Method for creating autoimmune hepatitis animal model
An autoimmune, animal model technology, applied in the field of creation of autoimmune hepatitis animal models, can solve the atypical characteristics of liver fibrosis, the inability to understand the pathogenesis and molecular mechanism of autoimmune hepatitis more broadly and accurately, and the inability to Issues in understanding and research of autoimmune hepatitis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
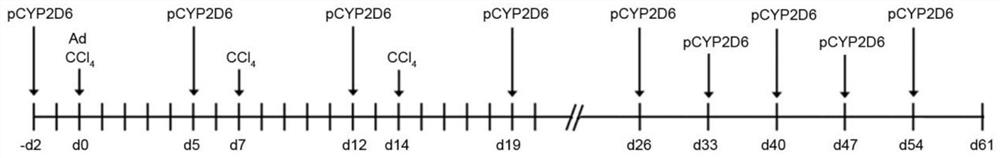
[0093] like figure 1 As shown, a method for creating an autoimmune hepatitis animal model comprises the following steps:
[0094] (1), d0 days, 48 mice were divided into control group and experimental group, wherein:
[0095] The 24 mice in the control group were divided into four groups on average, namely the control group A, the control group B, the control group C and the control group D;
[0096] The 24 mice in the experimental group were divided into four groups on average, namely the test group A, the test group B, the test C group and the test D group;
[0097] The 24 mice in the test group were intraperitoneally injected with CCl 4 , CCl 4 The injection dose is 0.5ml / kg, and
[0098] On day -d2 two days before, 24 mice in the test group were all injected with plasmid CYP2D6 (plasmid CYP2D6 referred to as pCYP2D6) by tail vein at a concentration of 300 μg / time / mouse;
[0099] (2), five days later, on day d5, 24 mice in the test group were injected with plasmid CY...
Embodiment 2
[0135] like figure 1 As shown, a method for creating an autoimmune hepatitis animal model comprises the following steps:
[0136] On days S1 and d0, 48 mice were divided into control group and experimental group, in which:
[0137] The 24 mice in the control group were divided into four groups on average, namely the control group A, the control group B, the control group C and the control group D;
[0138] The 24 mice in the experimental group were divided into four groups on average, namely the test group A, the test group B, the test C group and the test D group;
[0139] The 24 mice in the test group were injected with adenovirus (Ad) through the tail vein, and the injection dose was 2×10 9 pfu, and
[0140] On day -d2 two days before, 24 mice in the test group were all injected with plasmid CYP2D6 (plasmid CYP2D6 referred to as pCYP2D6) by tail vein at a concentration of 300 μg / time / mouse;
[0141] S2. On day d5 after five days, all 24 mice in the test group were injec...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com