A method for liver microsomes to metabolize chlorinated paraffin in vitro
A technology of chlorinated paraffin and liver microsomes, which is applied in the field of in vitro metabolism of chlorinated paraffins by liver microsomes, can solve the problems of limited metabolic capacity, reduced metabolic clearance rate, and low sensitivity, so as to improve metabolic clearance rate and be suitable for batch operation , the effect of reducing the reaction cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Metabolism of short-chain chlorinated paraffins (SCCPs) by chicken liver microsomes in vitro
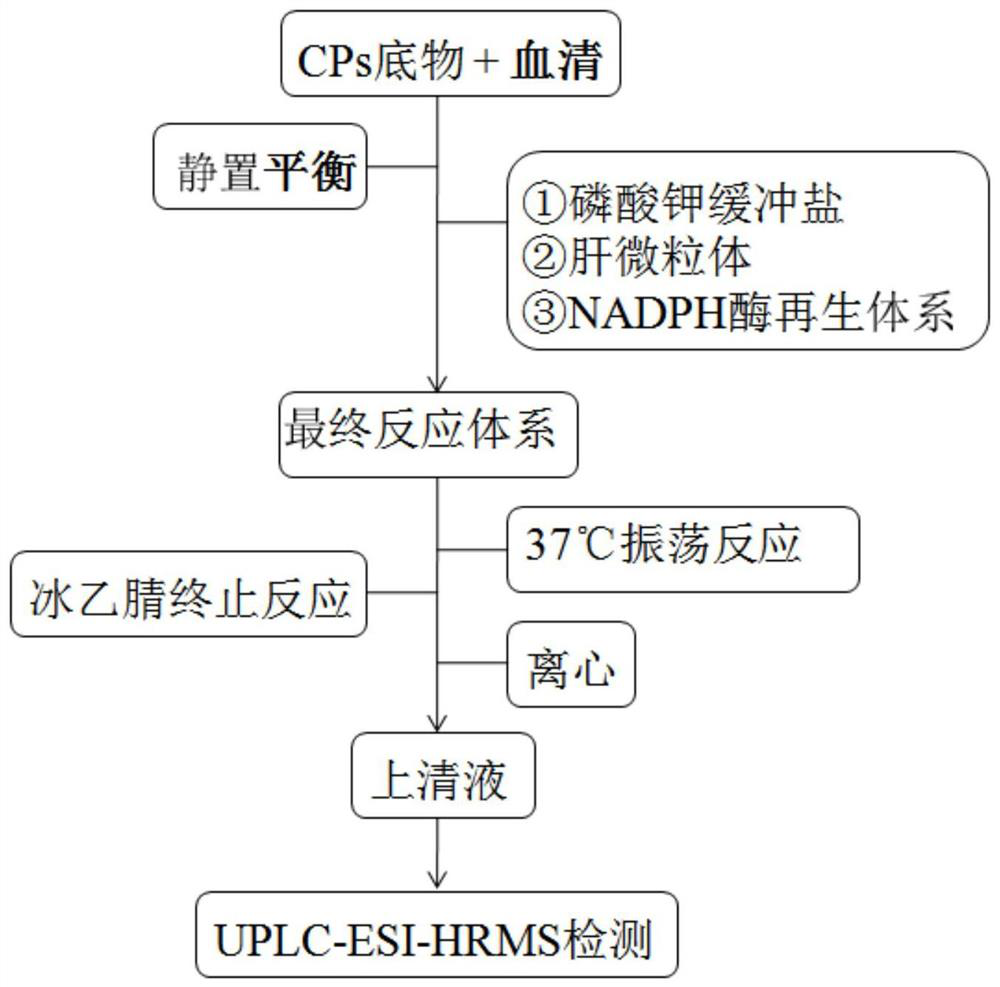
[0029] (1) Take 1 μL of SCCPs-acetonitrile solution and place it at the bottom of a 1.5 mL disposable centrifuge tube, add 10 μL of chicken serum, shake, vortex slightly, and let it stand at 4°C for 12 hours;
[0030] (2) Add 345 μL of potassium phosphate buffer solution with a pH value of 7.4, 12.5 μL of chicken liver microsomes, and 25 μL of A solution and 5 μL of B solution in the NADPH enzyme regeneration system, shake well, and quickly place in a 37°C water bath for shaking reaction 0.5h;
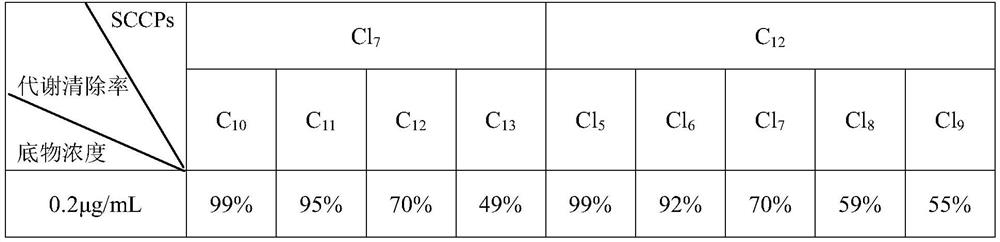
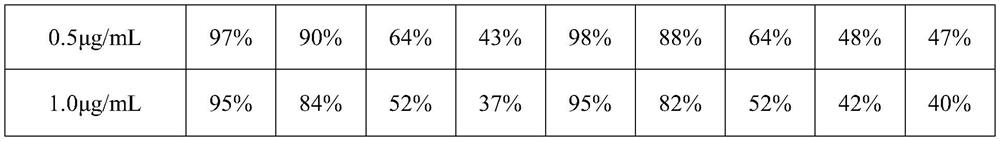
[0031] (3) Add 400 μL of ice-cold acetonitrile to stop the reaction, centrifuge at 10,000 rpm for 5 min at 4°C, then take 500 μL of the supernatant into a sample bottle, and use UPLC-ESI-HRMS to measure the content of SCCPs molecular formula homologues, the results are shown in the table 1. Table 1 shows the metabolic clearance rates of SCCPs with different carbon chains with 7 chlor...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Metabolism of medium-chain chlorinated paraffins (MCCPs) by chicken liver microsomes in vitro
