Hotspot event identification method and system
A technology of hotspot events and identification methods, applied in the field of hotspot event identification methods and systems, which can solve the problems of hotspot event identification and untimely processing, and achieve the effect of good domain adaptability and lower requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
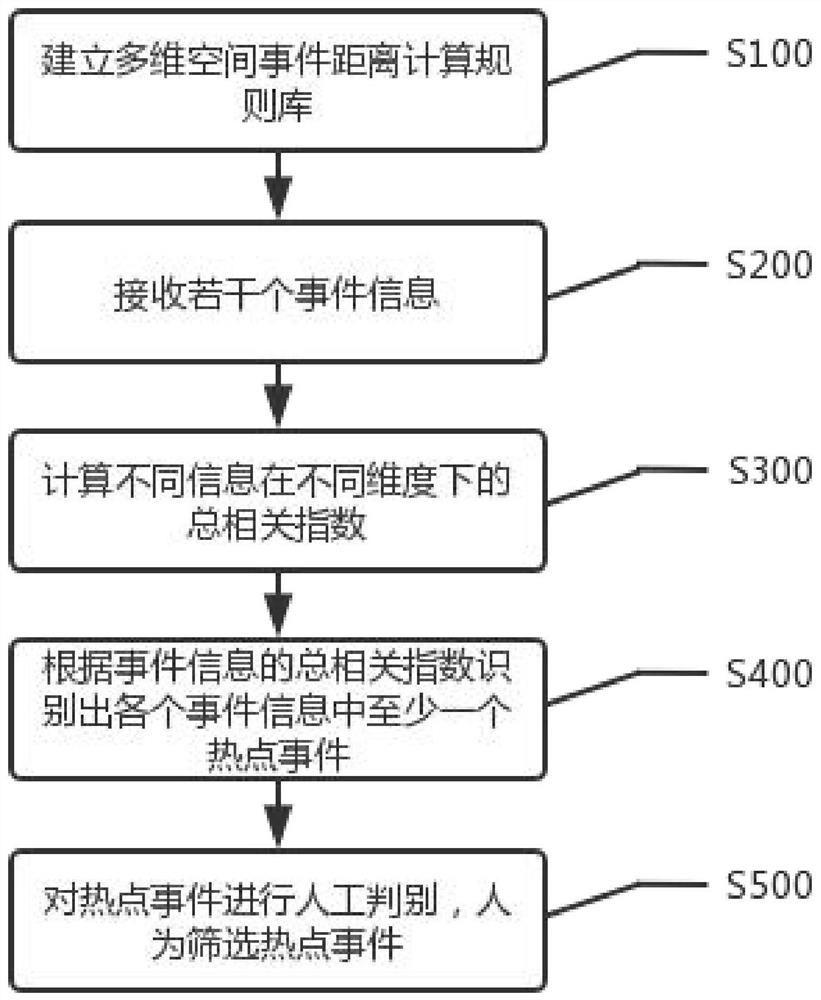
[0070] An embodiment of the present invention, such as figure 1 As shown, the present invention provides a kind of hot event identification method, comprises steps:
[0071] S100 establishes a multi-dimensional spatial event distance calculation rule base.
[0072] Specifically, the calculation rule base is used to calculate the total correlation index of event information in different dimensions, and the dimensions include time dimension, space dimension, category dimension, and attribute dimension.
[0073] S200 receives several pieces of event information.
[0074] Specifically, when receiving several pieces of event information, event messages from multiple sources and types can be received in a real-time, quasi-real-time, or batch manner. Among them, receiving event information in quasi-real time refers to receiving event information with a certain data delay, and receiving event information in batches refers to receiving event information uniformly after accessing the ...
