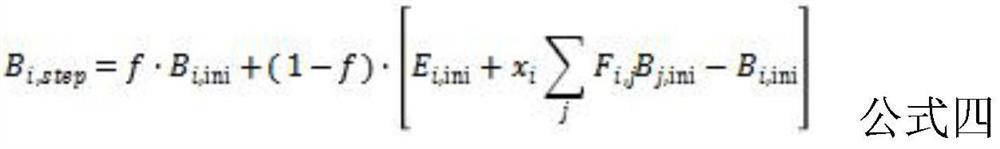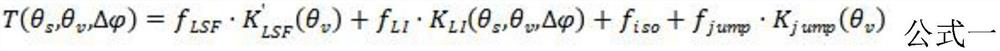Patents
Literature
34 results about "Surfel" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
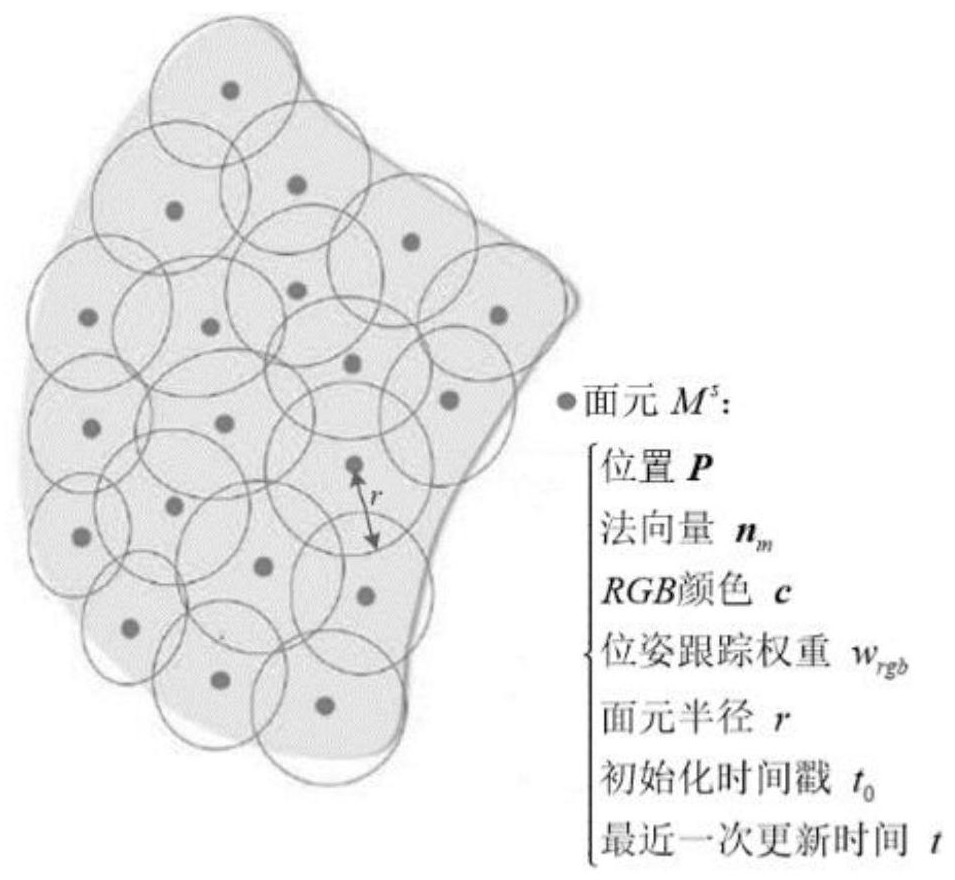
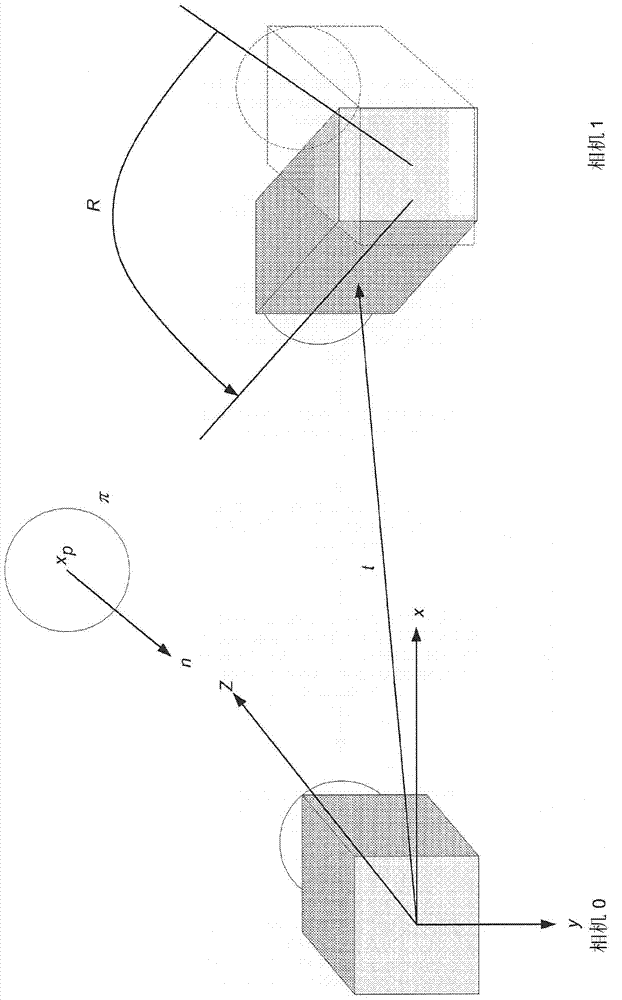
Surfel is an abbreviated term for a "surface element," analogous to a "voxel" (volume element) or a "pixel" (picture element). In 3D computer graphics, the use of surfels is an alternative to polygonal modeling. An object is represented by a dense set of points or viewer-facing discs holding lighting information. Surfels are well suited to modeling dynamic geometry, because there is no need to compute topology information such as adjacency lists. Common applications are medical scanner data representation, real time rendering of particle systems, and more generally, rendering surfaces of volumetric data by first extracting the isosurface.
Detecting objects in video data
ActiveCN109643368AImage analysisNeural learning methodsPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
Certain examples described herein enable semantically-labelled representations of a three-dimensional (3D) space to be generated from video data. In described examples, a 3D representation is a surface element or 'surfel' representation, where the geometry of the space is modelled using a plurality of surfaces that are defined within a 3D co- ordinate system. Object-label probability values for spatial elements of frames of video data may be determined (605) using a two-dimensional image classifier. Surface elements that correspond to the spatial elements are identified (610) based on a projection of the surface element representation using an estimated pose for a frame. Object-label probability values for the surface elements are then updated (615) based on the object-label probability values for corresponding spatial elements. This results in a semantically-labelled 3D surface element representation of objects present in the video data. This data enables computer vision and / or robotic applications to make better use of the 3D representation.
Owner:IMPERIAL INNOVATIONS LTD
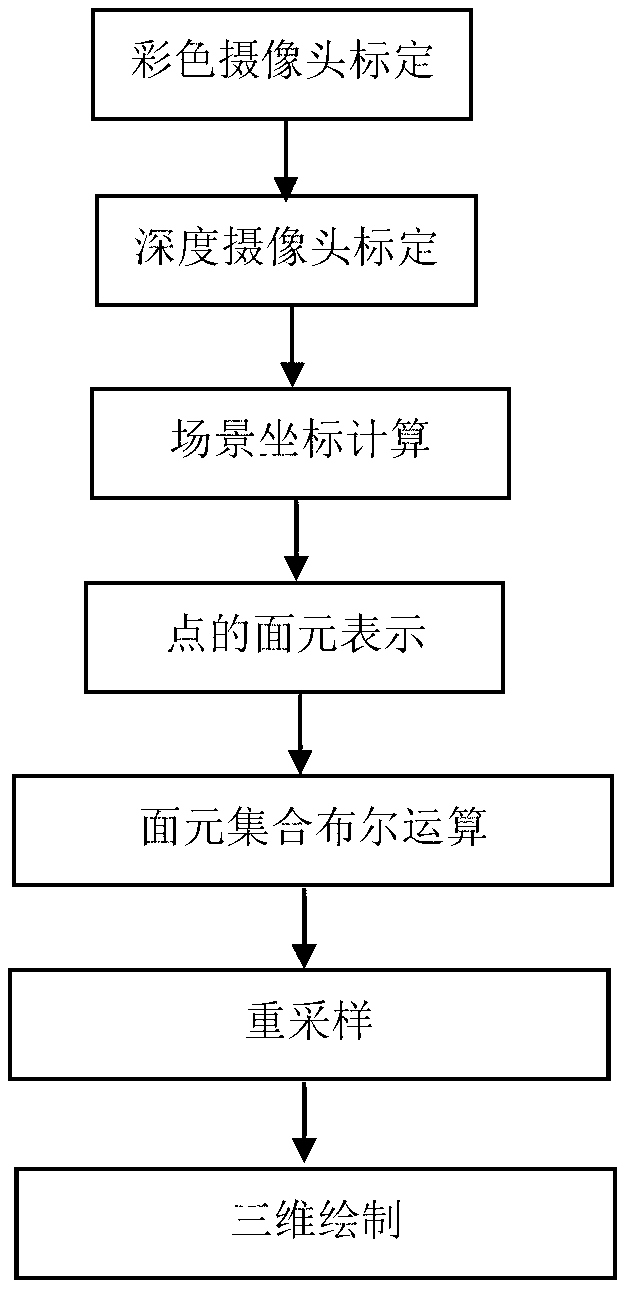
Facet-based complex scene three-dimensional reconstruction method
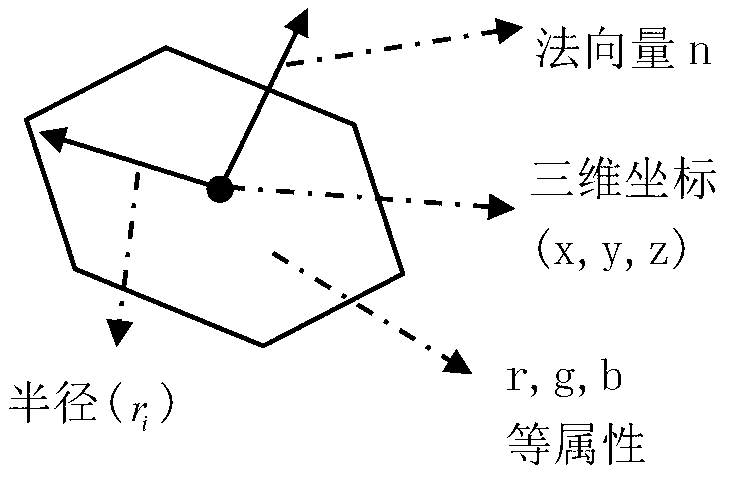
A facet-based complex scene three-dimensional reconstruction method is characterized by including: firstly, obtaining intrinsic and extrinsic parameters and distortion coefficients in a depth camera and a color camera by three-dimensional calibration; secondly, calculating three-dimensional information of a complex scene by the depth camera according to the principle of triangulation; thirdly, defining a point model as a facet, with each value as an attribute of the point model including the attributes such as normal vector and radius; fourthly, subjecting each facet to surface 'internal, external and intersection' relation test with another facet; fifthly, obtaining confidence neighborhood of the facets which are judged intersected, calculating boundaries of the most adjacent facets on the point model, and resampling the facets in the confidence neighborhood; sixthly, three-dimensionally drawing the complex scene according to results of Boolean operation in the step 5. The facet-based complex scene three-dimensional reconstruction method is highly timely and available for effectively extracting three-dimensional point cloud data of the complex scene.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Semantic segmentation method and system for removing dynamic objects
ActiveCN113570629AReliable Semantic SLAM MappingStable Semantic SLAM MappingImage enhancementImage analysisGraph mappingImaging processing
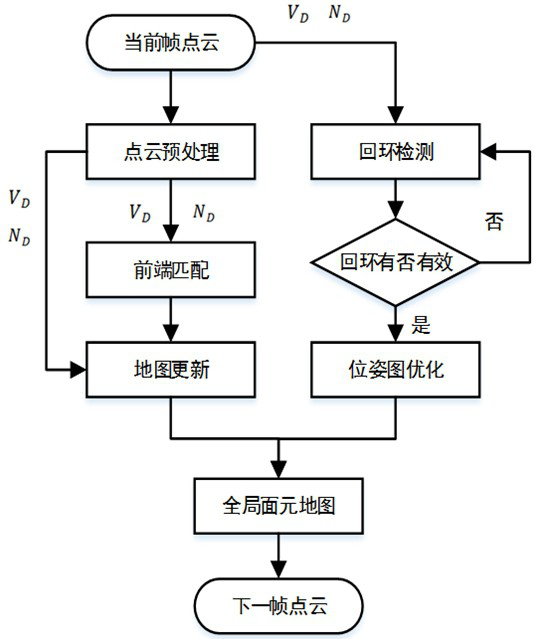
The invention belongs to the field of image processing, and provides a semantic segmentation method and system for removing dynamic objects. The semantic segmentation method comprises the following steps: acquiring a scene 3D point cloud, projecting the scene 3D point cloud into a 2D depth map, calculating normal vector information of the point cloud, and constructing a surface element map with a loop; carrying out point cloud semantic segmentation on the surface element map with the loop, constructing a semantic point cloud map, mapping the semantic point cloud map to a 3D point cloud map, and removing edge shadows and point cloud discretization phenomena; and removing the dynamic object by utilizing semantic point cloud information in the semantic point cloud map, and adding semantic iteration nearest point constraint to obtain an optimized semantic point cloud map.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV +1
Method for generating FDTD (Finite Difference Time Domain) grids
InactiveCN105279320AMeet processing needsFast solutionSpecial data processing applications3D modellingTime domainComputer Aided Design
This invention discloses a method for generating FDTD grids. The method comprises the following steps: generating a model of a triangle surface element based on a commercial software Hypermesh, and processing the model to generate the FDTD grids; generating FDTD grids with different specifications by freely selecting space intervals to solve the problem of the complex model composed of a variety of medium materials simultaneously; at last, checking the accuracy of the modeling result through the FDTD grids generated by CAD (Computer-Aided Design) detection. The method provided by this invention can solve the FDTD modeling problem of complex target model and the FDTD modeling problem of a variety of medium materials.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Complex terrain electromagnetic scattering rapid simulation method based on digital elevation map and GPU
PendingCN113376597AQuick estimateWave based measurement systemsDesign optimisation/simulationComputational scienceScattering cross-section
