Method and application of designing enzyme preparation feeding mode in fermentation process by computer
A technology of fermented raw materials and fermented liquid, which is applied in the fields of renewable energy and bioengineering, can solve problems such as the difficulty in the rational design of cellulase formulations, and achieve the effects of saving production costs, reducing additives, and improving economic efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0064] The second aspect of the invention provides a method of producing biohal ethanol comprising: forming a fermentable raw material by liquefied treatment, inoculation of ethanol fermentation strain to the fermentation raw material, and adds a glycosidase, nitrogen source Synchronized saccharification fermentation is performed, and the enzyme preparation feed during the fermentation process obtained according to the above method is added, and the respective enzyme component is added to the feed period.
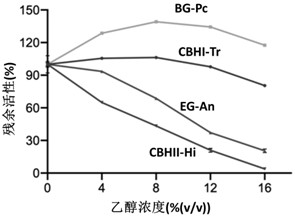
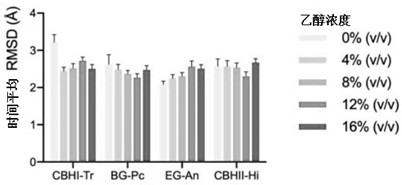
[0065]By activity of cellulase components measured at different simulated concentrations seen in all cellulase - ethanol system, the ethanol concentration is between 0-16% (v / v), gradually increasing the number of ethanol molecules, more significantly inhibited cellulase will occur with increasing concentration of ethanol, cellulase activity decreases, which certainly limits the efficient hydrolysis of starch the cellulose in the feedstock to glucose, thereby interfering with...
Embodiment 1
[0078] (1) Measurement of the activity of exo-cellulase I (CBHI-Tr): cutting the outer 0.1mL I cellulase solution, 0.7mL concentration of 10mmol / L of 4-nitrophenyl fibers -β-D- diglycoside 0.1mL solution at a concentration of 0.05M citrate buffer, mixed, and ethanol was added to obtain a mixture, such a mixture of ethanol concentration of 0 vol%, 4 vol%, 8 vol%, 12 vol%, 16 vol %, 20 vol%, 40min followed by reaction at 50 ℃, 2mL was added at a concentration of 1mol / L of Na 2 CO 3 10mL water and, measuring absorbance at 400nm, the results shown in Table 1;
[0079] (2) Measurement of the activity of exo-cellulase II (CBHII-Hi): 200-fold diluted to 0.1mL exocellulases II solution, 0.14mL concentration of 2 wt% solution of microcrystalline cellulose PH101, 0.1mL 0.05M citrate buffer at a concentration of mixed solution, and ethanol was added to obtain a mixture, such that the ethanol concentration in the mixture was 0% by volume, respectively, 4% by volume, 8 vol%, 12 vol%, 16 vo...
Embodiment 2
[0087] Culturing 24h (1) to add a YPD medium with glucose as a seed medium Saccharomyces cerevisiae (glucose concentration of 100g / L), at a temperature of 30 ℃, speed of 150rpm conditions to give a seed culture broth, the seeds the culture was centrifuged at 4000rpm 10min seed obtained wet cells;
[0088] (2) The corn flour was mixed with water such that the dry matter concentration of the corn is 30 wt%, 0.012 wt.% Alpha] amylase (relative to the dry corn weight), after the temperature of the liquefied 90min under conditions of 88 deg.] C, cooled to 60 ℃ fermentation feedstock obtained;
[0089] (3) 30g of step (2) as a raw material obtained in the fermentation broth, the step (1) seed obtained wet cells was inoculated to the dry cell weight 0.44g / kg broth, was added 0.0325 wt% (with respect to the maize dry weight) of glucoamylase and 0.012 wt% (relative to the dry weight of corn) urea, then the value of pH 4.0, rotation speed of 150 rpm, the fermentation temperature is at 3...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com