Embodiment 2
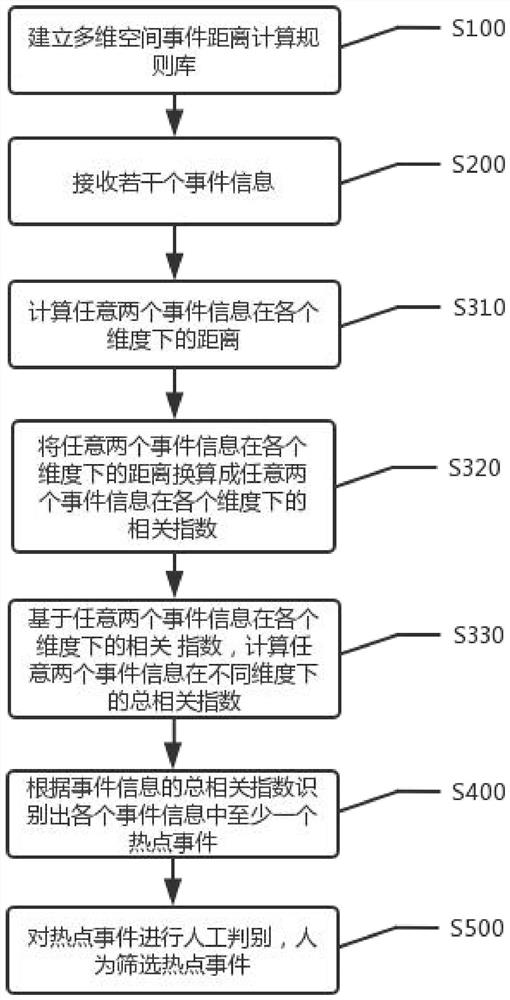
[0089] Another embodiment of the present invention, such as figure 2 As shown, the present invention provides a kind of hot event identification method, comprises steps:
[0090] The S100 pre-establishes a multi-dimensional spatial event distance calculation rule base.
[0091] Specifically, the calculation rule base is used to calculate the total correlation index of event information in different dimensions, and the dimensions include time dimension, space dimension, category dimension, and attribute dimension.
[0092] S200 receives several pieces of event information.
[0093] Specifically, when receiving several pieces of event information, event messages from multiple sources and types can be received in a real-time, quasi-real-time, or batch manner. Among them, receiving event information in quasi-real time refers to receiving event information with a certain data delay, and receiving event information in batches refers to receiving event information uniformly after ...
Embodiment 3
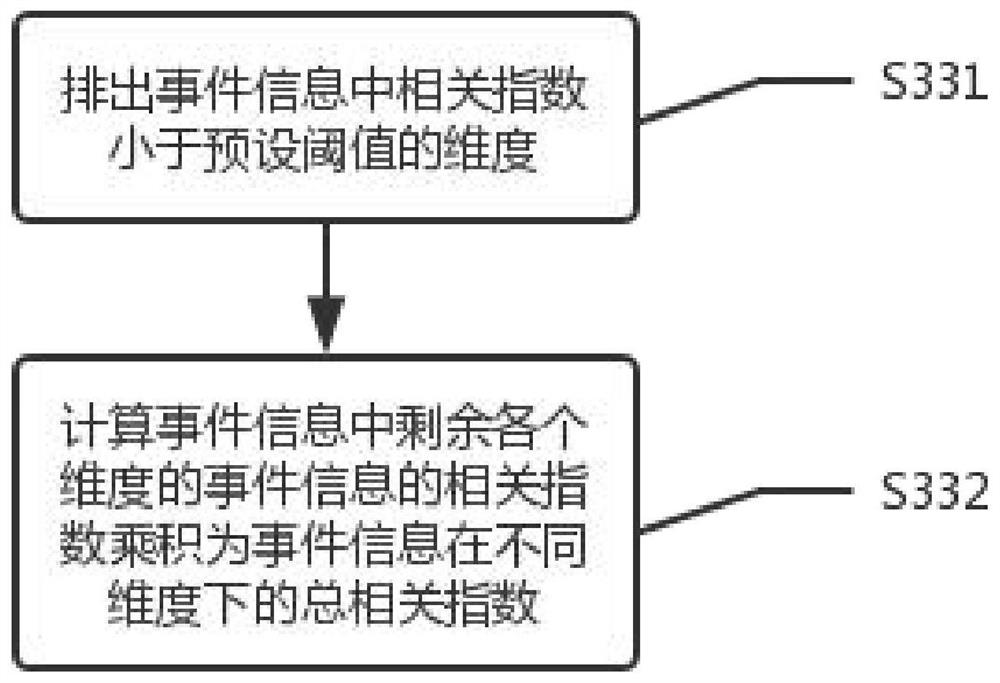
[0112] In an embodiment of the present invention, on the basis of Embodiment 1 or 2, calculating the distance between any two event information in each dimension includes steps:
[0113] S311 Calculate the start time difference and end time difference of any two event information in the time dimension, and the time difference between the start time of one event information and the end time of another event information is the distance in the time dimension.
[0114] S312 Calculate the distance between any two event information in the spatial dimension as the distance in the spatial dimension.
[0115] Preferably, the spatial dimension can be divided into distance operations between points, lines, and planes according to the type of spatial location of the event, such as point-to-point, point-to-line, line-to-plane, etc.
[0116] Further preferably, the calculation of the spatial dimension distance can have a specific relationship with the shape of the spatial object. For exampl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com