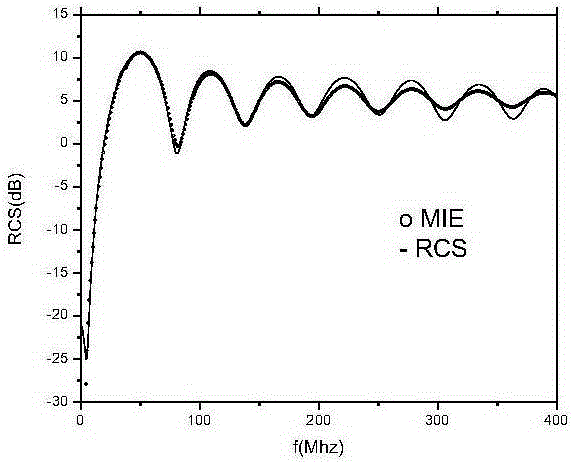
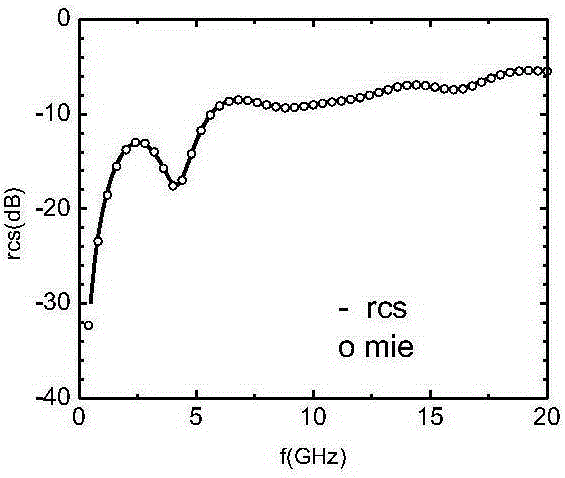
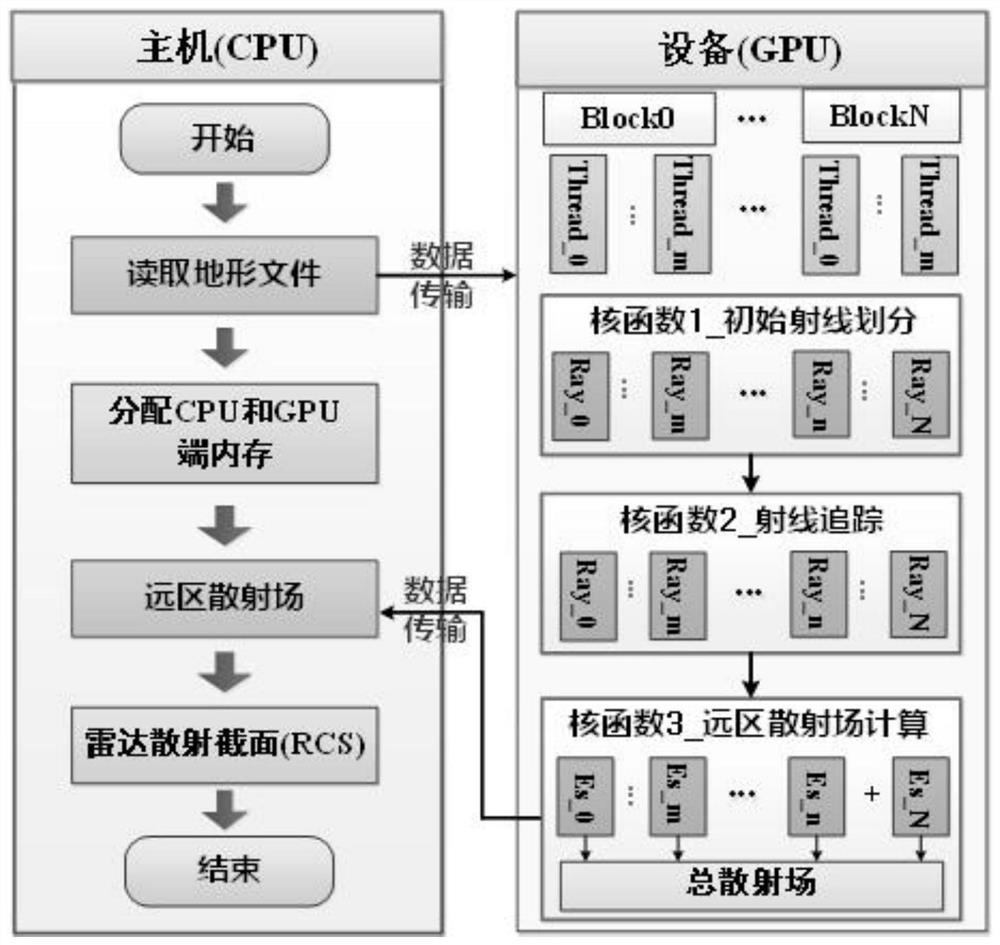
The invention discloses a complex terrain electromagnetic scattering rapid simulation method based on a digital elevation map and a GPU. The method comprises the following steps: taking a DEM as actual terrain geometric model information input, carrying out preprocessing on terrain data according to the DEM, and obtaining a triangular surface element model; performing parallel calculation of a GPU end, including initial ray division, ray tracing and far-zone scattered field calculation; and transmitting a calculation result to the CPU end, calculating a radar scattering cross section, and carrying out post-processing on data to obtain an electromagnetic scattering simulation model. DEM (Digital Elevation Model) data is used as input of the actual terrain geometric model, a complex terrain shielding effect and a multi-scattering problem are further considered, a bounce ray (SBR) algorithm is combined with a GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) parallel acceleration technology, the electromagnetic scattering rapid simulation model suitable for the actual complex terrain is established, and rapid estimation of scattering echoes of each region of the complex terrain is realized.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Human body digital model design method, system and model for radiation protection
PendingCN111008461AShorten production timeImprove manufacturing precisionDesign optimisation/simulationCAD numerical modellingHuman bodyVoxel
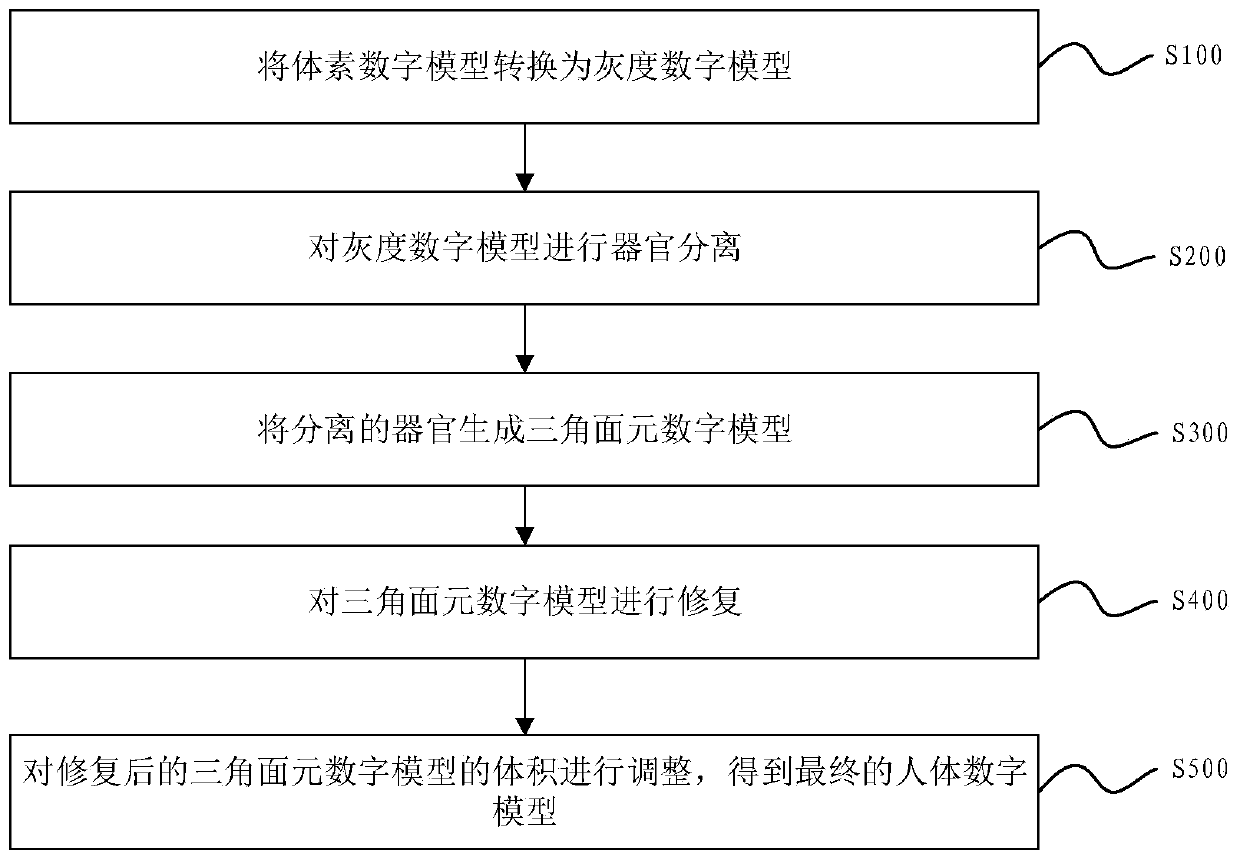
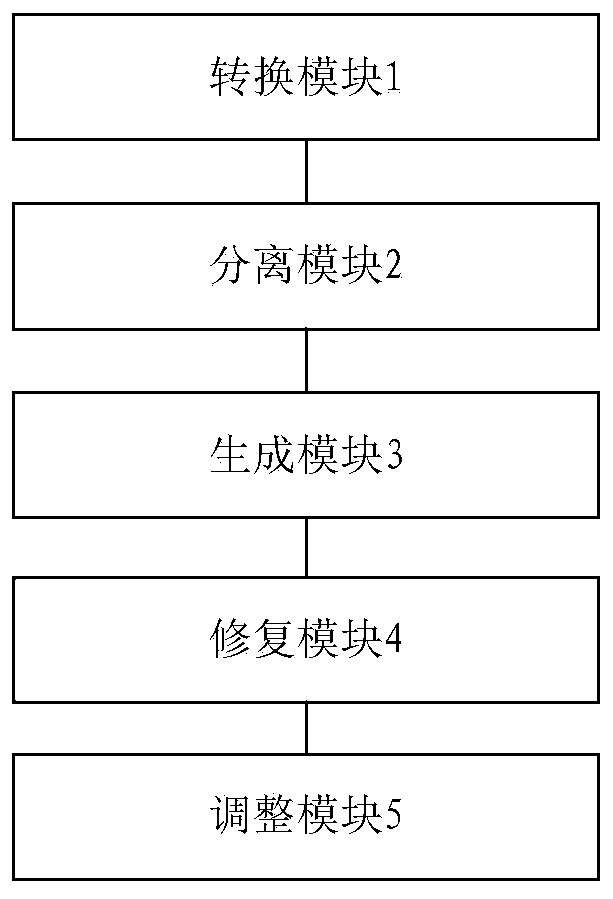
The invention discloses a human body digital model design method, system and model for radiation protection. The design method comprises the following steps: S100, converting a voxel digital model into a grayscale digital model; S200, carrying out organ separation on the grayscale digital model; S300, generating a triangular surface element digital model from the separated organs; S400, repairingthe triangular surface element digital model; and S500, adjusting the volume of the repaired triangular surface element digital model to obtain a final human body digital model. The method can be applied to a rapid prototyping technology so as to replace a traditional physical model casting method, the physical model manufacturing time can be shortened, the physical model manufacturing precision can be improved, customization of the physical model can be achieved, and the method is closer to the requirement for radiation protection in the nuclear industry.
Owner:CHINA INST FOR RADIATION PROTECTION
Instant dense reconstruction method for space target
PendingCN114419246AReduce power consumptionLow costImage analysis3D modellingPattern recognitionPoint cloud
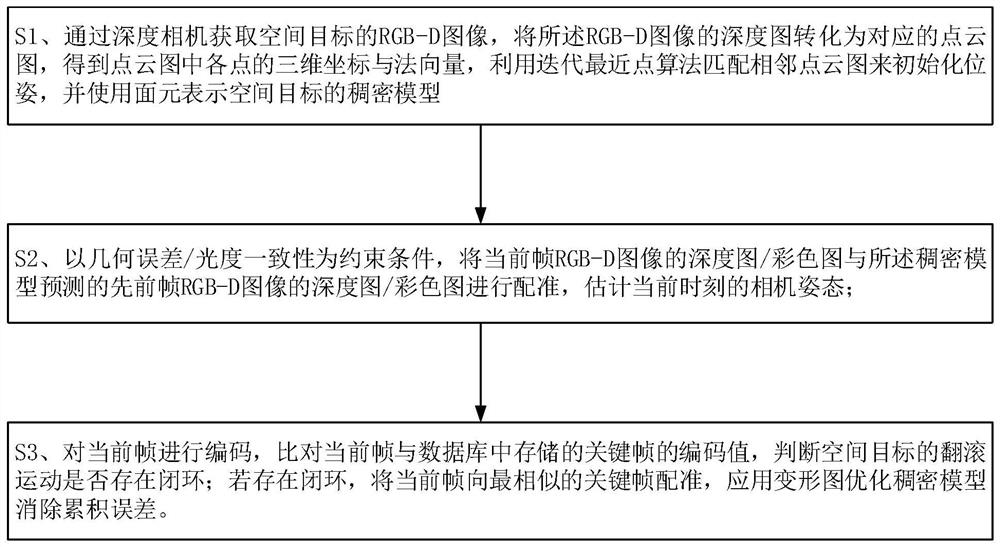
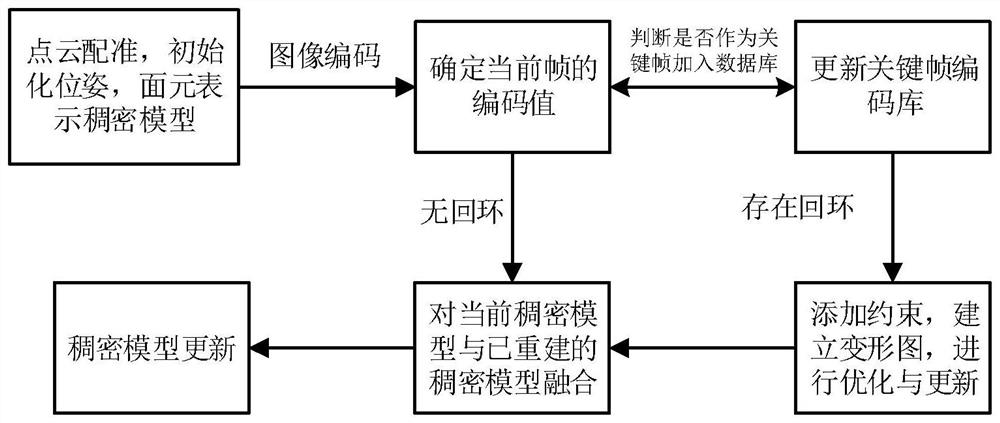
The invention provides an instant dense reconstruction method for a space target, which comprises the following steps: S1, acquiring an RGB-D image of the space target through a depth camera, converting a depth map of the image into a corresponding point cloud, obtaining a three-dimensional coordinate and a normal vector of each point in the point cloud, initializing the pose of an adjacent depth map by using an iterative nearest point algorithm, and obtaining a three-dimensional coordinate of each point in the point cloud; surface elements are used for representing a dense model of the space target; s2, by taking geometric error / luminosity consistency as a constraint condition, registering the depth map / color map of the current frame with the depth map / color map of the previous frame predicted by the dense model, and estimating the camera attitude at the current moment; s3, encoding the current frame, comparing the current frame with the encoding value of the previous frame stored in the database, and judging whether to update the key frame; and judging whether a closed loop exists in the rolling motion of the space target or not, if so, registering the current frame to the most similar key frame, and optimizing the dense model by using the deformation graph to eliminate accumulative errors.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE CONTROL TECH INST
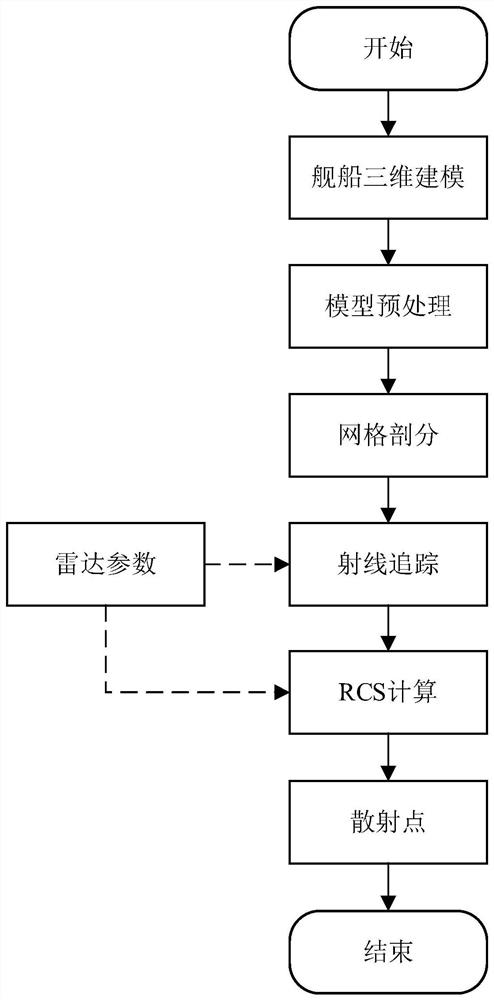
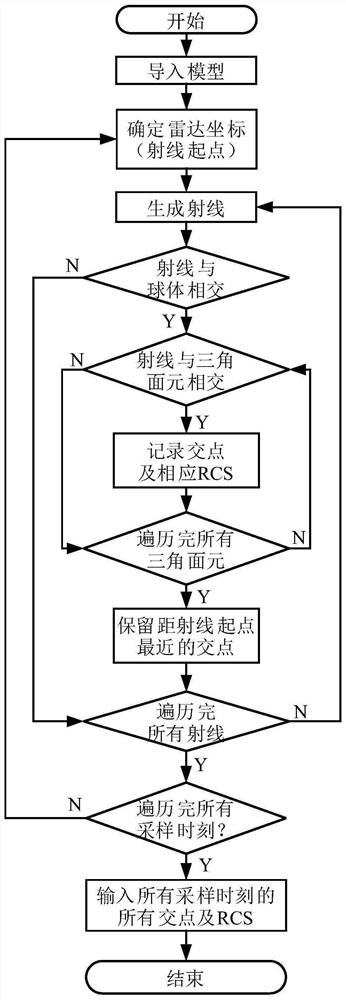
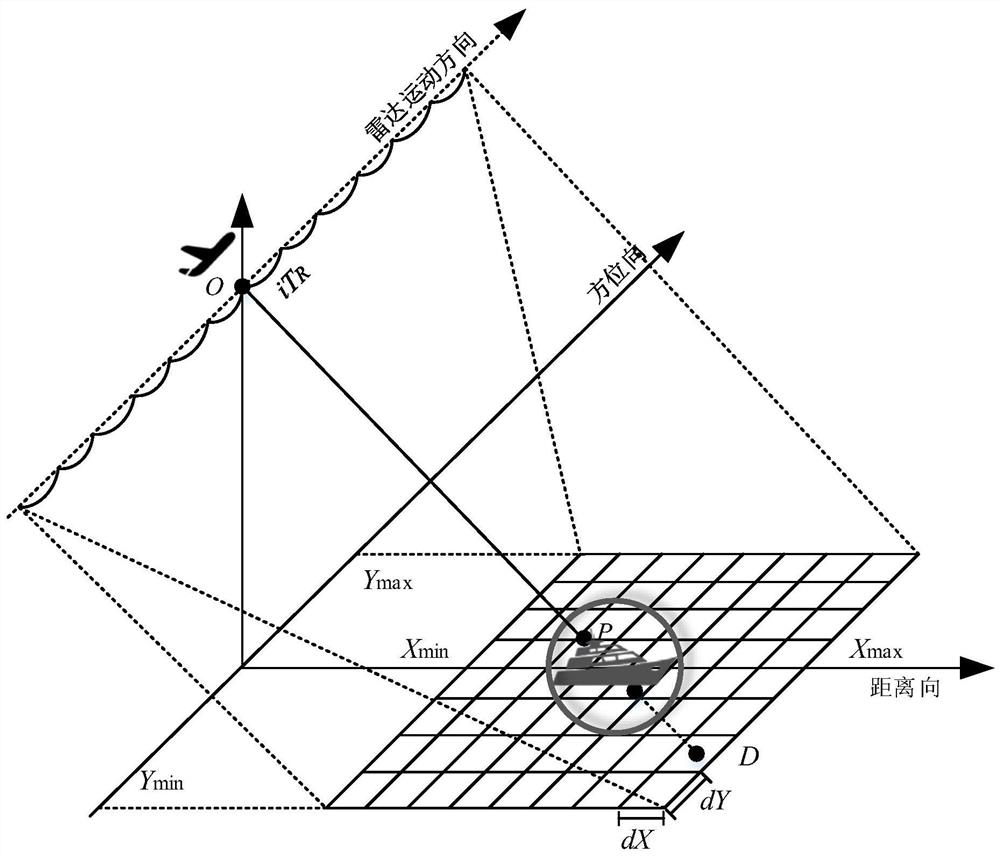
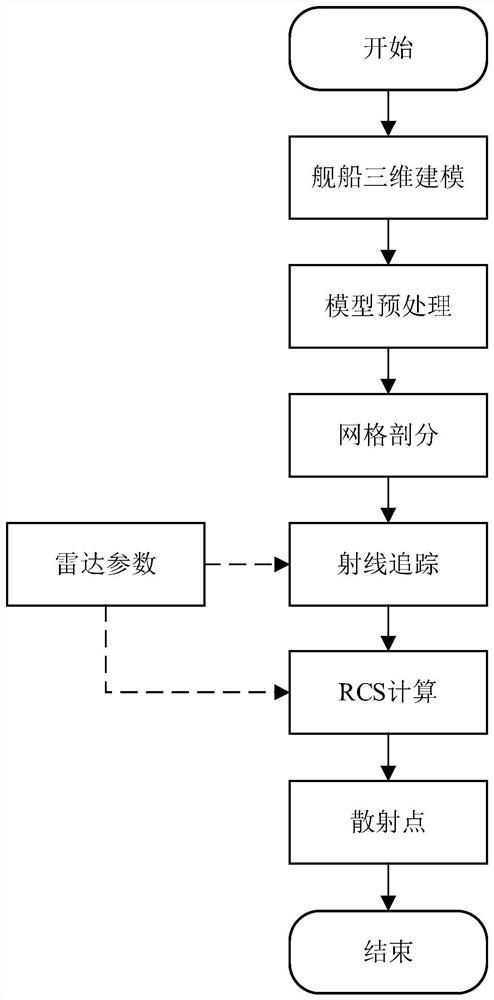
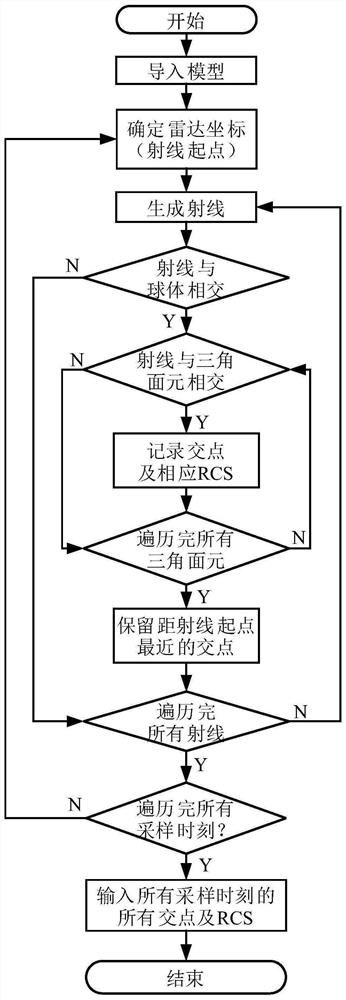
Complex field structured SAR ship target dynamic simulation and speed estimation method
ActiveCN113176573ASolve the problem that it is difficult to accurately describe the SAR images of moving ship targetsResolve accuracyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionAlgorithmImage manipulation
The invention discloses a complex field structured SAR ship target dynamic simulation and speed estimation method, which belongs to the field of SAR image processing. The method aims at solving the problems that a large number of simulation samples are lacked during SAR ship target simulation, and an existing SAR ship target simulation method cannot obtain an accurate ship target SAR image, so that an accurate ship target cannot be obtained. The method comprises the following steps of acquiring a ship 3D model, preprocessing the ship 3D model, and dividing the preprocessed ship 3D model into a plurality of triangular surface elements, conducting ray tracing according to set radar parameters, and acquiring ship target scattering point space coordinates, conducting ship target imaging, inputting the training sample into the AlexNet network to obtain a trained AlexNet pre-training model, inputting a to-be-tested sample into the trained AlexNet pre-training model, and calculating to obtain an AlexNet network complex number domain speed estimation result. The method is used for SAR ship target dynamic simulation and speed estimation.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
