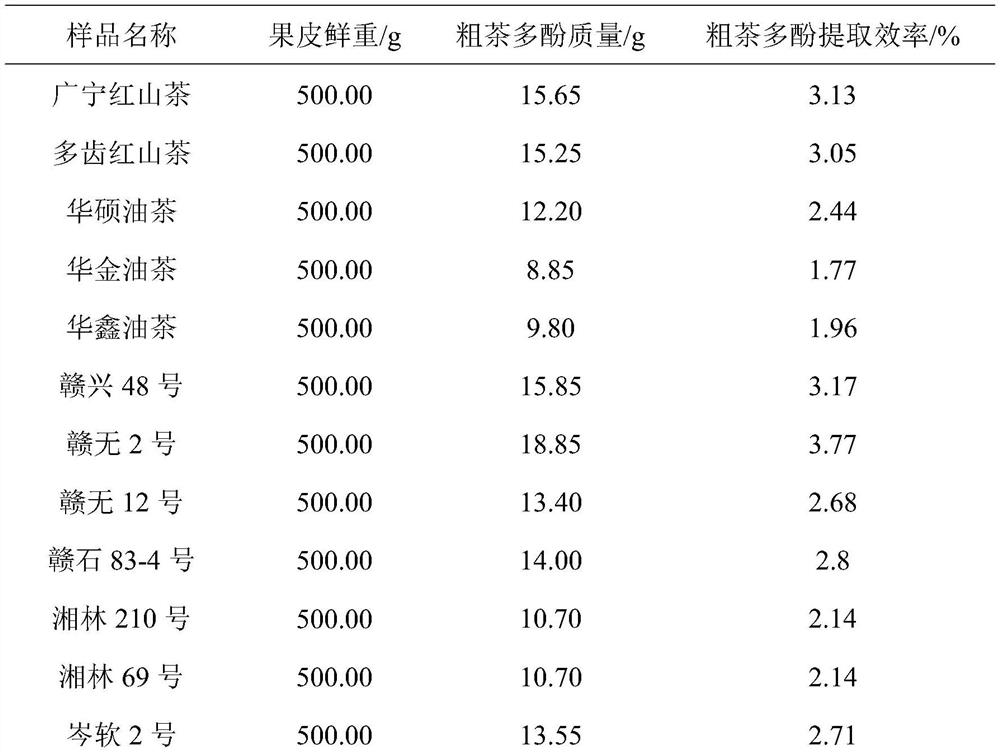
[0025] The selected camellia varieties include Huashuo Camellia, Huajin Camellia, Huaxin Camellia, Ganxing No. 48, Ganwu No. 2, Ganwu No. 12, Ganshi No. 83-4, Xianglin No. 210, Xianglin No. 69, Cenruan No. 2, Cenruan No. 3, Changlin No. 53, Changlin No. 4, Changlin No. 40, and Changlin No. 3. Other Camellia plants selected include Guangning Red Camellia, Multi-toothed Red Camellia, Golden Camellia, Pingguo golden camellia, Zhejiang safflower camellia, Tengchong safflower camellia, red skin rough fruit tea, Liping small fruit camellia No. 2, Liping small fruit camellia No. 3; collect fresh fruits respectively, remove the seeds and leave the peel.
[0026] b. Pretreatment of raw materials:
[0027] After washing the peel, cut it into thin slices with a thickness of 0.3 mm.
[0028] c. Extraction method:
[0029] Soak 500 g of the pericarp flakes obtained after the treatment in step b with 1000 mL of food-grade ethanol aqueous solution w...
