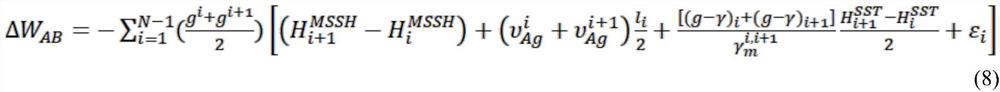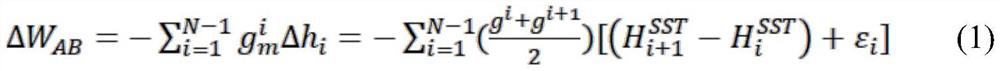Method for calculating gravitational potential difference between sea-crossing elevation points
A calculation method and elevation point technology, which is applied in complex mathematical operations, height/horizontal measurement, satellite radio beacon positioning system, etc., can solve the problem of reducing the accuracy of the calculation results of gravity headroom, and achieve high-precision cross-sea elevation points Gravity potential difference calculation, effect of improving calculation accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
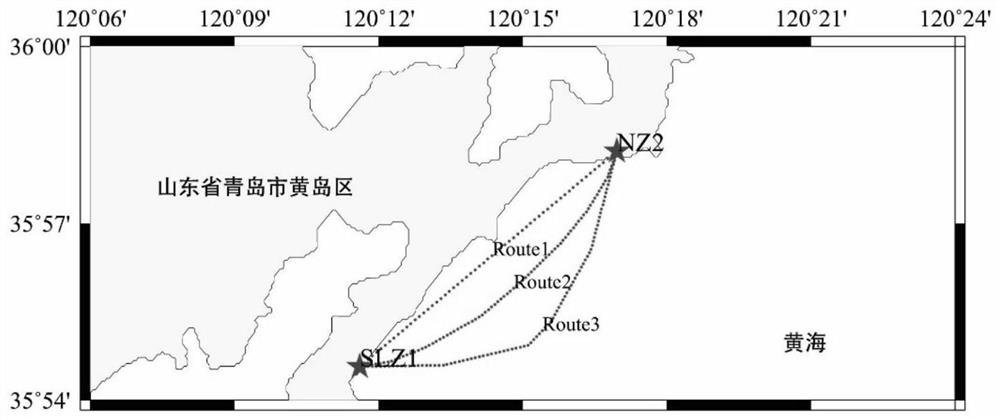
[0087] As shown in the figure, there are two known points SLZ1 and NZ2 along the seaside, about 10.5km from the two points, known the two points of CGCS2000 coordinates and normal high (Table 1), and in these two points Astronomical Ground Vertical Deviation Measurement. One point (SLZ1) is selected as the land known, and the other (NZ2) is analog test in the island to be measured. The experiment was carried out by analog route, and three routes were selected, and the ship measurement gravity data G of I I was measured. i , Use DTU 10 to calculate the gravity abnormal ΔG i Plus normal gravity γ i Simulation get, g i = Γ i + ΔG i
[0088]The average sea surface high by the ship-in-load GNSS line detection point I is obtained by the DTU 10 simulation, and the remaining method is calculated. The number of route measuring points is related to the distance of the measurement section on the route. Three routes are simulated in the test, and the measurement of each route is 0.2km, 0.5km...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com