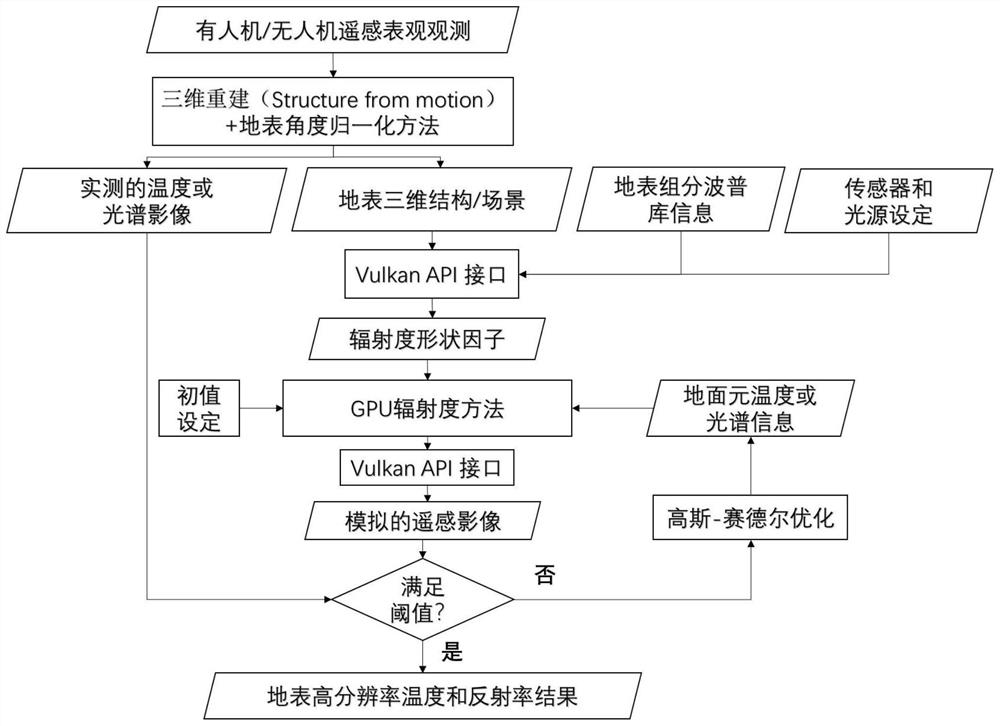
Remote Sensing Retrieval Method of Surface High Resolution Spectral Information Based on Radiosity
ActiveCN113012276BBoth stablePracticalScattering properties measurementsThermometers using physical/chemical changesImage resolutionRadiance
The invention discloses a remote sensing inversion method for surface high-resolution spectral information based on irradiance, comprising the following steps: S1, three-dimensional scene reconstruction; S2, angle normalization; S3, setting sensors and light sources; S4, calculating shape Factor; S5, set temperature and initial value of reflectivity; S6, output simulated image through GPU fast radiosity method; S7, threshold judgment; S8, optimize temperature and reflectivity of surface element; S9, end process and output result. The present invention fully considers the influence of multiple scattering on the ground surface, so that the temperature and reflectance results of the inversion are both stable and accurate; the strategy based on GPU instead of CPU makes the present invention more practical for inversion, and this method is expected to become Effective tool for high-resolution surface temperature and albedo production from drones or manned aircraft.
Owner:AEROSPACE INFORMATION RES INST CAS
A dynamic three-dimensional display method of electromagnetic waves suitable for complex curved surfaces
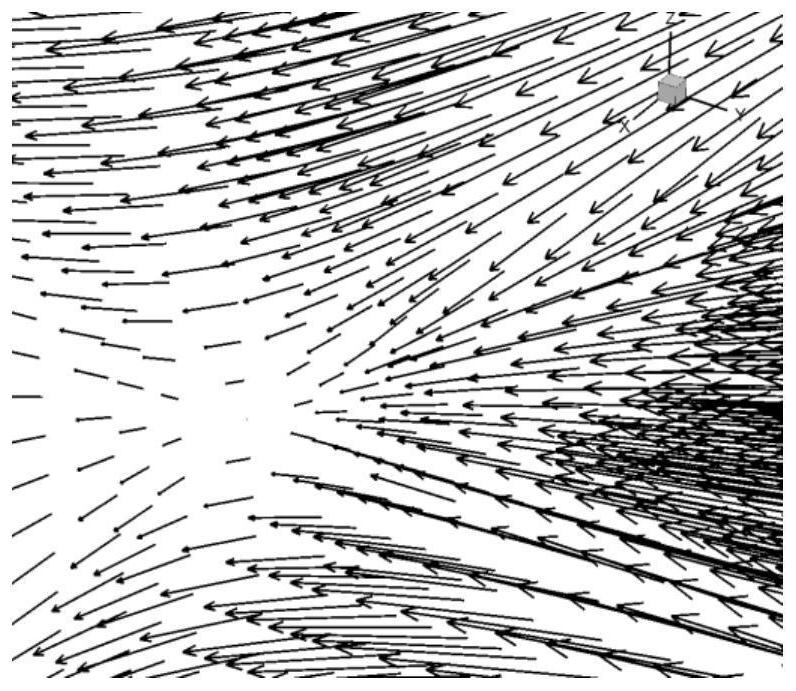
ActiveCN114049465BIntuitive reproduction of 3D wave effectsReproduce the three-dimensional wave effect3D modellingEngineeringComputational physics
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
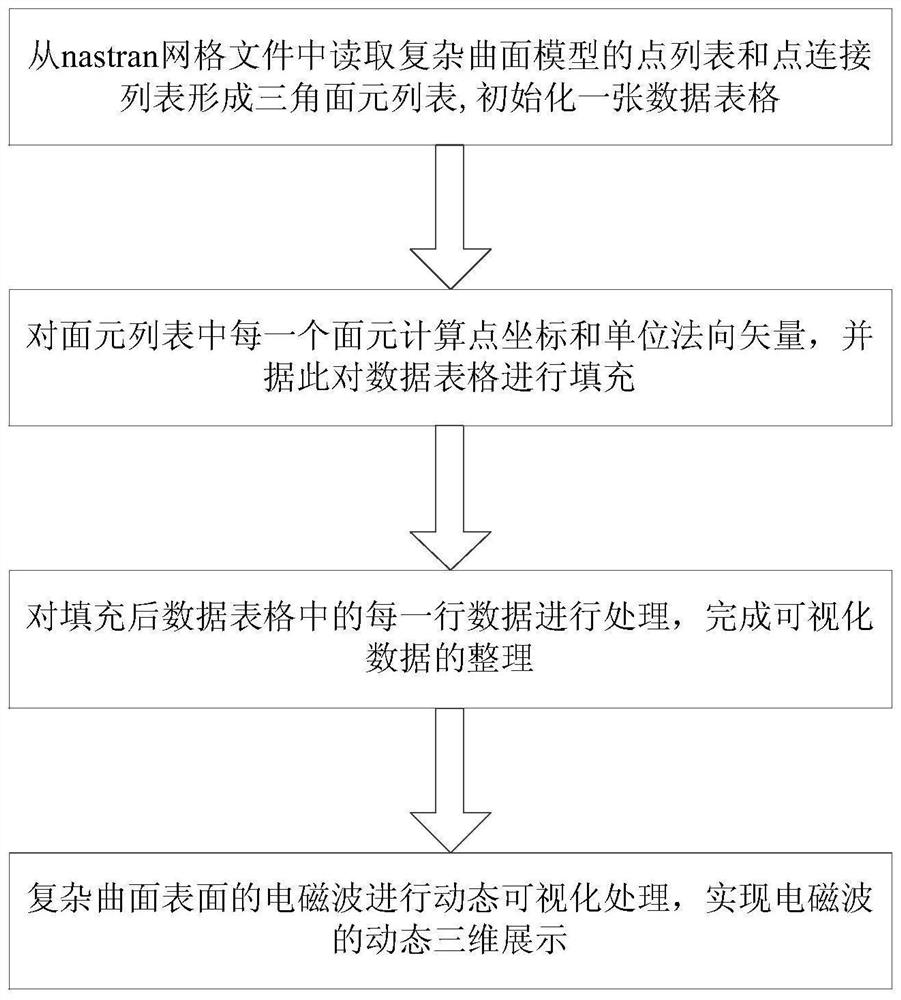
A method of surface element blanking for space target imaging simulation
ActiveCN110095767BFast occlusion judgmentOcclusion judgment high speedWave based measurement systemsSurfelIr camera
The invention discloses a space target imaging simulation surface element blanking method, relates to a space target imaging simulation surface element blanking method, and belongs to the technical field of target imaging simulation. In order to solve the problem of long time and low efficiency in the method of traversing all the facets to judge the occlusion of the facet under the condition of a large number of micro-facets. A method for blanking surface elements of space object imaging simulation according to the present invention includes a surface element blanking part to the sun light source and a camera blanking part, and the surface element blanking part to the sun light source refers to judging each micro-facet on the surface of the space object Whether the element can receive sunlight, the part of the face element to the camera blanking refers to judging the visibility of each micro-facet element of the space object to the camera. Intersect the surface elements visible to the sun light source and the surface elements visible to the camera to get all the surface elements visible to both the sun light source and the camera. The present invention is suitable for surface element blanking in space object imaging simulation.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Dynamic Simulation and Velocity Estimation Method of Complex Number Domain Structured SAR Ship Target
ActiveCN113176573BAccurate acquisitionSimplify complexityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionImaging processingAlgorithm
The invention relates to a dynamic simulation and velocity estimation method of a complex number domain structured SAR ship target, which belongs to the field of SAR image processing. The invention aims to solve the problem that there is a lack of a large number of simulation samples when doing SAR ship target simulation, and the existing SAR ship target simulation method cannot obtain accurate ship target SAR images, resulting in the inability to obtain accurate ship target problems. The method of the present invention comprises: obtaining a 3D model of a ship, preprocessing the 3D model of a ship, dividing the preprocessed 3D model of a ship into a plurality of triangular surface elements; performing ray tracing according to set radar parameters, and obtaining a ship Spatial coordinates of target scattering points; ship target imaging; input training samples into AlexNet network to obtain a trained AlexNet pre-training model, input the samples to be tested into the trained AlexNet pre-training model, and calculate the speed estimation result of AlexNet network complex number domain. The invention is used for dynamic simulation and speed estimation of SAR ship target.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Target radar scattering cross-section pre-estimation system with graphics electromagnetic computation accelerated by index information
InactiveCN101430376BLess memory swappingDepth accurateWave based measurement systemsGraphicsScattering cross-section
The invention discloses a pre-evaluation system for accelerating computation of target radar scattering cross section by graphical electromagnetic computation through index information. The system comprises a surface element modeling module (1), an index information compilation module (2), an entity display module (3), an index information unscrambling module (4), a geometric information analysismodule (5) and a target radar scattering cross section acquisition module (6). The surface elements of a target model are numbered, an index list of the surface elements is established, the surface element index and the surface element color are subject to one to one correspondence, the background color is set as black, components of three primary colors namely red, green and blue are zero, the surface element blanking is finished by a GPU, the corresponding surface element index is obtained by the color of pixels so as to obtain normal vectors and depth values of the pixels. The whole process needs no illumination, the surface normal vector is pre-obtained in a drawing process of the surface elements, a color value is read only for once, and twice memory exchange is executed, which is one computation less than the normal graphical electromagnetic computation, thus shortening the computation time.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