[0038] (1) Take 12 μL of MCCPs acetonitrile solution and place it at the bottom of a 1.5 mL disposable centrifuge tube, add 30 μL of chicken serum, shake, vortex slightly, and let it stand at room temperature for 3 hours;
[0039] (2) Add 415 μL of potassium phosphate buffer solution with a pH value of 7.4, 12.5 μL of chicken liver microsomes, and 25 μL of A solution and 5 μL of B solution in the NADPH enzyme regeneration system, shake well, and quickly place in a 37°C water bath for shaking reaction 6h;
[0040] (3) Add 500 μL of ice-cold acetonitrile to terminate the reaction, centrifuge at 10,000 rpm for 5 min at 4°C, then take 500 μL of the supernatant into a sample bottle, and use UPLC-ESI-HRMS to determine the content of MCCPs molecular formula homologues, the results are shown in the table 2. Table 2 shows the metabolic clearance rates of MCCPs with different carbon ...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Metabolism of long-chain chlorinated paraffins (LCCPs) in chicken liver microsomes in vitro
[0046] (1) Take 25 μL of LCCPs acetonitrile solution and place it at the bottom of a 1.5 mL disposable centrifuge tube, add 25 μL of chicken serum, shake, vortex slightly, and let stand at 4°C for 6 hours;
[0047] (2) Add 510 μL of potassium phosphate buffer solution with a pH value of 7.4, 12.5 μL of chicken liver microsomes, and 25 μL of A solution and 5 μL of B solution in the NADPH enzyme regeneration system, shake well, and quickly place in a 37°C water bath for shaking reaction 2h;
[0048] (3) Add 600 μL of ice-cold acetonitrile to terminate the reaction, centrifuge at 10,000 rpm for 5 min at 4°C, then take 500 μL of the supernatant into a sample bottle, and use UPLC-ESI-HRMS to determine the content of LCCPs molecular formula homologues, the results are shown in the table 3. Table 3 shows the metabolic clearance rates of LCCPs with different carbon chains with 7 chlo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com