Screwed joint based on position control
A technology of threaded joints and threads, which is applied in the field of threaded joints based on position control, to avoid the problem of overtightening
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0034] The present invention will be further elaborated below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
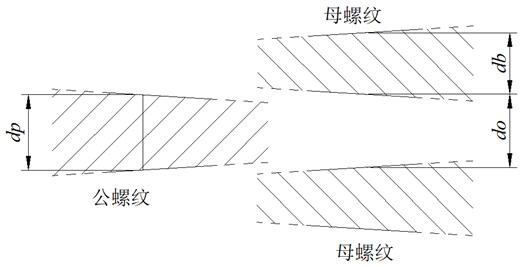
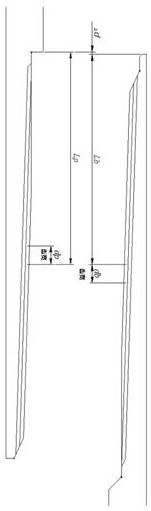
[0035]A threaded joint based on position control, including a male thread and a female thread. The cross-sectional shape of the male thread and the female thread is a trapezoidal thread, a rectangular thread or an inverted trapezoidal thread; in the thread structure, the tooth top is parallel to the tooth bottom, and the tooth side is parallel to the tooth The angle between the top or tooth bottom is ≥80°, the thread taper is 1:8~1:14, the thread tooth height is 1.0mm~1.6mm, and the pitch is 6mm / tooth~8mm / tooth. The section of the male thread and the female thread gradually changes along the helical direction of the thread, showing that the tooth height remains unchanged, the tooth width of the male thread gradually increases, and the tooth width of the female thread gradually decreases. The change rate of the tooth width of the male thread and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com