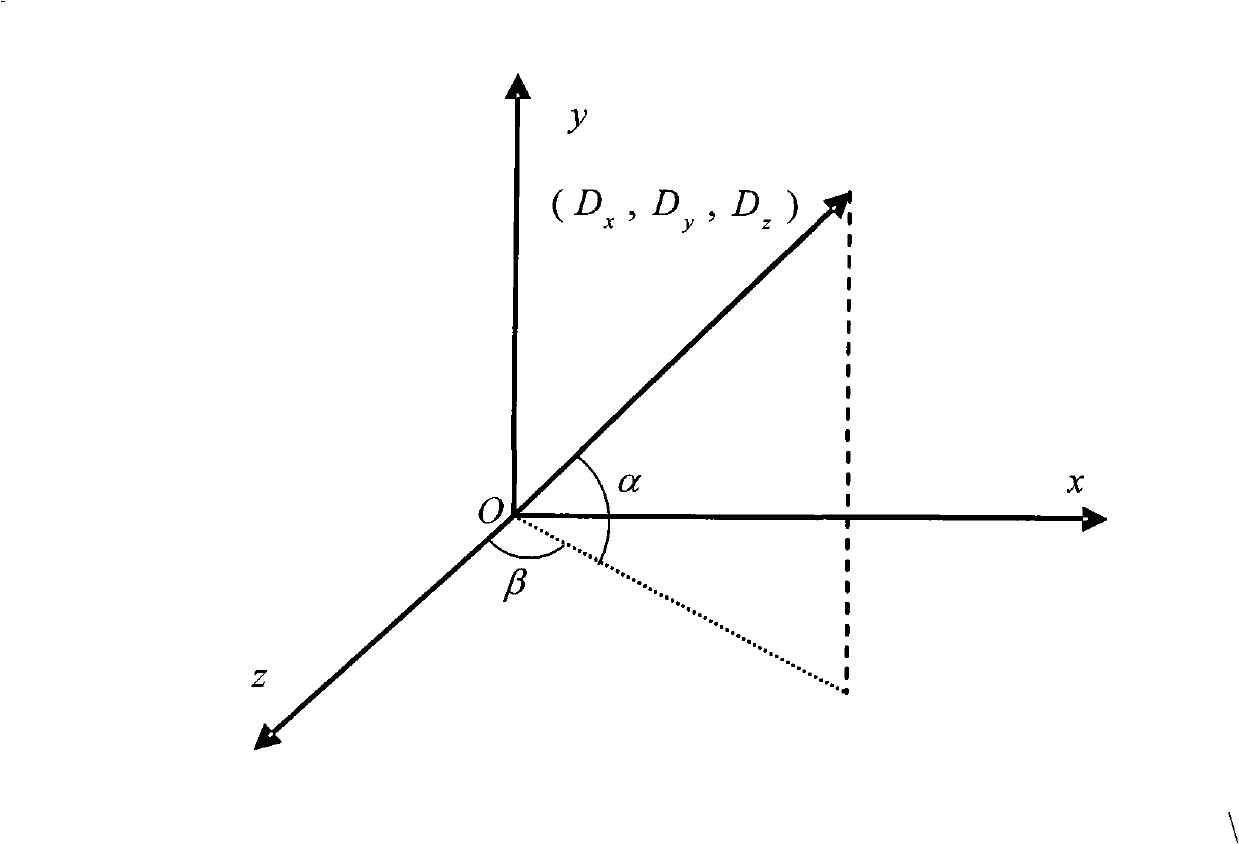
Method for initializing and solving the local geometry or surface normals of surfels using images in a parallelizable architecture
A system and method is described herein for solving for surface normals of objects in the scene observed in a video stream. The system and method may include sampling the video stream to generate a set of keyframes; generating hypothesis surface normals for a set of mappoints in each of the keyframes; warping patches of corresponding mappoints in a first keyframe to the viewpoint of a second keyframe with a warping matrix computed from each of the hypothesis surface normals; scoring warping errors between each hypothesis surface normal in the two keyframes; and discarding hypothesis surface normals with high warping errors between the first and second keyframes.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
A Simulation Method of Microwave Correlation Imaging Based on Analytical Surfing
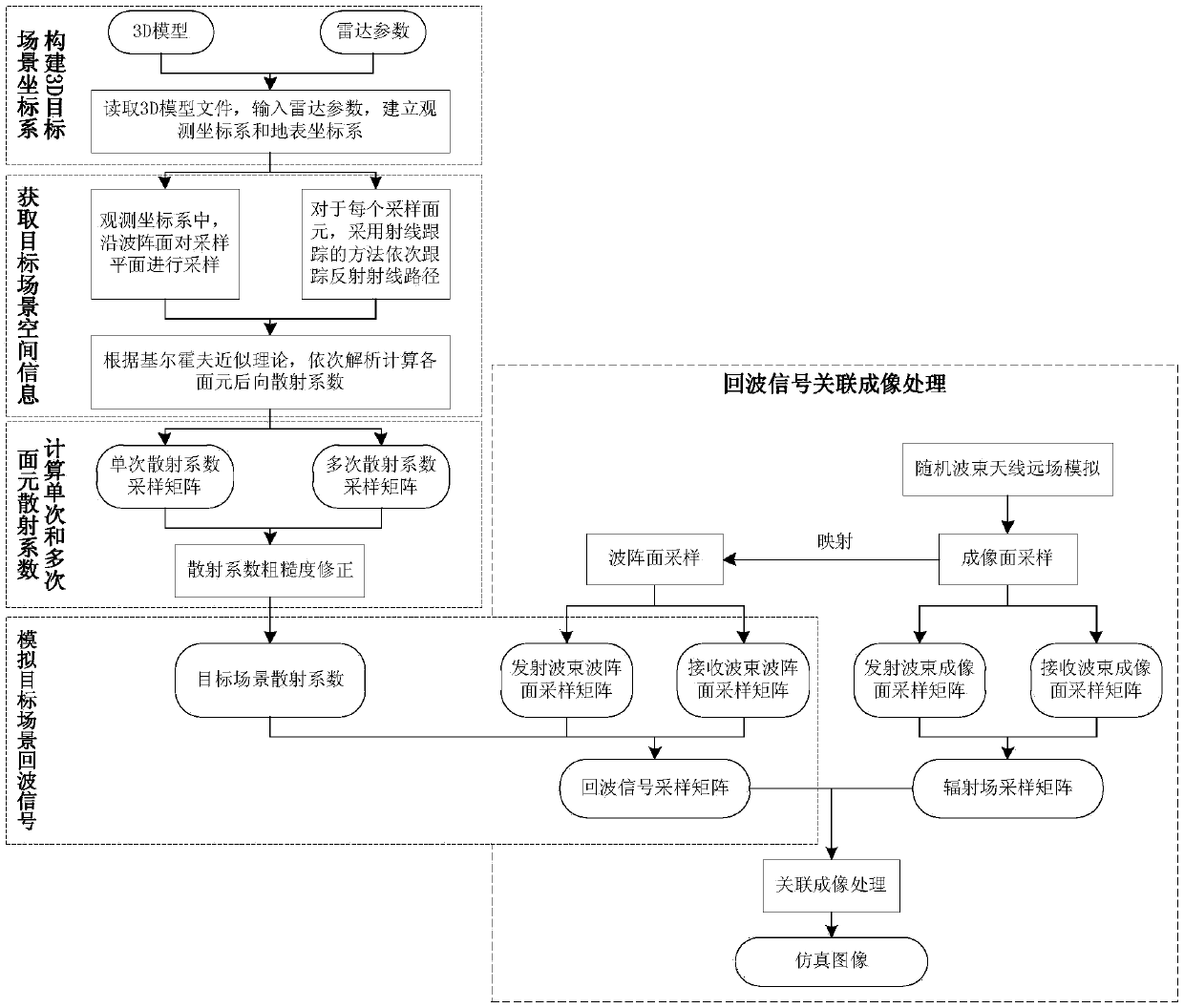
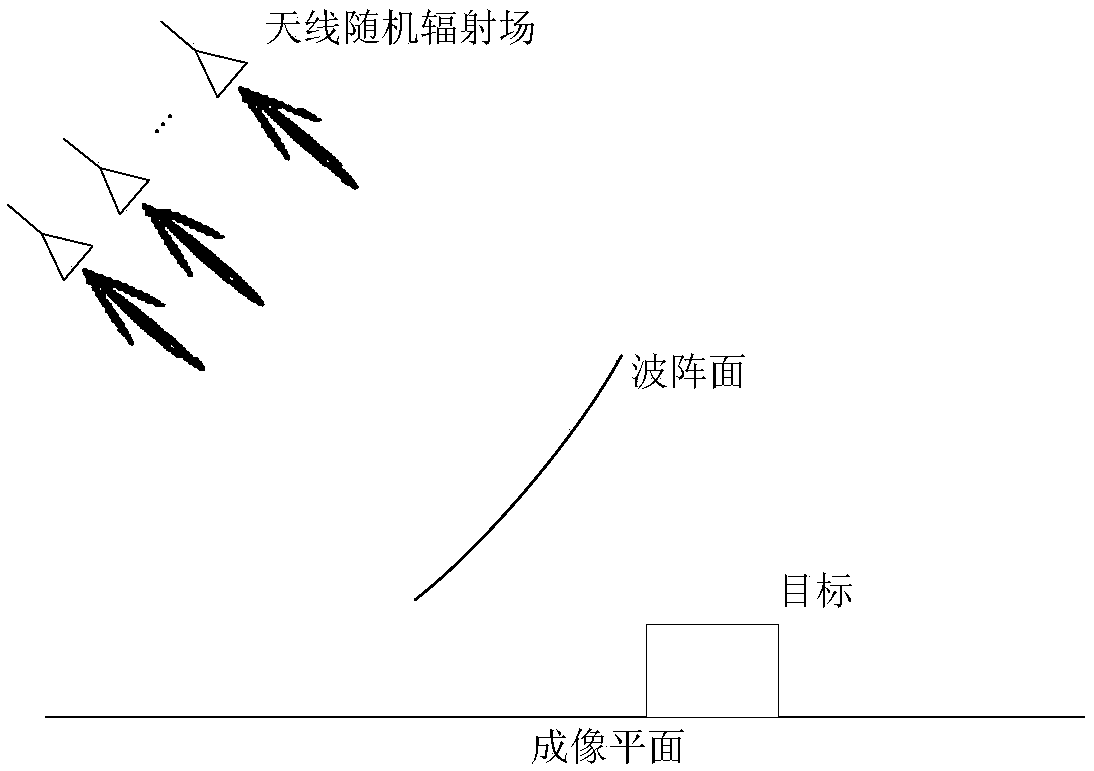
ActiveCN106680812BEfficient Electromagnetic ComputingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionImaging interpretationImaging chain
The invention discloses a microwave correlated imaging simulation method based on an analysis surface element. The method comprises the steps: firstly constructing a target 3D model scene, obtaining the space information of a corresponding target scene according to observation parameters, calculating a single-scattering coefficient and a multi-scattering coefficient of the target scene, and obtaining the scattering coefficient distribution of the observation scene; secondly calculating an echo signal of the target scene according to a radiation field of a random antenna wave beam in an imaging plane; finally carrying out the correlating of the radiation field and the echo signal, and obtaining a simulation image result. The method achieves a quick simulation process in correlation imaging under the condition of the random radiation field, gives a solution for distributed scene correlation imaging high-efficiency simulation, can deepen the understanding of the imaging mechanism and scattering mechanism in a whole correlated imaging link, provides support for the design and index argument of the design of a correlated imaging radar system, also can be used for subsequent correlated imaging evaluation and image interpretation, and is high in practical value.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
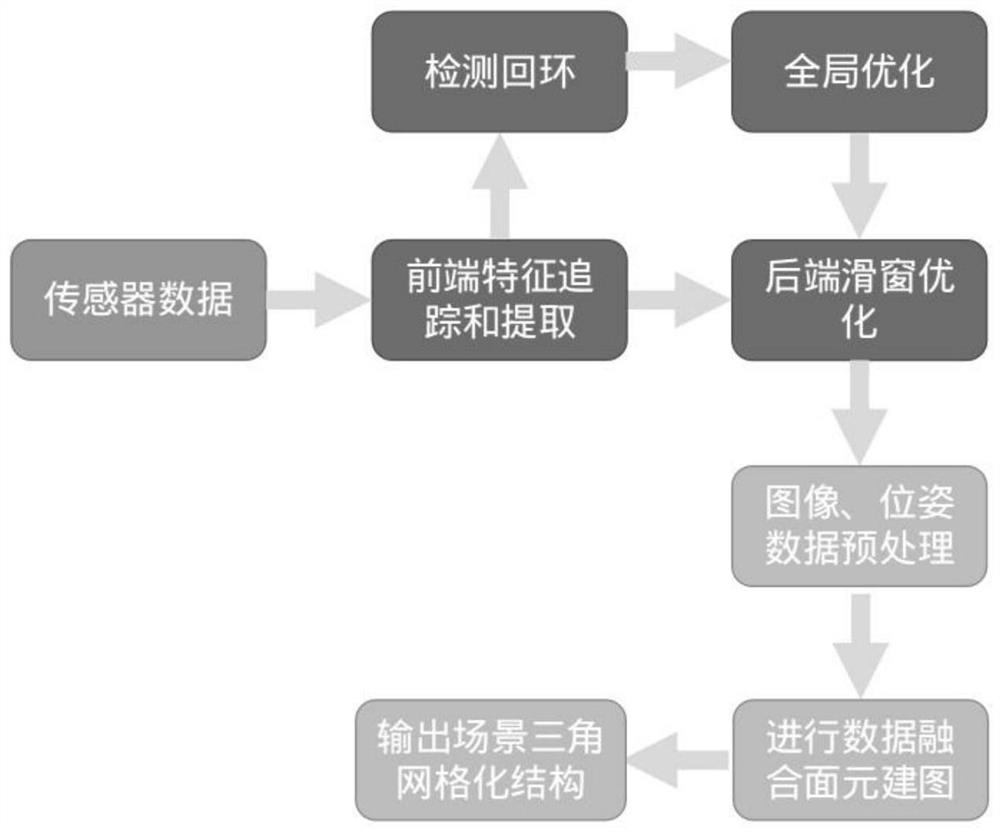
Three-dimensional dense surface element mapping method and system based on SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) and electronic equipment
PendingCN114445549AReal-time deploymentImage enhancementImage analysisSimultaneous localization and mappingRadiology
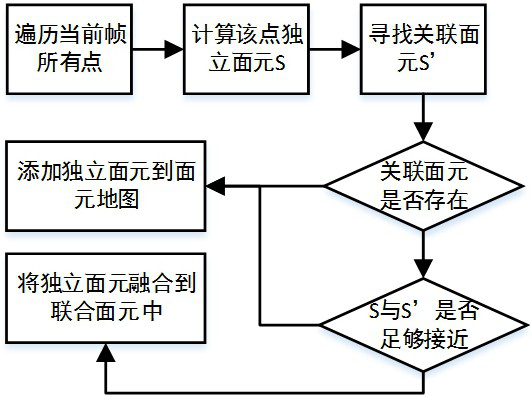
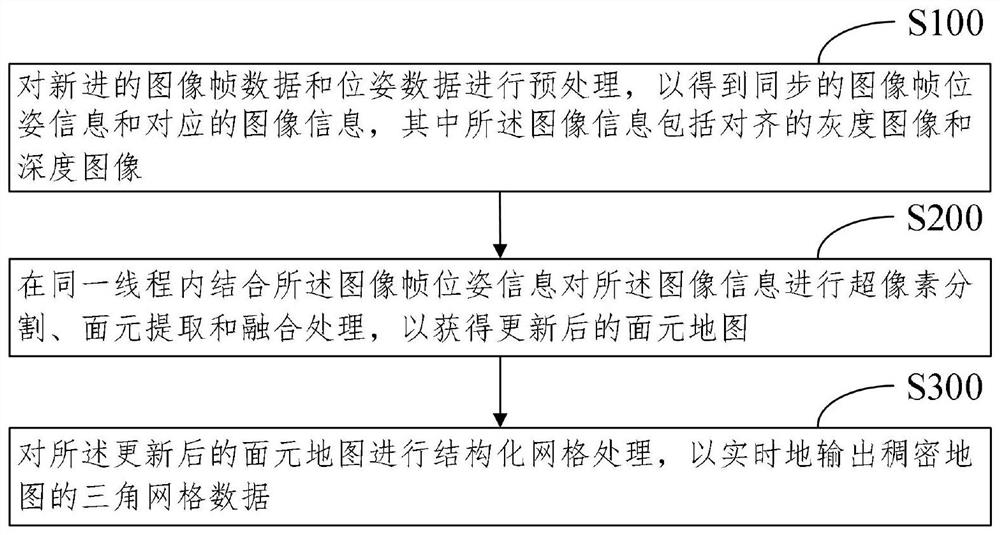
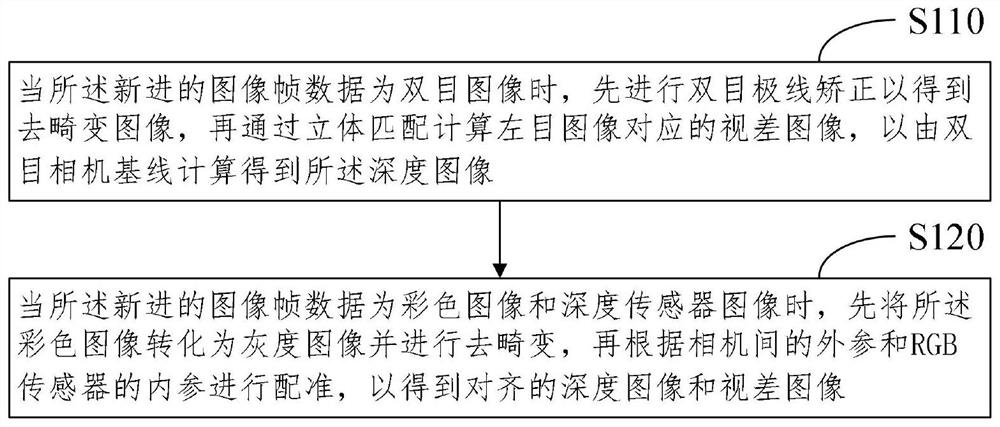
The invention discloses a three-dimensional dense surface element mapping method and system based on SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) and electronic equipment. The three-dimensional dense surface element mapping method based on the SLAM comprises the steps that new image frame data and pose data are preprocessed to obtain synchronous image frame pose information and corresponding image information, and the image information comprises a gray level image and a depth image which are aligned; performing superpixel segmentation, surface element extraction and fusion processing on the image information in combination with the image frame pose information in the same thread so as to obtain an updated surface element map; and performing structured mesh processing on the updated surface element map to output triangular mesh data of the dense map in real time.
Owner:SUNNY OPTICAL ZHEJIANG RES INST CO LTD
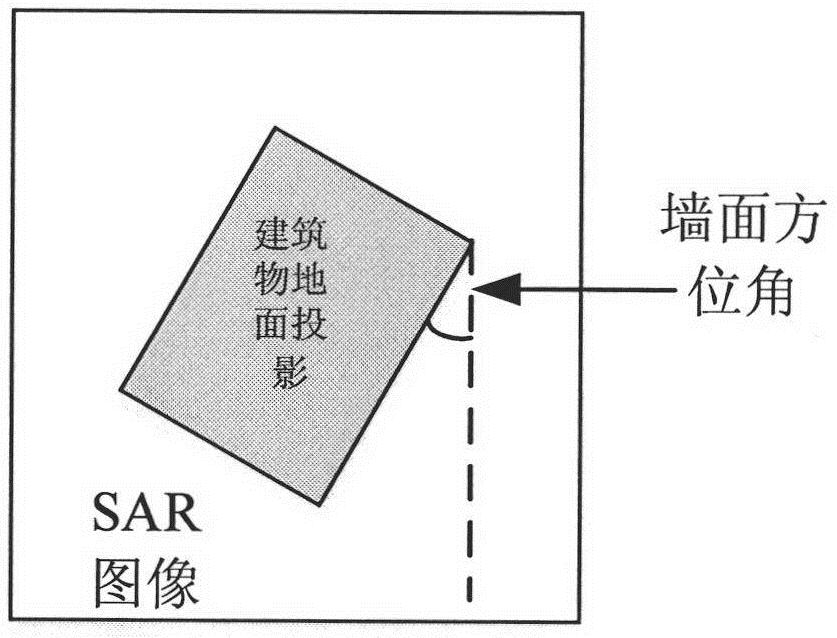
A method for extracting building wall and window information from SAR images
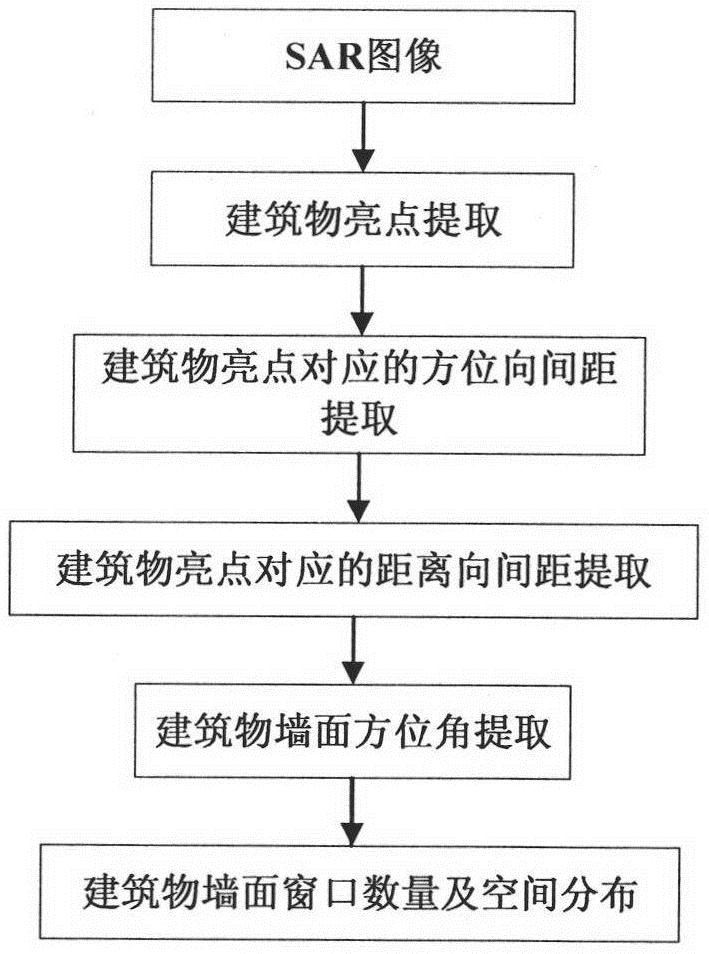
The invention discloses a method for extracting building wall and window information in a SAR image. The specific steps are: 1) using a point feature extraction method to obtain building bright spots in the SAR image; 2) using Radon transform to obtain the corresponding building bright spots in the SAR image Azimuth spacing; 3) Use the maximum texture correlation method to obtain the distance spacing corresponding to the bright spots of the building in the SAR image; 4) Use the Radon transform projection variance method to obtain the azimuth angle of the building wall in the SAR image; 5) Based on the SAR image building The Delaunay triangulation network of the highlight uses the triangular surface element matching method to extract the exact number and spatial distribution of windows on the building wall. The invention performs a series of image processing processes on the SAR image, extracts the number of windows on the wall of the building and their distribution, and realizes the extraction of the fine structure of the target wall of the building, which can satisfy the fine recognition and interpretation of the artificial target in the SAR image. It has great application prospects in areas such as city rules and land monitoring.
