Unsupervised domain adaptive method for beneficial feature alignment under class condition
A feature pair, conditional technology, applied in neural learning methods, computer components, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of sub-optimal performance, impact performance, underutilization of class-level distribution differences, etc., and achieve the effect of good domain adaptation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
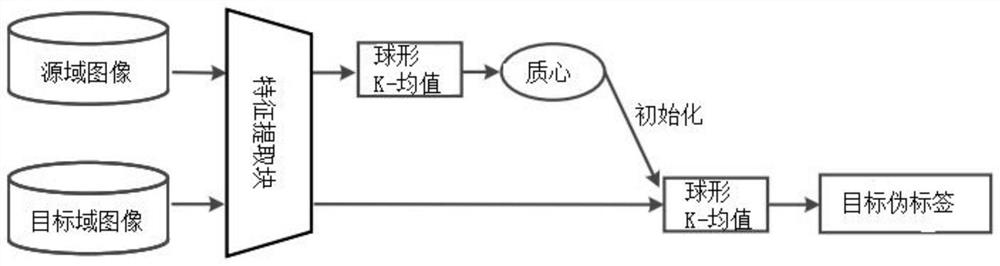
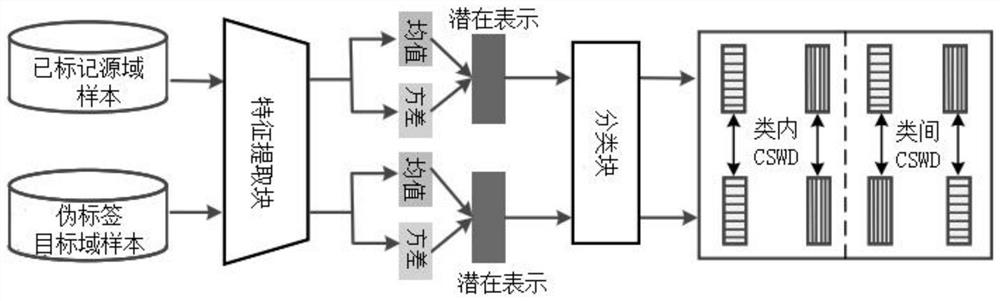
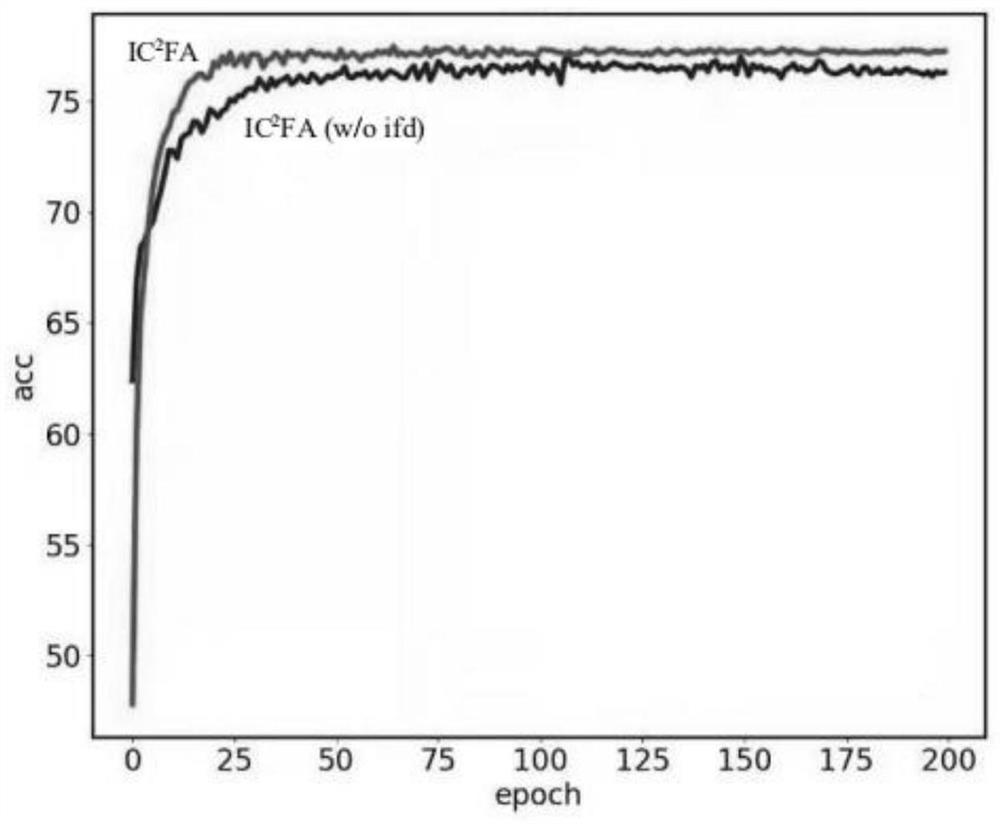
[0038] A framework for unsupervised domain adaptation methods for beneficial feature alignment under class conditions such as figure 1 shown. IC 2 The training of FA consists of two stages, which work alternately. In the first training stage, all source-domain images and target-domain images are applied to compute target pseudo-labels. The second stage consists of two main components, beneficial feature decoupling and discriminative feature alignment, both of which are integrated into a single framework and work together. Specifically include:
[0039] Calculate the source domain image and the target domain image to obtain the pseudo label of the target domain image, the source domain image is a marked image, and the target domain image is an unmarked image;
[0040] Use the variational information bottleneck to decouple the pseudo labels of the source domain image and the target domain image respectively, and obtain the beneficial and transferable features of the source d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com