Self-starting permanent magnet auxiliary synchronous reluctance motor rotor and motor
A technology for assisting synchronous and reluctance motors, applied in the field of motors, can solve problems such as insufficient torque output capacity and small permanent magnet torque, and achieve improved anti-demagnetization ability, increased permanent magnet torque, and increased permanent magnet magnetism. chain effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 2
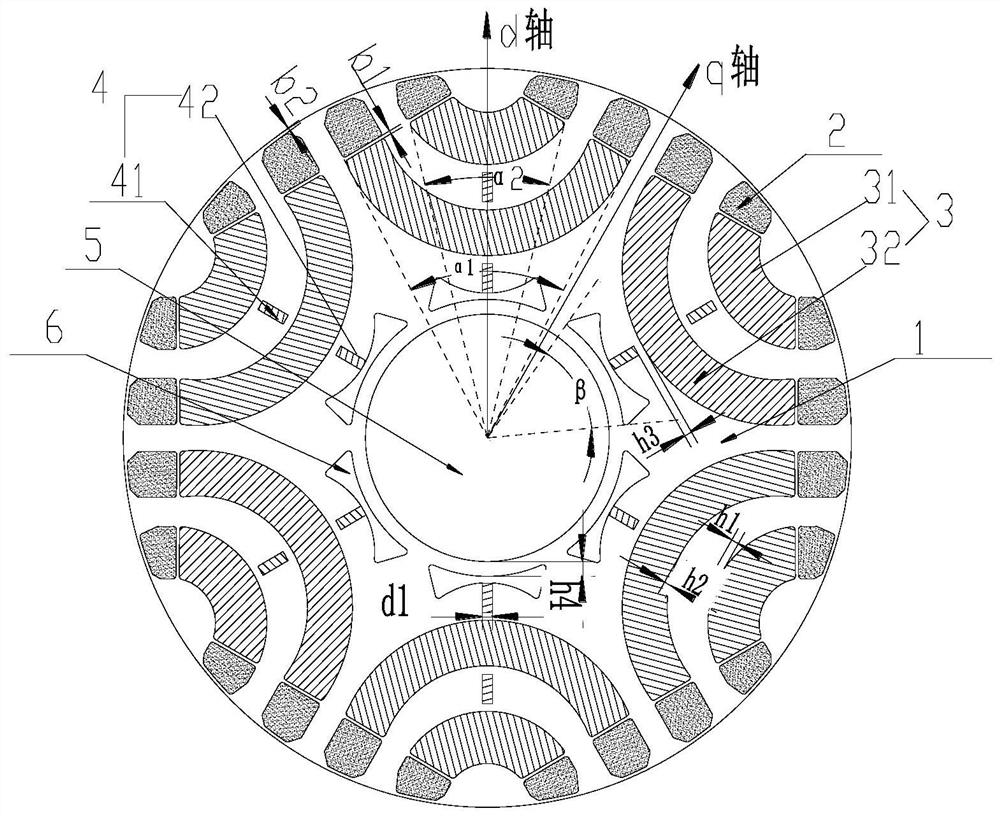
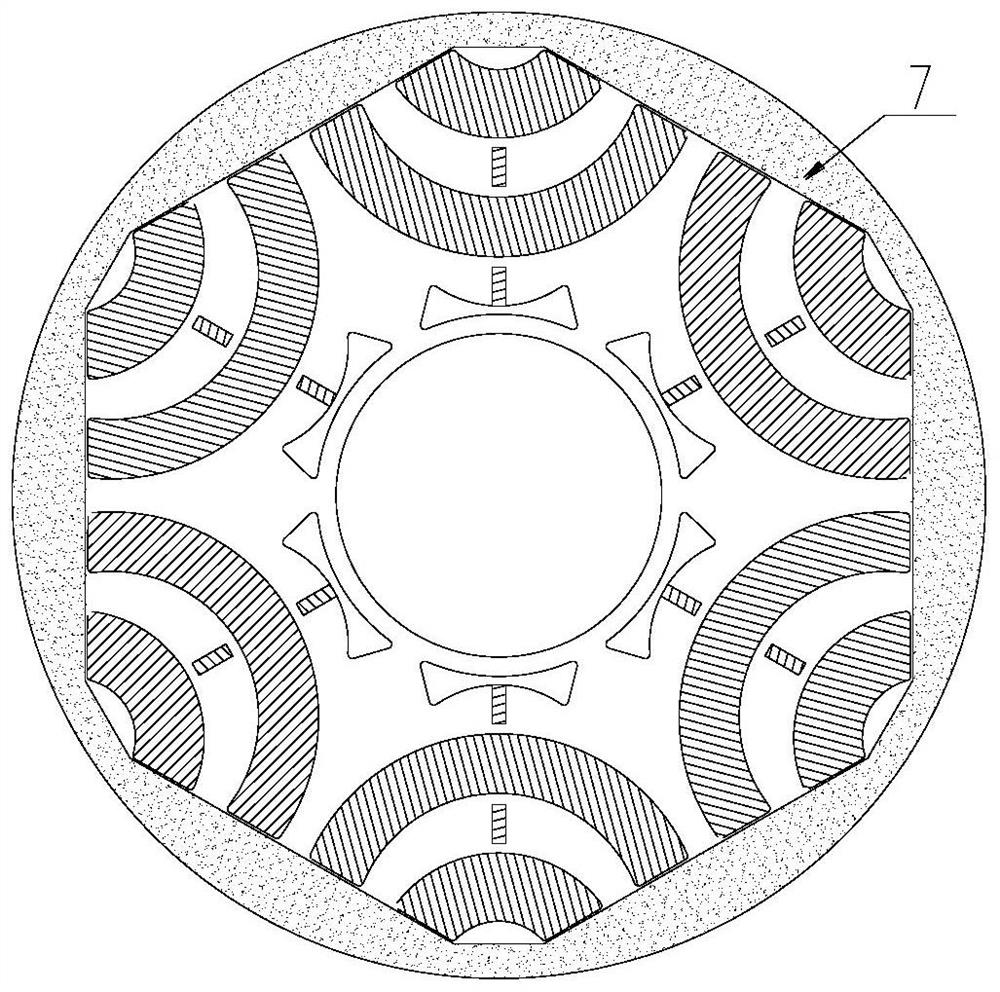
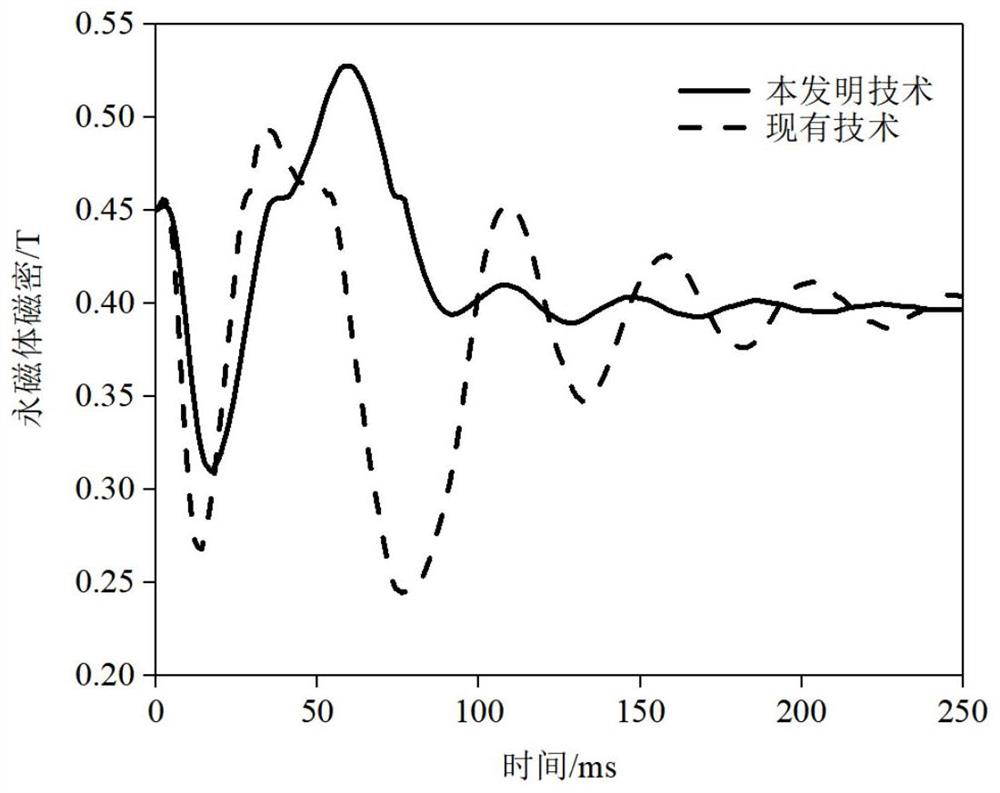
[0074] Figure 4 Shown is a structural diagram of the rotor punching according to the second embodiment of the present invention. As shown in the figure, the NdFeB is only arranged between the ferrite layers. This arrangement can not only increase the flux linkage in the q-axis direction, increase the salient pole ratio, enhance the torque output capability, but also reduce the NdFeB as much as possible. The amount of iron boron is used to reduce material costs; since the inner layer of NdFeB is eliminated, there is no need to open magnetic isolation holes, thereby greatly increasing the safety of the rotor mechanical structure. The rotor structure described can also be used for 2-pole motors or multi-pole motors. Adopting this technical solution can achieve the same technical effect as that of the first embodiment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com