Owner:北京市遥感信息研究所
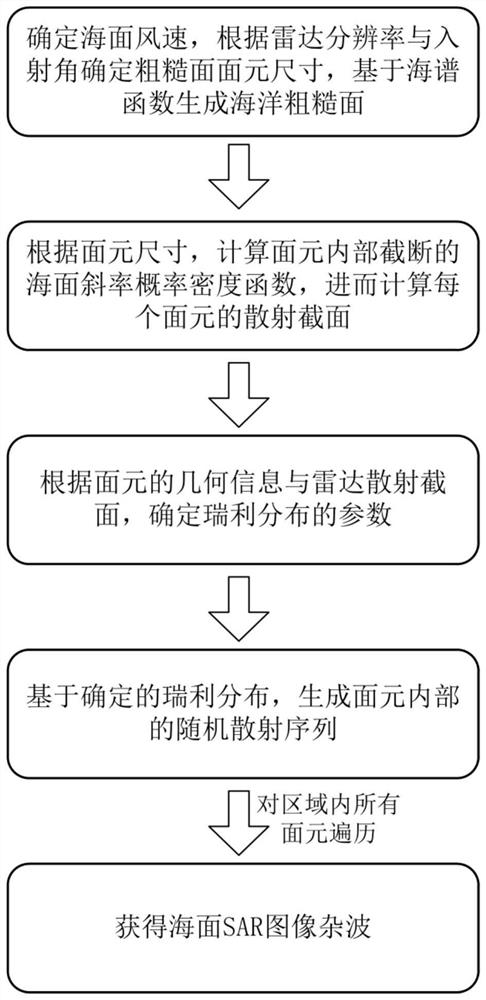
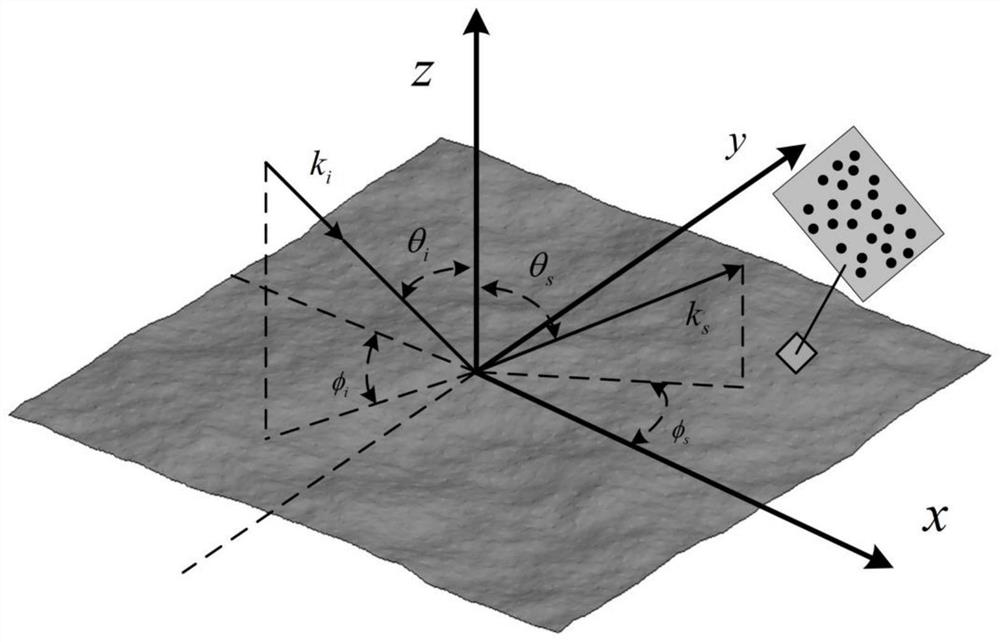
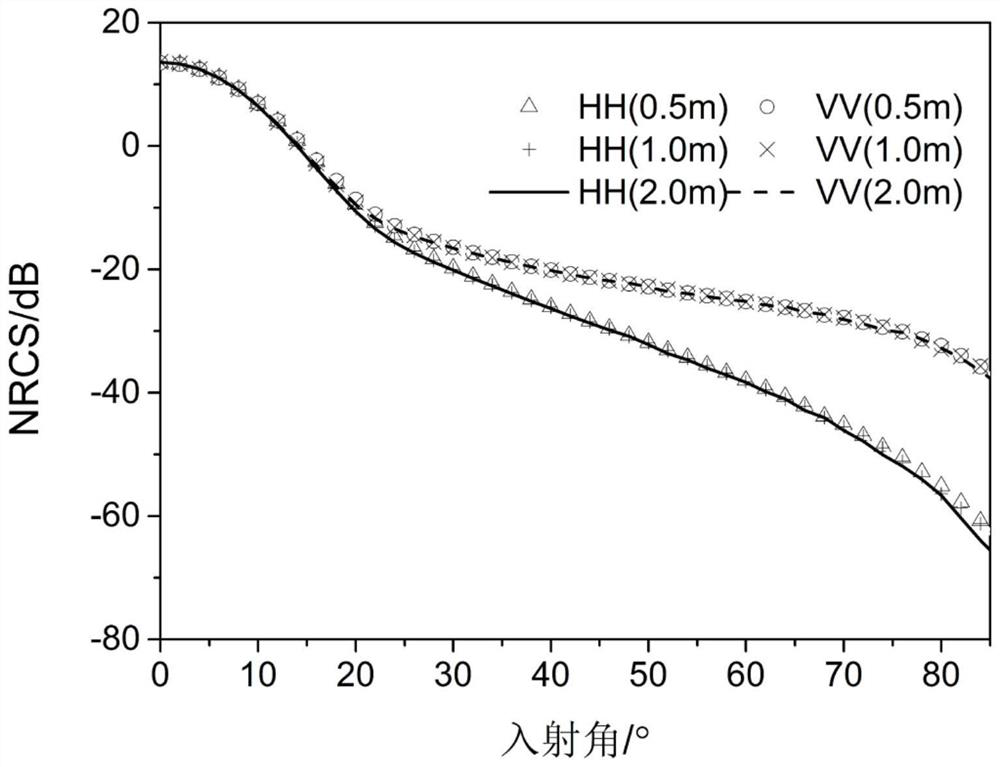
Sea surface SAR image clutter generation method based on electromagnetic and statistical hybrid model
PendingCN112764030AReduce the number of simulation unitsWell formedRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRough surfaceScattering cross-section
The invention provides a sea surface SAR image clutter generation method based on an electromagnetic and statistical hybrid model. The method comprises the following specific steps: S1, determining a power spectrum density function of a rough surface, and constructing a sea rough surface model; S2, cutting off the power spectral density function, and calculating a slope probability density function in each surface element; S3, calculating a scattering cross section of each surface element based on geometrical optics and a perturbation model; S4, calculating clutter data of each surface element; and S5, superposing the clutter data of all the surface elements to obtain a final environment SAR image. Accurate texture information of the electromagnetic model is reserved, and the statistical model is simple and efficient.
Owner:AIR FORCE UNIV PLA
A Quick Matching Method for Points Applicable to Method of Moments
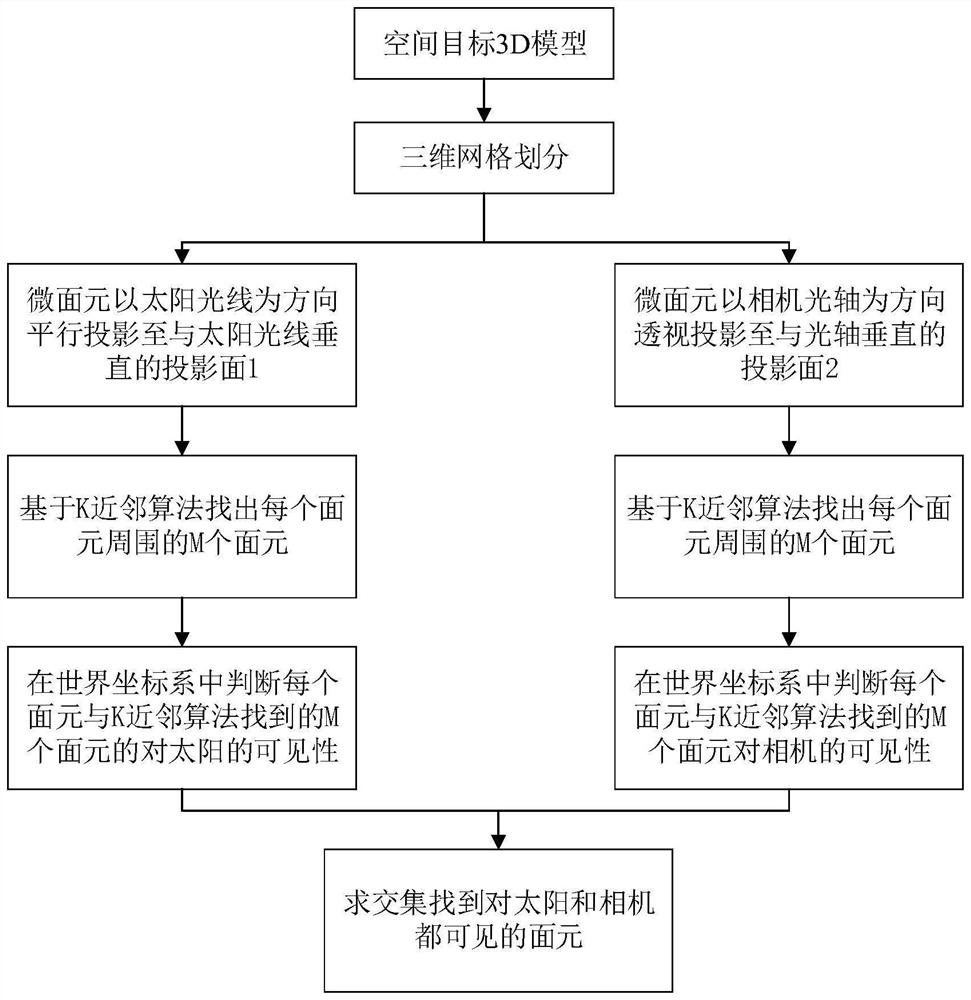
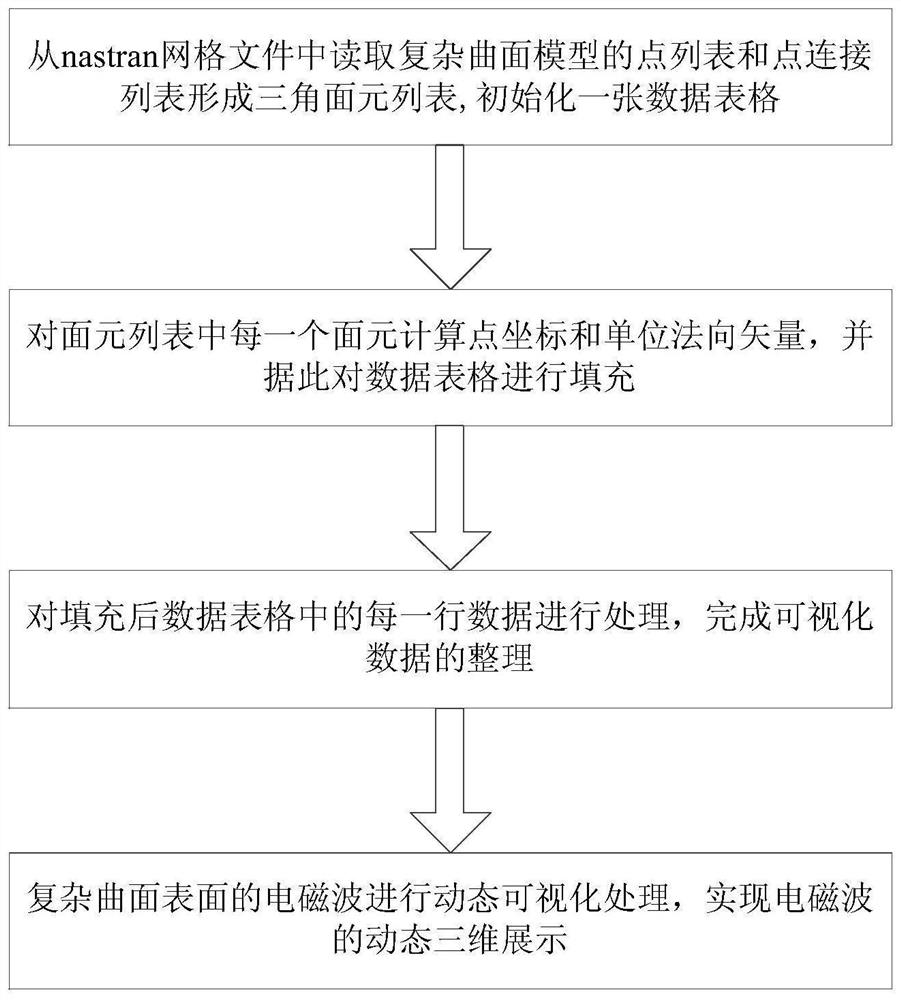
ActiveCN113989440BImprove matching efficiencyFacilitates precise extraction3D modellingAlgorithmTheoretical computer science
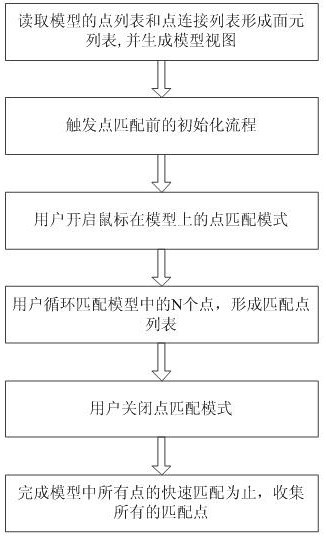
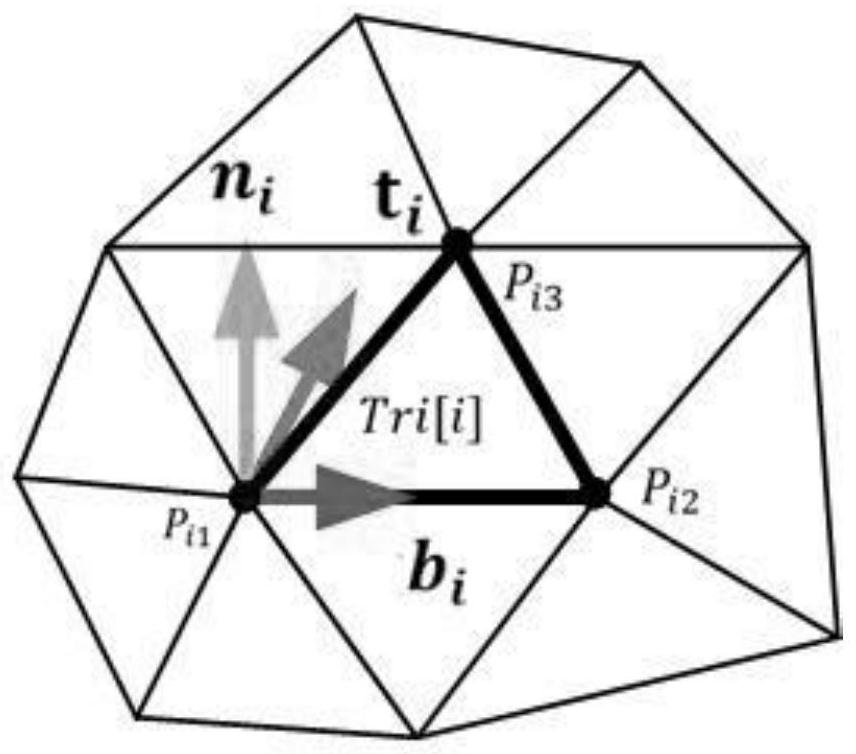
The invention discloses a kind of point fast matching method applicable to the method of moments, comprising the following steps: S1. read the point list of the model from the nastran grid file [P n ] Nnode Concatenate list with points to form list of surfels[Elem] Nelem , and generate a model view; S2. The user operates the model view to perform rotation, translation, zoom in / out, and restore operations, modify the coordinate axis, coordinate range, and upper left corner coordinates of the current screen display area, and trigger the initialization process before point matching; S3 .The user turns on the point matching mode of the mouse on the model; S4. The user circulates and matches N points in the model to form a list of matching points [P track ] N ; S5. The user closes the point matching mode; S6. Repeat steps S2-S5 until the quick matching of all points in the model is completed, and all matching points are collected to form [P track ] N′ . The invention effectively improves the speed and accuracy of point matching in surface element grids.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
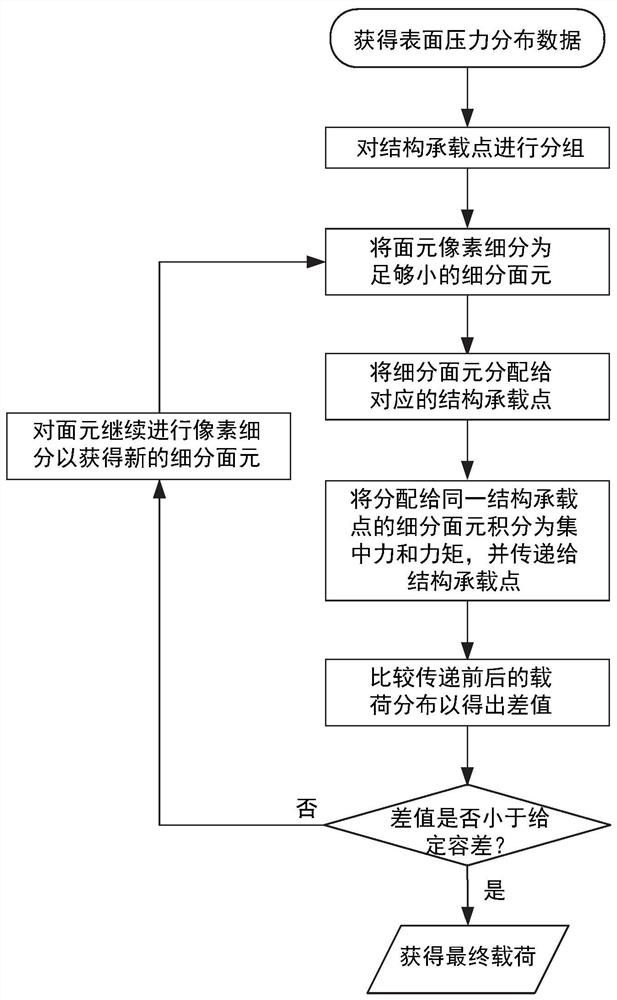
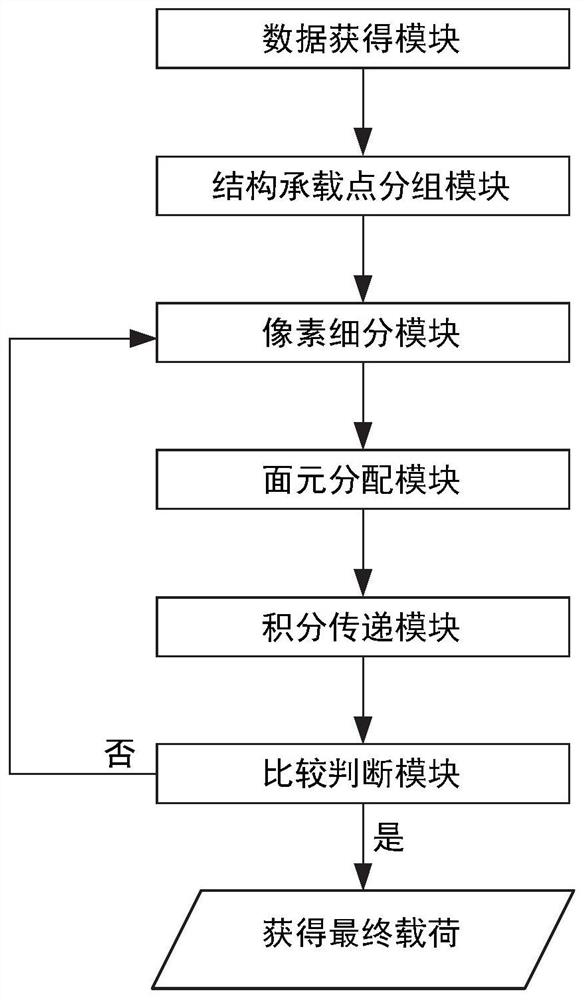
Pixel subdivision payload transfer method and system
Owner:COMAC +1
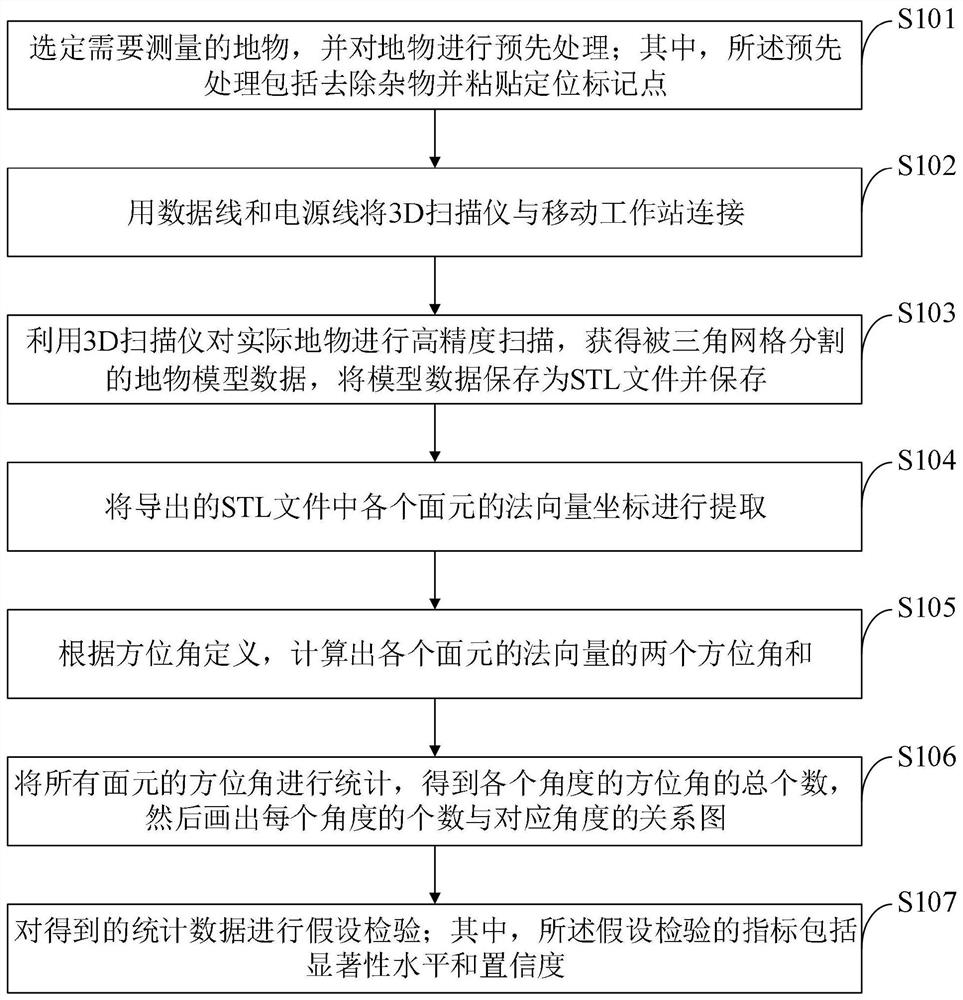
Ground object spectrum testing method and system based on high-definition 3D scanning
The invention belongs to the technical field of electronics and science, and discloses a ground object spectrum testing method and system based on high-definition 3D scanning. The method comprises the steps: selecting a ground object to be measured, and carrying out preprocessing; connecting a 3D scanner with a mobile workstation through a data line and a power line; performing high-precision scanning on an actual ground object by using the 3D scanner to obtain ground object model data segmented by a triangular mesh and storing the ground object model data; extracting normal vector coordinates of each surface element; calculating two azimuth angles theta of the normal vector of each surface element and counting the azimuth angles of all the surface elements to obtain the total number of the azimuth angles of each angle, and then drawing a relational graph of the number of the angles and the corresponding angles; and performing hypothesis testing on the obtained statistical data. The method fills the blank in the field of establishing models based on specific terrain and ground features in China in the current market, and provides a basis for deducing the shape of the ground feature according to the ground feature spectrum.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
