Semantic segmentation method and system for removing dynamic objects
A semantic segmentation and object technology, applied in neural learning methods, image analysis, biological neural network models, etc., can solve environmental positioning and map construction errors, low precision and stability of three-dimensional positioning and mapping, and cannot meet dynamic and complex Environmental positioning and mapping requirements, etc., to achieve reliable results in dynamic environments
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] This embodiment provides a semantic segmentation method for removing dynamic objects, which specifically includes the following steps:
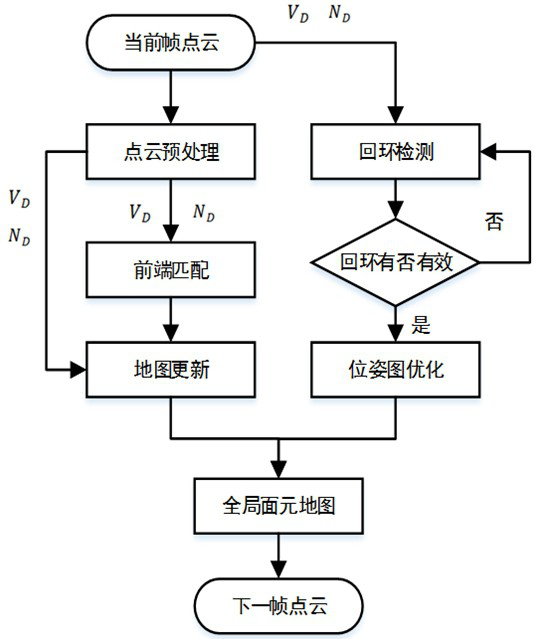
[0043] Step 1: Obtain the 3D point cloud of the scene and project it into a 2D depth map, calculate the normal vector information of the point cloud, and construct a surfel map with loop closure.
[0044] In a specific embodiment, a 16-line lidar is used to acquire 2D depth map and normal vector information.
[0045] It can be understood here that in other embodiments, laser radars with other numbers of lines can also be used to obtain 2D depth maps and normal vector information, and those skilled in the art can make specific choices according to actual conditions, and will not repeat them here. .
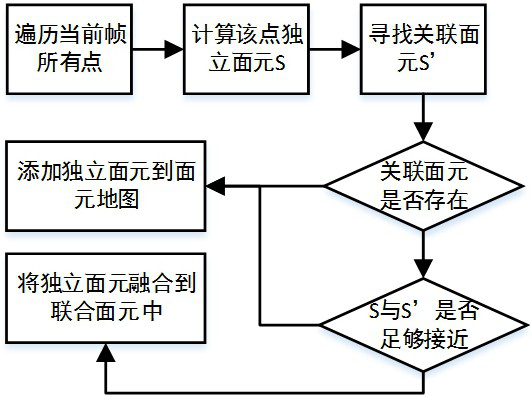
[0046] Among them, the facet map construction flow chart is as follows figure 2 shown in figure 2 middle, V D Represents a 2D depth map, N D Representation vector information. Specifically, the specific process of step 1 includes:...
Embodiment 2
[0088] This embodiment provides a semantic segmentation system for removing dynamic objects, which specifically includes the following modules:
[0089] A surfel structure map building module, which is used to obtain the 3D point cloud of the scene and project it into a 2D depth map, calculate the normal vector information of the point cloud, and construct a surfel map with loops;
[0090] Semantic point cloud map building module, which is used to carry out point cloud semantic segmentation on surface element maps with loopbacks, construct semantic point cloud maps, map semantic point cloud maps into 3D point cloud maps and remove edge shadows and Point cloud discretization phenomenon;
[0091] The semantic point cloud map optimization module is used to remove dynamic objects by using the semantic point cloud information in the semantic point cloud map, and add semantic iteration closest point constraints to obtain the optimized semantic point cloud map.
[0092] Wherein, in ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com