Beam failure processing method, terminal and network equipment
A processing method and technology of network equipment, applied in the field of communication, can solve problems such as poor communication performance, and achieve the effect of reducing transmission delay and solving poor communication performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
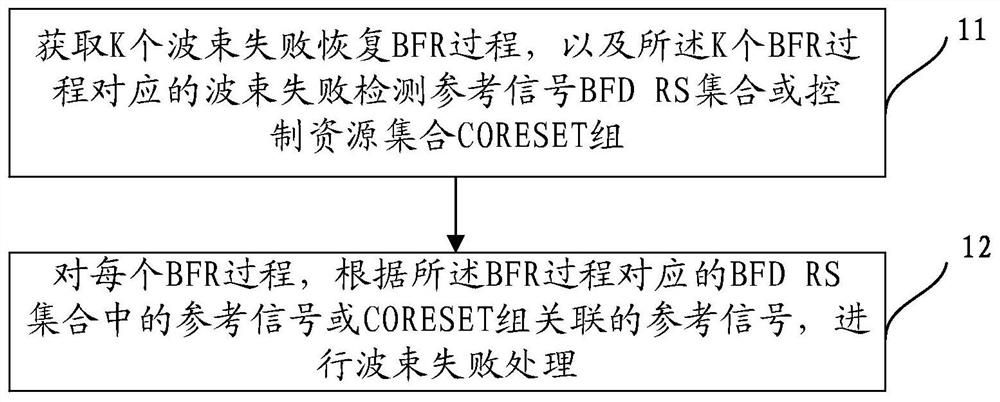
[0368] Embodiment 1: The network device explicitly configures the BFR process and the BFD RS set contained in each BFR.
[0369] The network device explicitly configures K BFR processes for each bandwidth part of each serving cell of the terminal (or K BFR processes for all bandwidth parts), and each BFR process includes a BFD RS set. Wherein, each BFR process may correspond to the transmission of one TRP or multiple TRPs, or the transmission of the entire cell; K is a positive integer.
[0370] For example: all BFR procedures on a serving cell are configured by a BFR procedure list related parameter, such as a beam failure recovery procedure list (BeamFailureRecoveryProcedureList), which contains multiple BFR procedures, and each BFR procedure is configured by a high-level parameter, Such as beam failure recovery procedure (BeamFailureRecoveryProcedure) parameters, each BFR process includes a BFD RS set, such as q0, the corresponding high-level parameters are failure detectio...
Embodiment 2
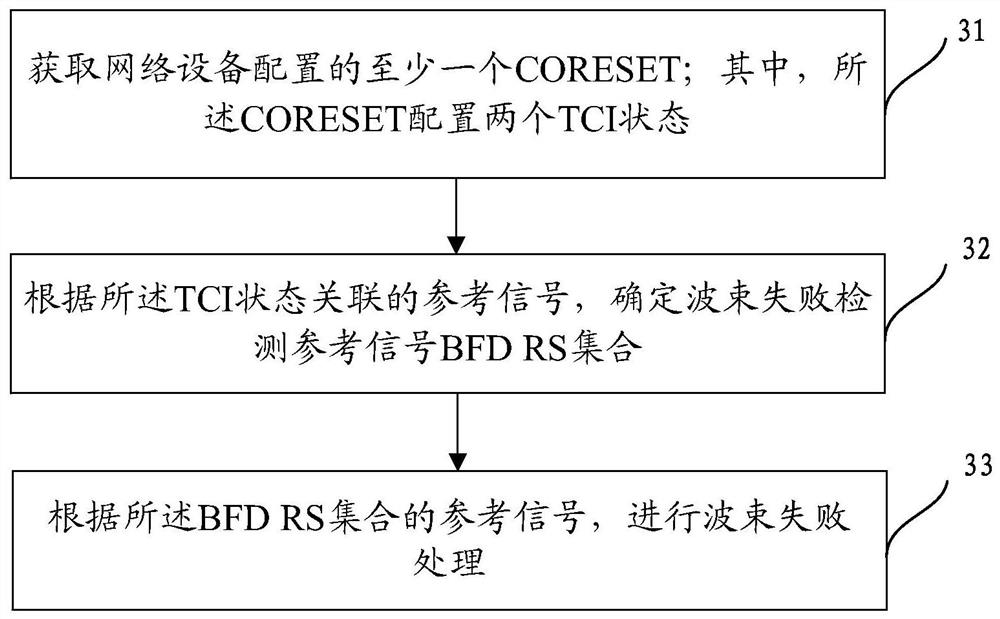
[0387] Embodiment 2: The network device explicitly configures the BFR process and the CORESET group corresponding to each BFR process. Wherein, a CORESET group includes at least one CORESET.
[0388] The network device explicitly configures K BFR processes for each bandwidth part of each serving cell of the terminal (or K BFR processes for all bandwidth parts), and configures a CORESET group for each BFR process, for example, it can be determined by high-level parameters Control resource set list (controlResourceSetList) to represent; wherein, K is a positive integer.
[0389] The CORESET group includes: a CORESET corresponding to one or more CORESET indexes configured by the network device, or a CORESET whose high-level parameter is configured as a specific value, for example, the high-level parameter may be a control resource set pool index (CORESETpoolIndex).
[0390] The specific signaling can be,
[0391] BeamFailureRecoveryProcedure ::= SEQUENCE {
[0392] …
[0393] ...
Embodiment 3
[0414] Embodiment 3: The network device explicitly configures the number of BFR processes, and the terminal determines the corresponding CORESET group for the BFR process in a predefined manner.
[0415] The network device explicitly configures K BFR processes for each bandwidth part of each serving cell of the terminal (or K BFR processes for all bandwidth parts), that is, only the number of BFR processes is configured, and K is a positive integer; the terminal A CORESET group is determined for each BFR process by predefined rules.
[0416] When the terminal detects that the RS associated with the CORESET group corresponding to any BFR process is lower than a certain threshold, it reports the BFR process index, or the CORESET group index or the BFD RS set index to the network device.
[0417] Optionally, predefined rules include but are not limited to the following methods:
[0418] When one BFR process is explicitly configured for each bandwidth part, it can be pre-defined ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com