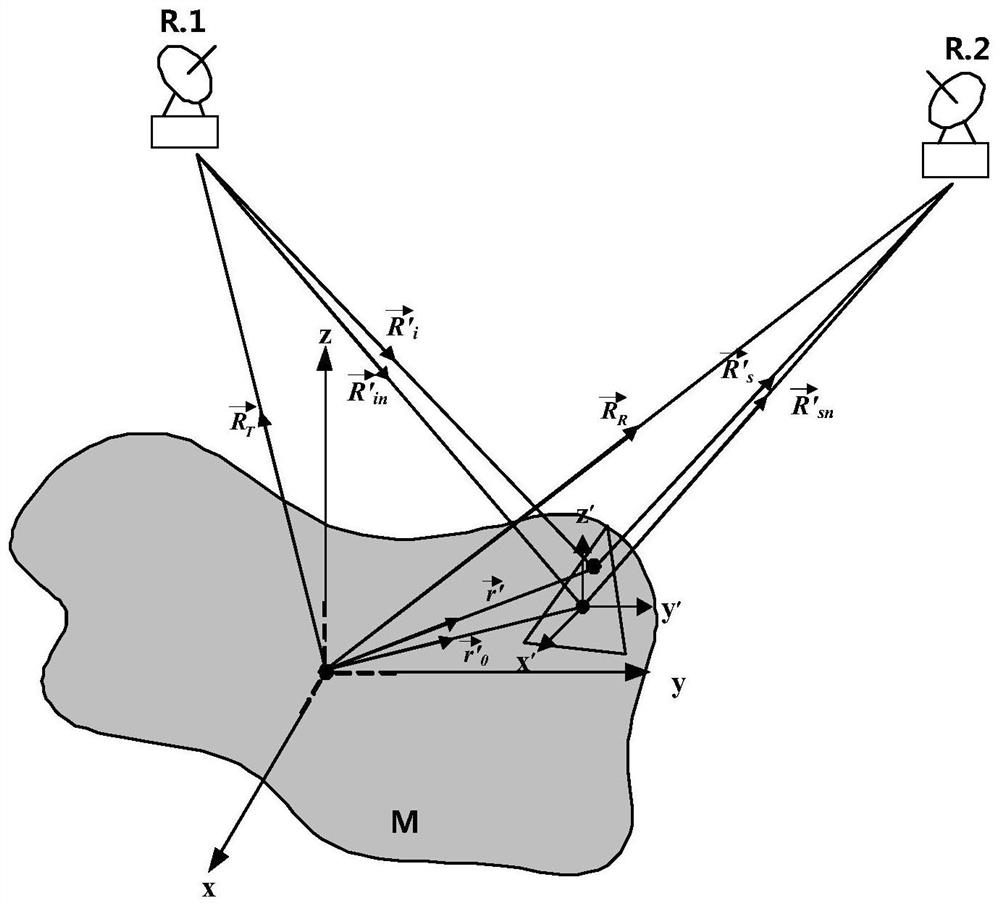
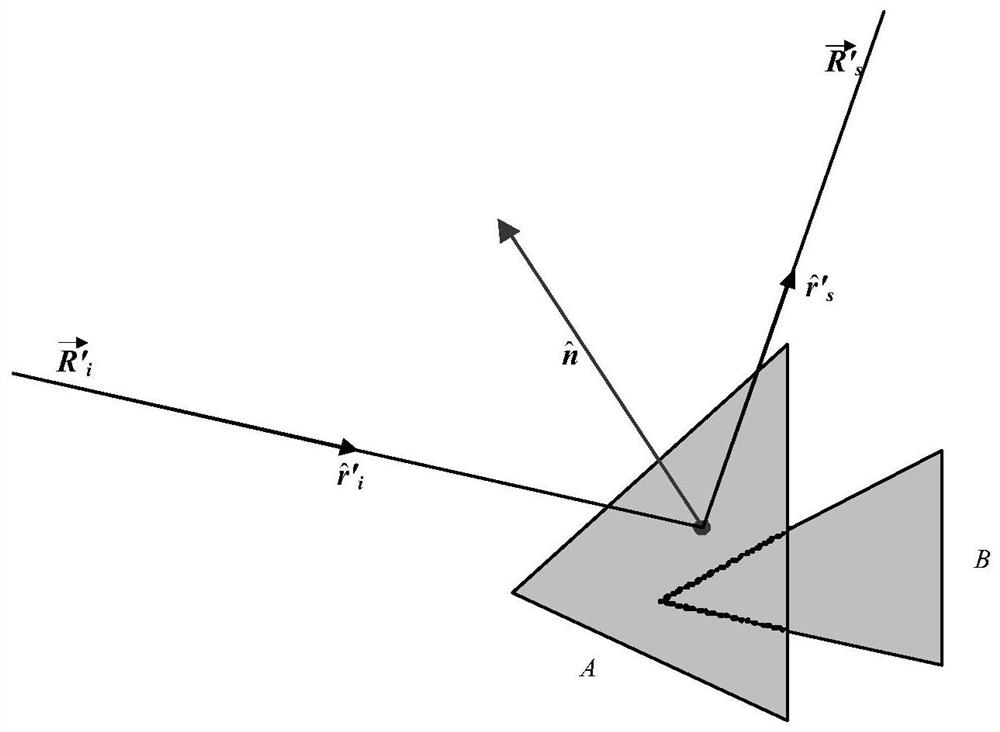
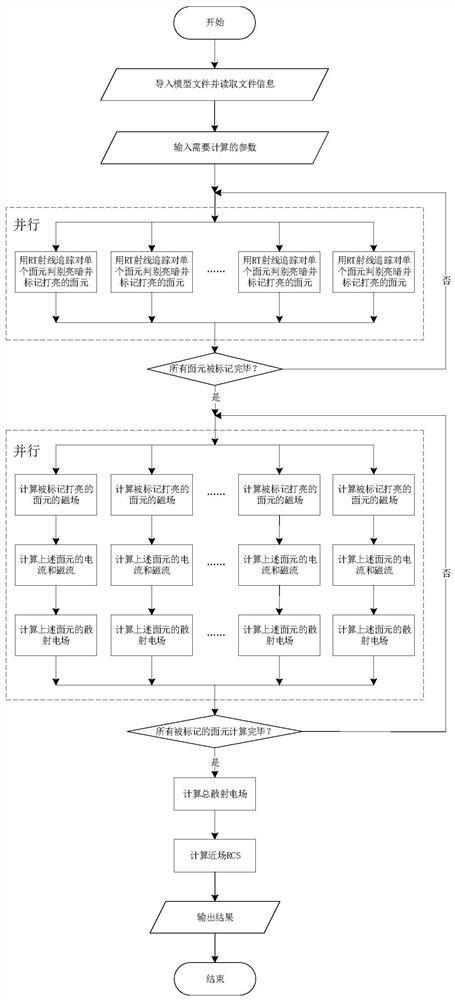
A Near-Field Electromagnetic Scattering Simulation Method for Superelectric Large-Scale Targets
ActiveCN110705058BAdapt to actual engineering scenariosQuick solveDesign optimisation/simulation3D modellingMagnetic currentParticle physics
The invention discloses a near-field electromagnetic scattering simulation method for ultra-electric large-scale targets: import a model file in STL format, read the relevant information of each triangular surface element that constitutes a radar target; input parameters that need to be calculated; judge the surface Whether the element is illuminated by the incident wave, and mark the illuminated surface element; for each triangular surface element marked as illuminated, calculate its surface current and magnetic current: solve each triangular surface element marked as illuminated The resulting scattered field will be the scattered field E of all triangular surfels marked as illuminated sn After all are solved, according to the principle of vector superposition, add them all up to get the total scattering field; get the RCS value σ of the radar target in the near field according to the following formula 0 , and output the result: the present invention fills the gap in the field of target near-field RCS simulation algorithm, especially the electromagnetic simulation processing method of different surface elements under near-field scattering conditions, which is more suitable for actual engineering scenarios.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Three-dimensional reconstruction method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium
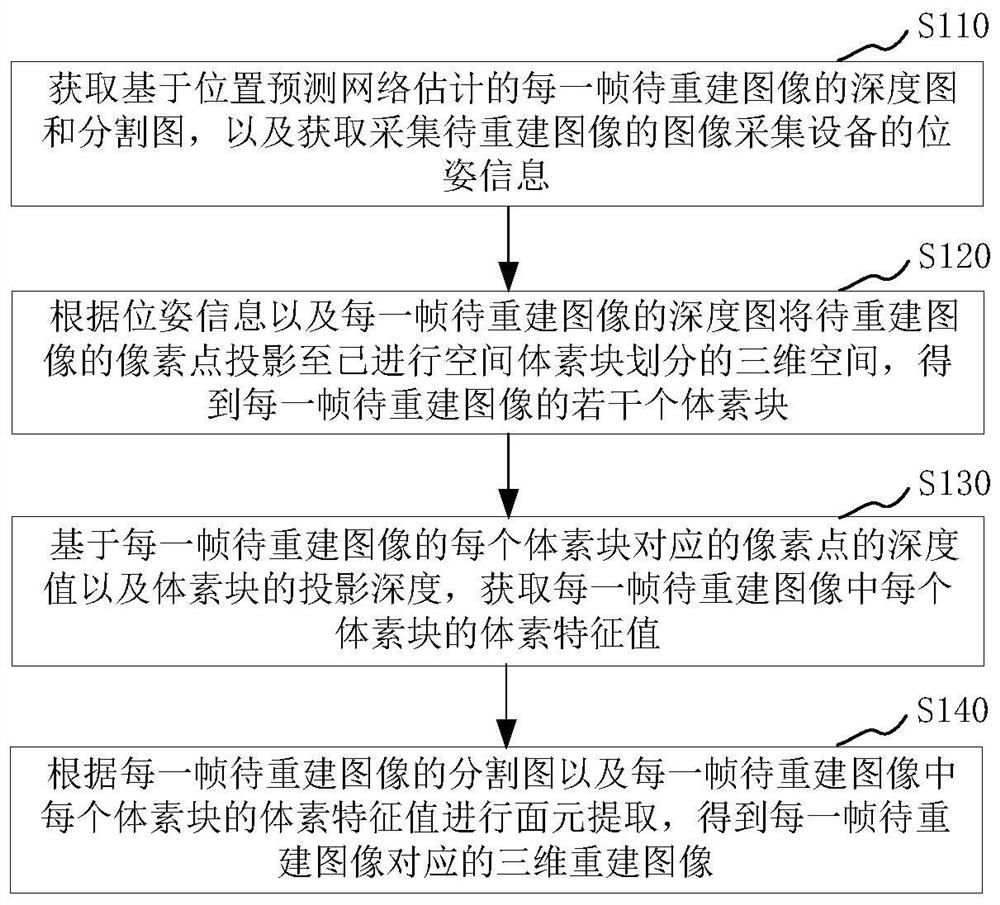
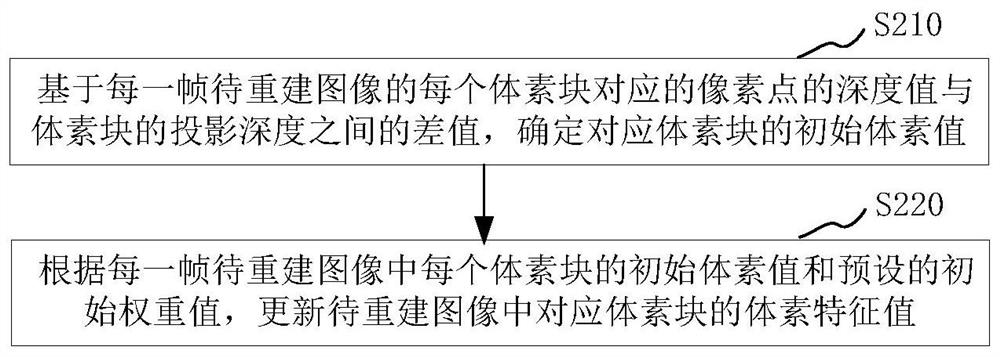
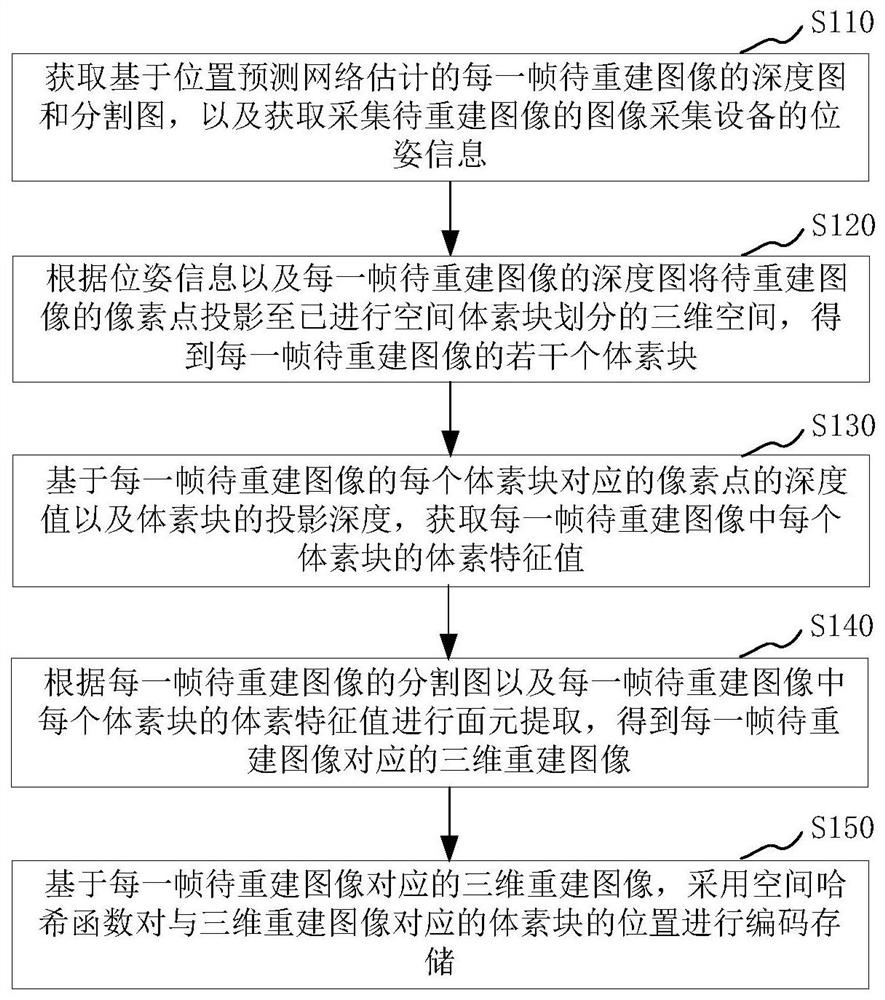
The invention relates to a three-dimensional reconstruction method and device, electronic equipment and a storage medium, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining a depth image and a segmentation image of each frame of to-be-reconstructed image estimated based on a position prediction network, obtaining the pose information of image collection equipment for collecting the to-be-reconstructed image, according to the pose information and the depth map of each frame of the to-be-reconstructed image, projecting pixel points of the to-be-reconstructed image to a three-dimensional space subjected to space voxel block division to obtain a plurality of voxel blocks of each frame of the to-be-reconstructed image, obtaining a voxel feature value of each voxel block in each frame of the to-be-reconstructed image, then performing surface element extraction, and obtaining a three-dimensional reconstruction image corresponding to each frame of to-be-reconstructed image. In the three-dimensional reconstruction process, the depth map and the segmentation map of each frame of image to be reconstructed are estimated through the position prediction network, so that the method does not depend on a depth sensor, surface element extraction is carried out through space voxel division, and high-quality curved surface modeling can be realized.
Owner:BEIJING DAJIA INTERNET INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
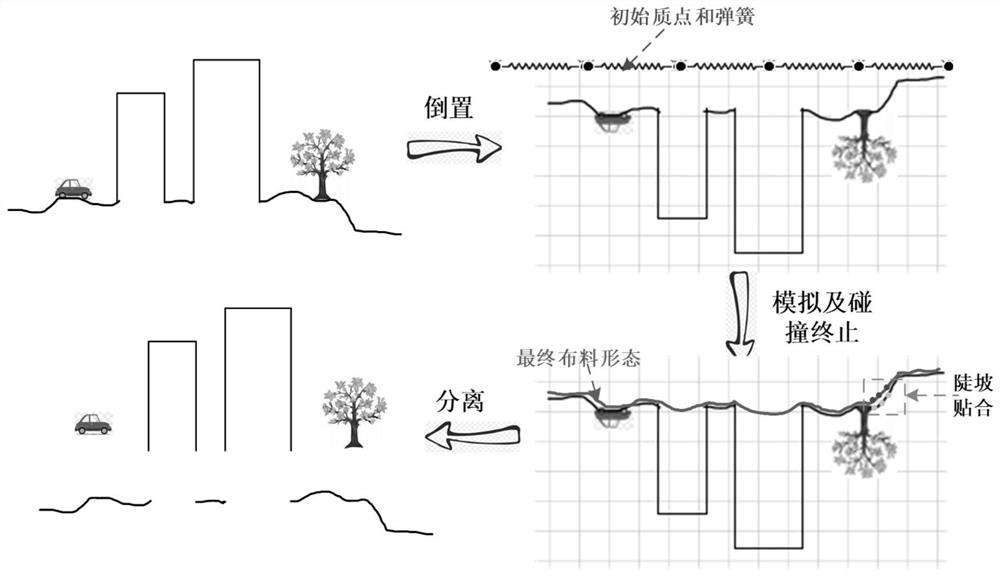
A method for automatic separation of ground model and non-ground model of real 3D model
The invention discloses an automatic separation method for a ground model and a non-ground model for a three-dimensional model of a real scene. The present invention simulates the free fall of the cloth on the inverted three-dimensional model of the real scene by using the particle physics model with the distance constraint for the surface element, and determines the final form of the cloth through the collision detection between the particle and the three-dimensional model of the real scene, which is used as an approximation of the ground model, The ground model and the non-ground model are locally distinguished by comparing the spatial relationship between the particle and the surfel of the 3D model of the real scene. The invention has the advantages of high efficiency, high robustness and high precision, and can be used for the separation of the ground model and the non-ground model of the real scene three-dimensional model of urban, woodland, rural and other scenes and any surface element density.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV +1
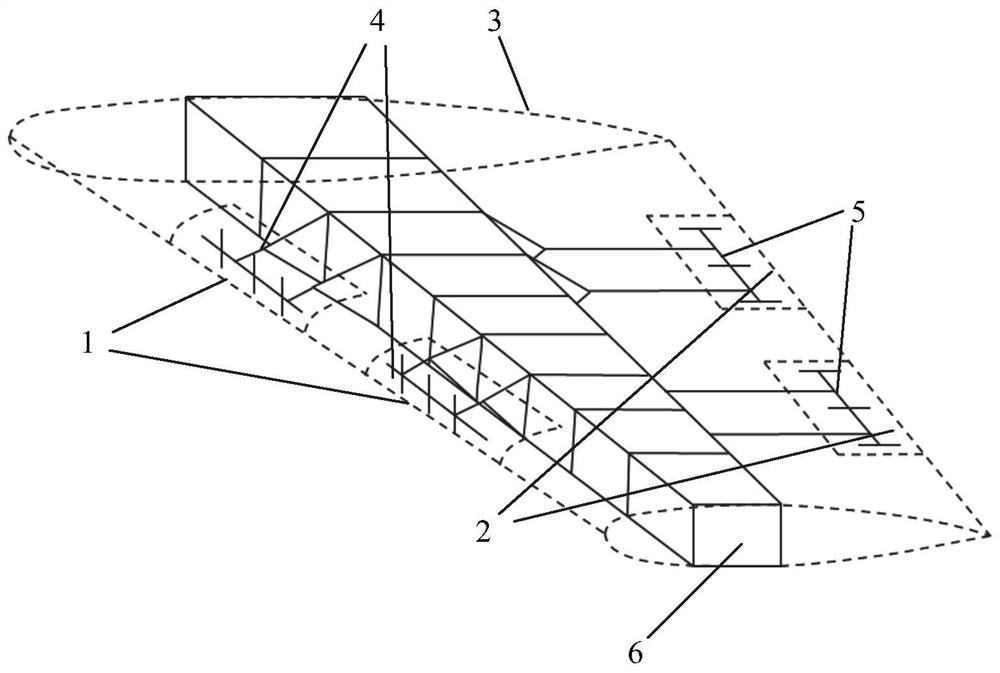
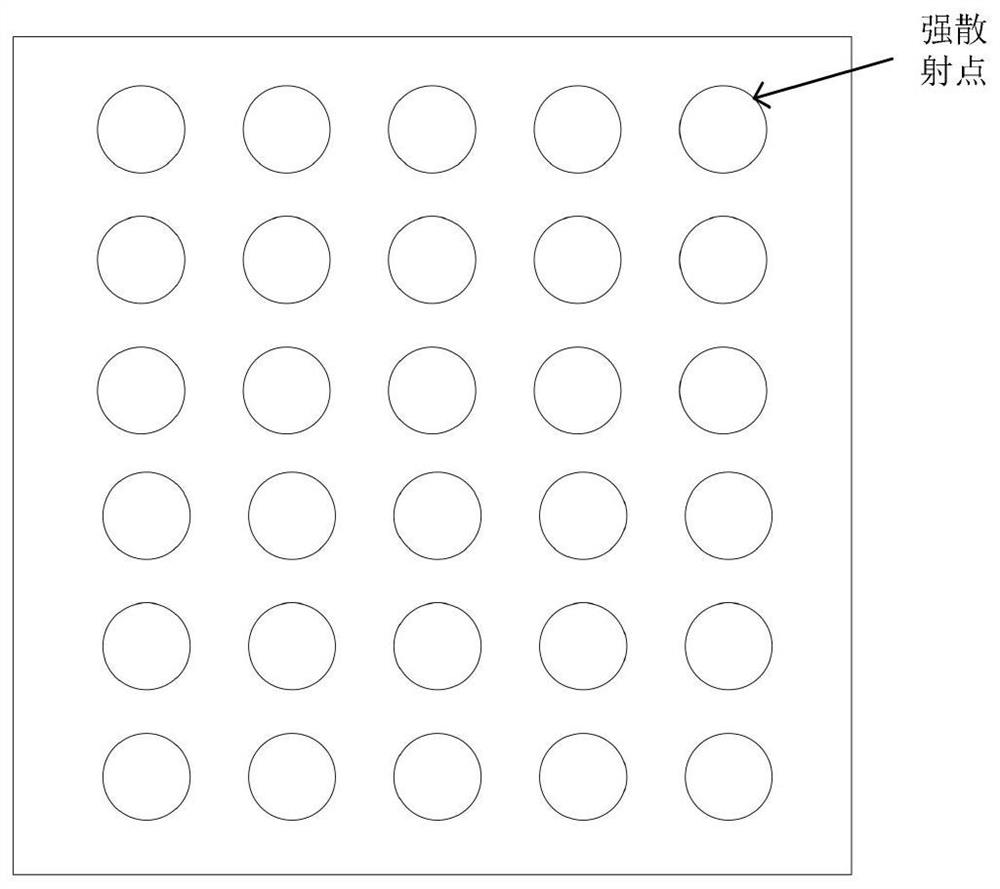
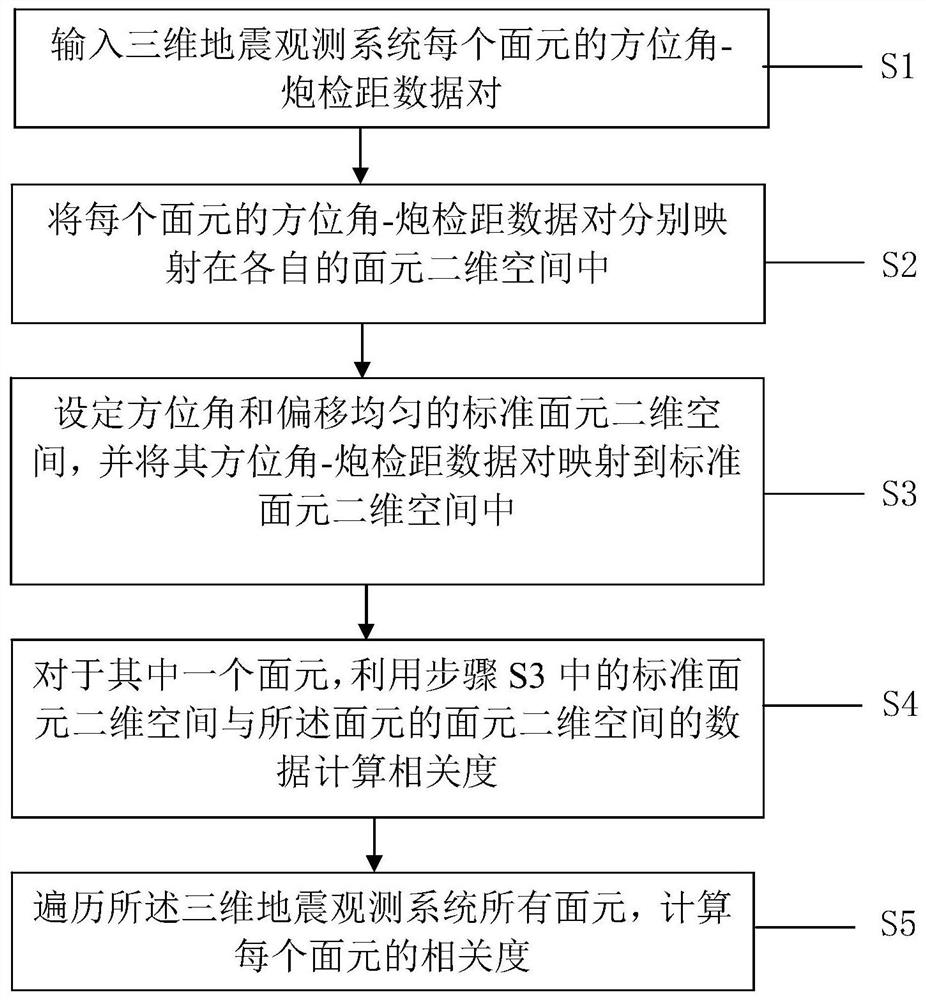
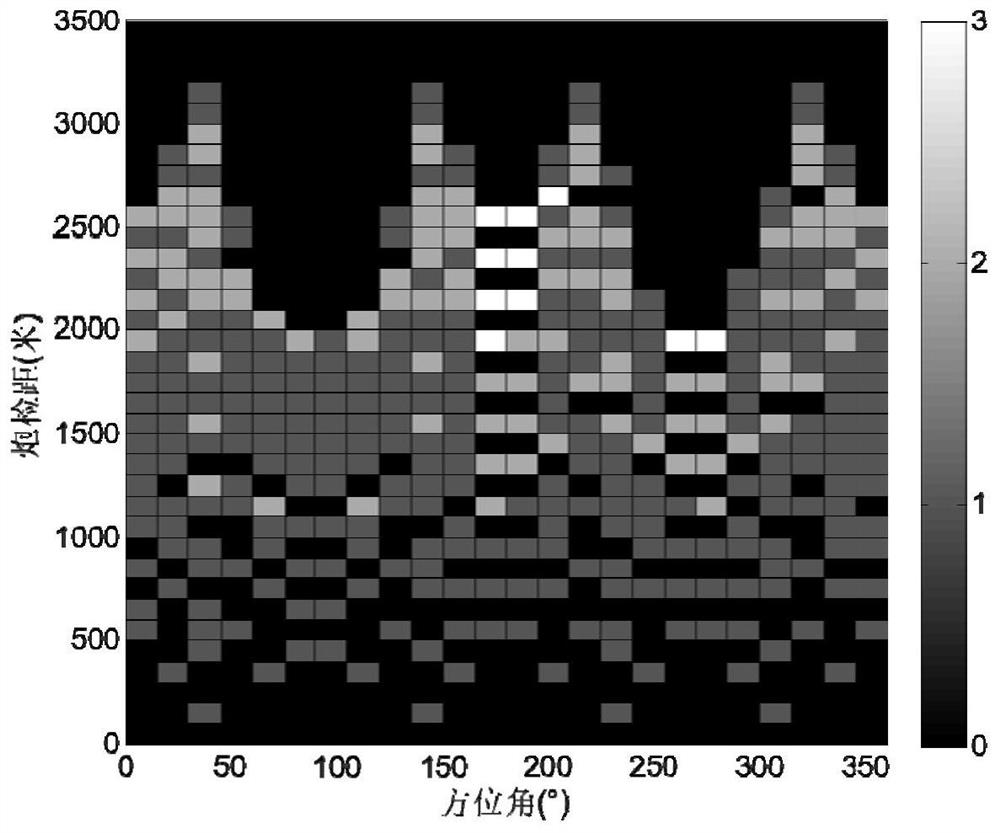
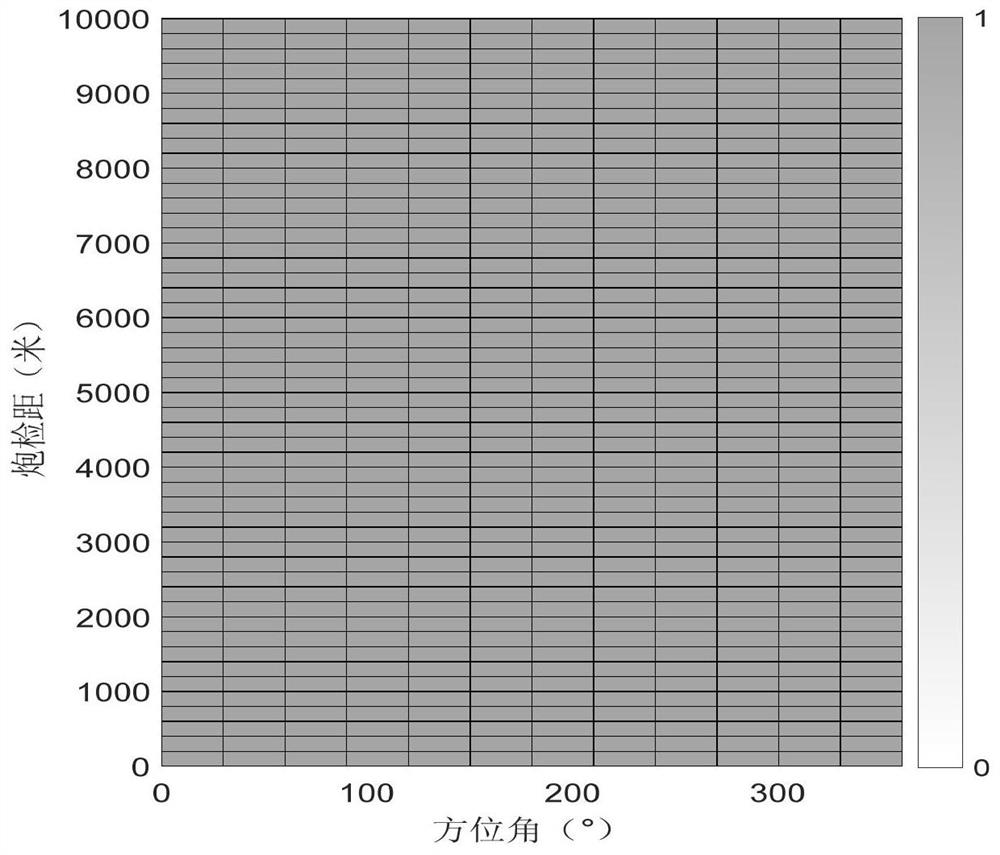
Method and system for evaluating bin uniformity of 3D seismic observation system
A method and system for evaluating bin uniformity of a 3D seismic observation system. The method includes: 1) inputting the azimuth-offset data pair of each bin in the 3D seismic observation system; 2) mapping the azimuth-offset data pair of each bin on the respective bin 3) Set a standard bin two-dimensional space with uniform azimuth and offset, and map its azimuth-offset data pair into the standard bin two-dimensional space; 4) For one of the bins, Utilize the standard bin two-dimensional space in step 3) and the data calculation correlation of the bin two-dimensional space of the bin; 5) traverse all bins of the three-dimensional seismic observation system, and calculate the correlation of each bin . The present invention quantitatively calculates the correlation degree of each bin azimuth and offset two-dimensional space with the standard bin azimuth and offset two-dimensional space distribution, and quantitatively evaluates the bin azimuth and offset of the observation system Distribution uniformity, and can give evaluation results through intuitive data graphics.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
A Multi-Order FDTD Grid Modeling Method
The invention discloses a multi-order FDTD grid modeling method. The method generates a triangular surface element model based on commercial software Hypermesh, and then processes the triangular surface element model to generate a multi-order precision FDTD grid. The method achieves the free selection of space step, generates the multi-order precision FDTD grid, and solves a problem of complex models of various types of dielectric materials. Finally, the method verifies the accuracy of a modeling result through the FDTD grid generated through CAD detection. The method can solve a problem of FDTD modeling of a complex target model, a problem of FDTD modeling of various types of materials, and a problem of the refining of features of a special part.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Three-dimensional reconstruction method and device based on surface elements
PendingCN114170288AIncrease constraintsImprove robustnessDetails involving processing stepsImage enhancementPattern recognitionColor image
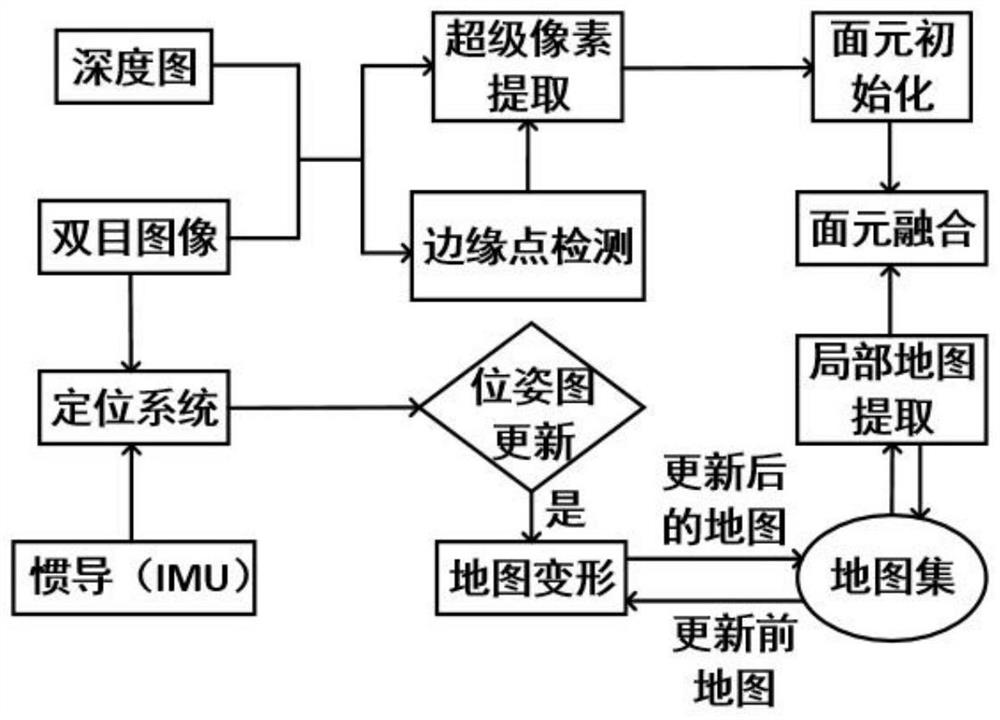
The invention discloses a surface element-based three-dimensional reconstruction method and device, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out the edge point detection and super pixel extraction based on a surface element method in combination with a depth image and a binocular color image of a to-be-reconstructed scene, and introducing regularization constraint to obtain a dense three-dimensional map. According to the method, generation of edge'holes' in a reconstructed image can be obviously reduced, the plane reconstruction smoothness and the three-dimensional reconstruction robustness are improved, and the reconstruction accuracy and stability of surface element-based three-dimensional reconstruction at the edge are greatly improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Electromagnetic wave dynamic three-dimensional display method suitable for complex curved surface
ActiveCN114049465AAddresses situations where it cannot be applied to complex curved surfaces3D modellingEngineeringComputational physics
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
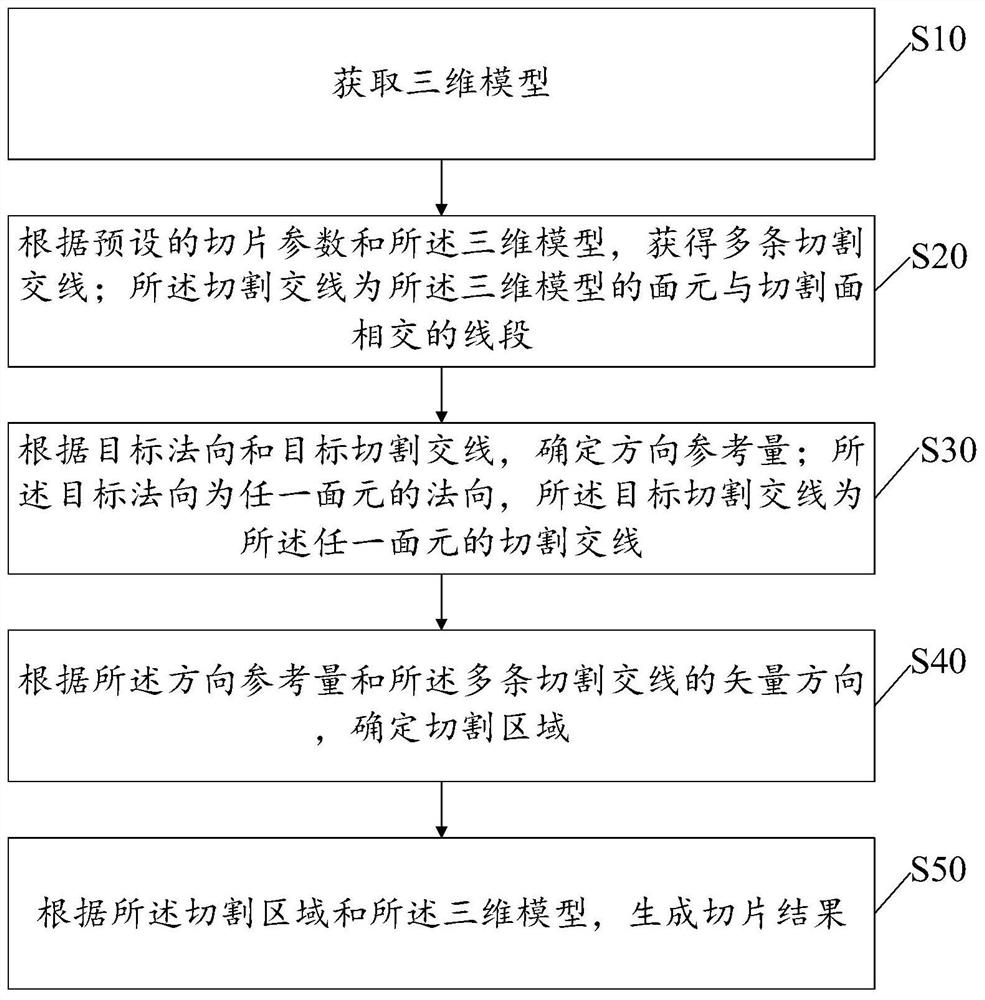
3D model slicing processing method and device
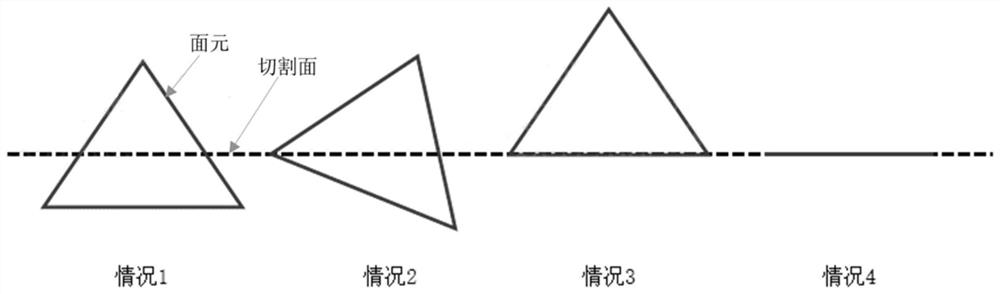
PendingCN113674294AReduce computational overheadImprove slice processing efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisAlgorithmSlicing
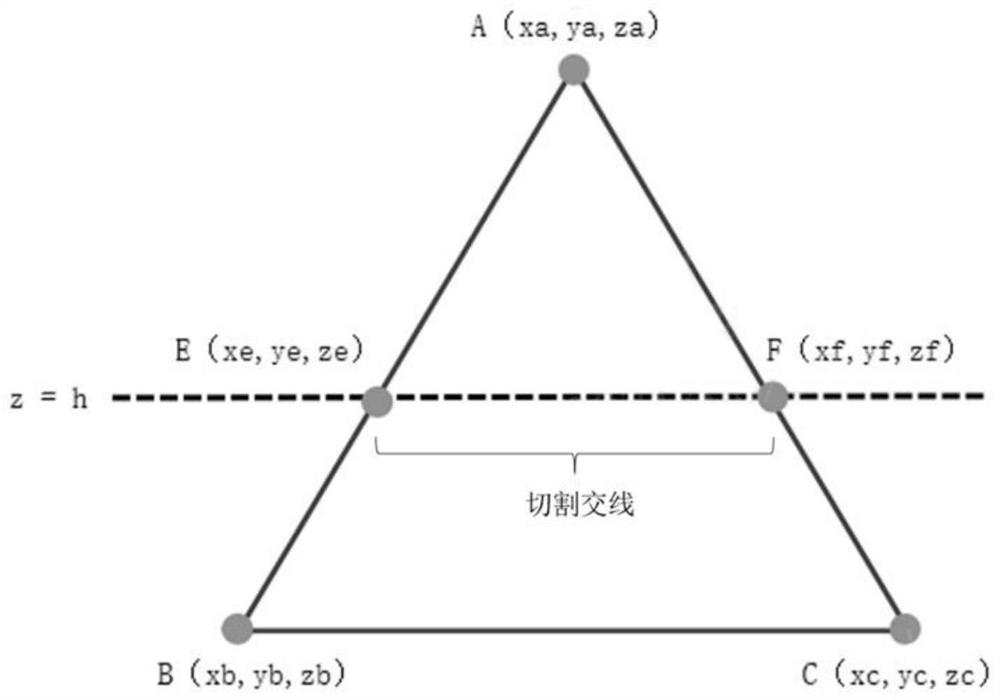
The invention discloses a 3D model slicing processing method and device. The method comprises the steps of acquiring a 3D model; obtaining a plurality of cutting intersecting lines according to preset slicing parameters and the three-dimensional model; the cutting intersection line is a line segment where the surface element of the three-dimensional model intersects with the cutting surface; determining a direction reference quantity according to the target normal direction and the target cutting intersection line; the target normal direction is the normal direction of any surface element, and the target cutting intersection line is the cutting intersection line of any surface element; determining a cutting area according to the direction reference quantity and the vector direction of the plurality of cutting intersecting lines; and generating a slicing result according to the cutting area and the three-dimensional model. According to the method, the calculation overhead of the whole slice processing process can be greatly reduced, and the slice processing efficiency is remarkably improved.
Owner:BEIJING BOE TECH DEV CO LTD +1
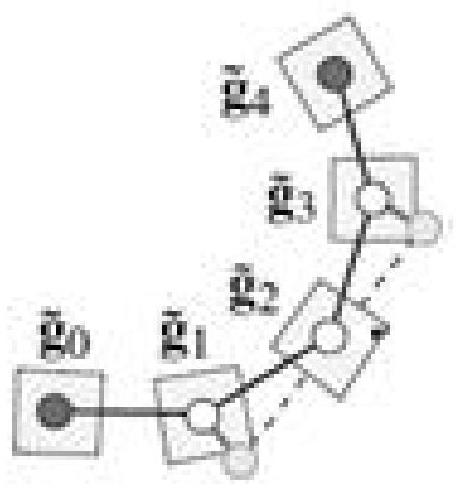
Complex curved surface electromagnetic wave vector dynamic visualization method
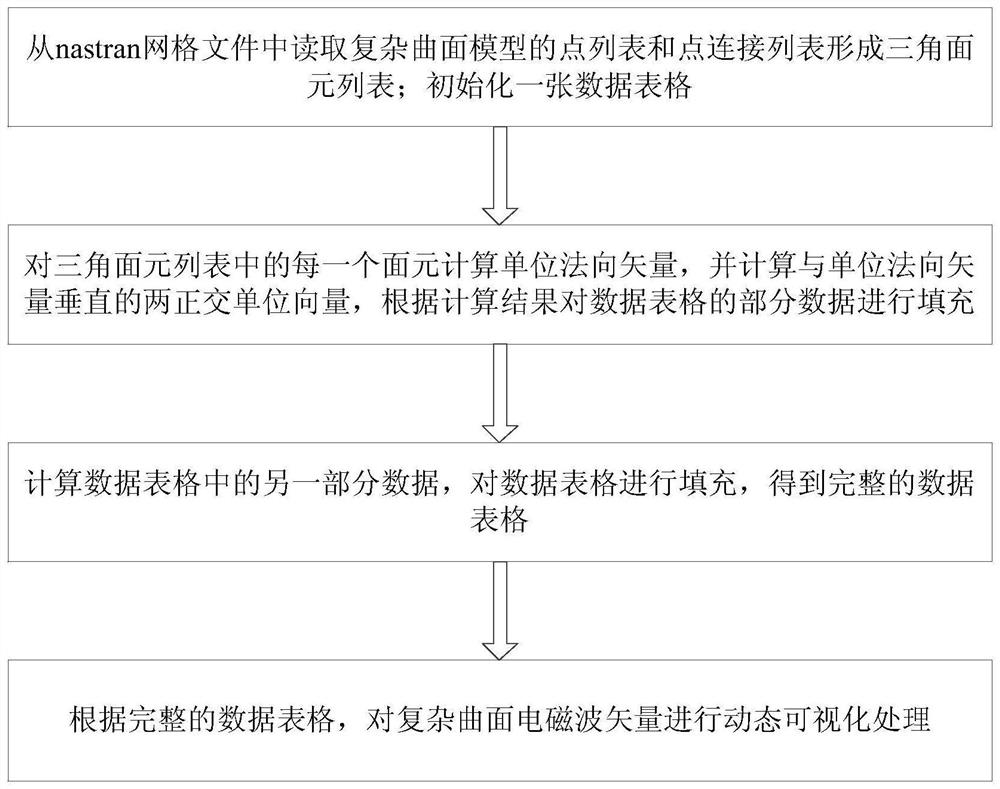
ActiveCN114067079AReveal the phenomenon of decomposition and synthesisIncrease flow direction3D modellingDatasheetComplete data
The invention discloses a complex curved surface electromagnetic wave vector dynamic visualization method. The method comprises the following steps: S1, reading a point list [P] N and a point connection list of a complex curved surface model from a nastran grid file to form a triangular surface element list [Tri] M; initializing a data table [Tbl] N, 18 with the dimension of N * 18; s2, calculating a unit normal vector ni for each surface element in the triangular surface element list, calculating two orthogonal unit vectors bi and ti perpendicular to the ni, and filling partial data of the data table [Tbl] N, 18 according to a calculation result; s3, processing the data table obtained in the step S2, calculating the other part of data in the data table [Tbl] N, 18, and filling the data table to obtain a complete data table; and S4, according to the complete data table, carrying out dynamic visualization processing on the complex curved surface electromagnetic wave vector. According to the invention, the fluctuation of the electromagnetic wave can be dynamically displayed in a coupling manner, and the vector fluctuation condition of the electromagnetic wave on a complex curved surface is effectively visualized.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com