Embodiment 2
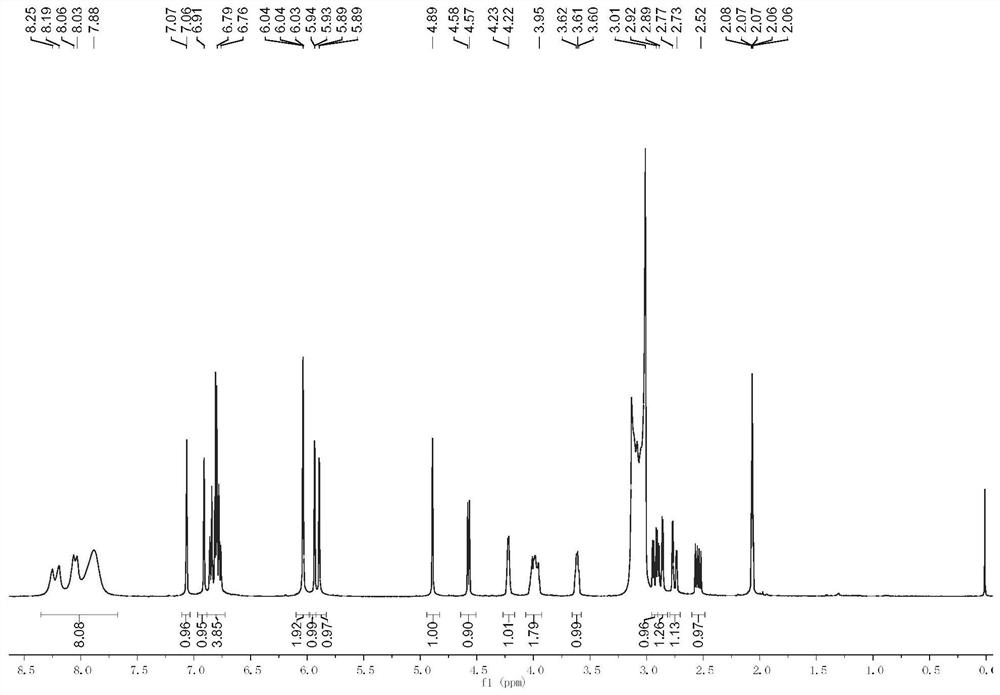
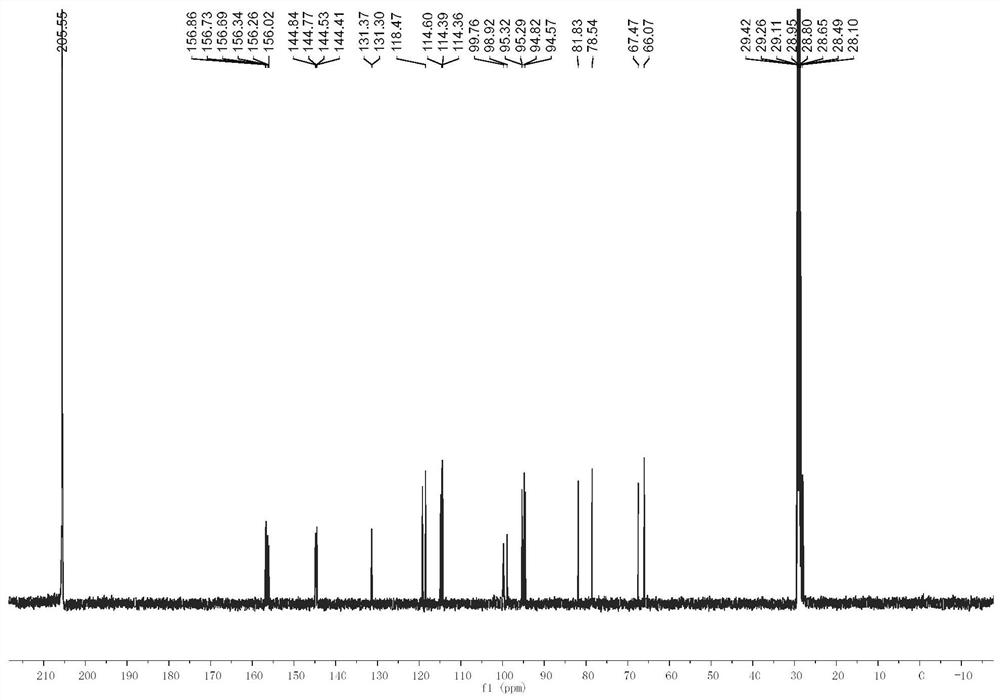
[0034] Take 500g of freshly picked Guangning Red Camellia pericarp, chop it up, and extract it with 1000mL volume fraction of 95% ethanol aqueous solution, soak for 12 hours each time, extract 4 times, combine the extracts, then concentrate under reduced pressure, add Disperse with 100mL ethanol, and filter to retain the filtrate. The filtrate was concentrated by rotary evaporation in vacuo, and then freeze-dried at low temperature to obtain 15.65 g of crude tea polyphenol mixture with a yield of 3.13%. Further purification analysis found that the main components of the crude tea polyphenol mixture were catechin, epicatechin, and catechin glycosides.
[0035] 15.65 g of the extracted crude tea polyphenol mixture was dispersed with a 50% volume fraction of ethanol aqueous solution, and then extracted three times with a mixed solvent of ethyl acetate and n-hexane at a volume ratio of 1:1, 100 mL each time. The organic phases were combined and washed once each with distilled wat...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Take 500g of freshly picked multidentate red camellia pericarp, chop it up, and extract it with 1000mL ethanol solution with a volume fraction of 95%, soaking it for 12 hours each time, extracting it 4 times, combining the extracts, concentrating under reduced pressure, adding Disperse with 100mL ethanol, and filter to retain the filtrate. The filtrate was concentrated by rotary evaporation in vacuo, and then freeze-dried at low temperature to obtain 15.25 g of crude tea polyphenol mixture with a yield of 3.05%. Further purification analysis found that the main components of the crude tea polyphenol mixture were catechin, epicatechin, and catechin glycosides.
[0044] 15.25 g of the extracted crude tea polyphenol mixture was dispersed with a 50% ethanol aqueous solution by volume, and then extracted three times with a mixed solvent of ethyl acetate and n-hexane at a volume ratio of 1:1, 100 mL each time. The organic phases were combined and washed once each with distil...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap