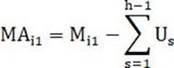Master selection method
A computing device and linear topology technology, applied in the computer field, can solve the problems of waste of power consumption, long distance of computing devices, large delay, etc., and achieve the effect of improving information interaction efficiency, wide utilization value, and minimum delay
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
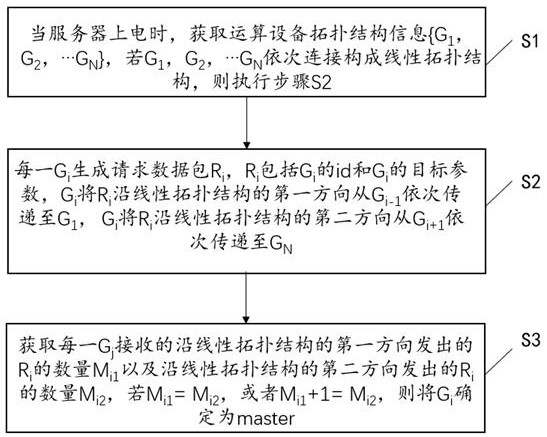
[0015] Embodiment 1 provides a method for selecting a master, which is applied to a scenario where multiple computing devices interact, such as figure 1 shown, including:
[0016] Step S1, when the server is powered on, obtain the computing device topology information {G 1 , G 2 ,…G N }, if G 1 , G 2 ,…G N Connect sequentially to form a linear topology structure, then execute step S2;
[0017] Among them, when the server is powered on, that is, when the server is started, when the computing devices inside the server need to increase, decrease or adjust the topology, the server needs to be shut down, and the number of computing devices needs to be adjusted and then powered on again. The method described in the embodiment can also adaptively determine the optimal master based on the current latest number of computing devices and the topology structure of computing devices. The server is specifically a single server or a cluster composed of multiple servers. The CPU in the...
Embodiment 2
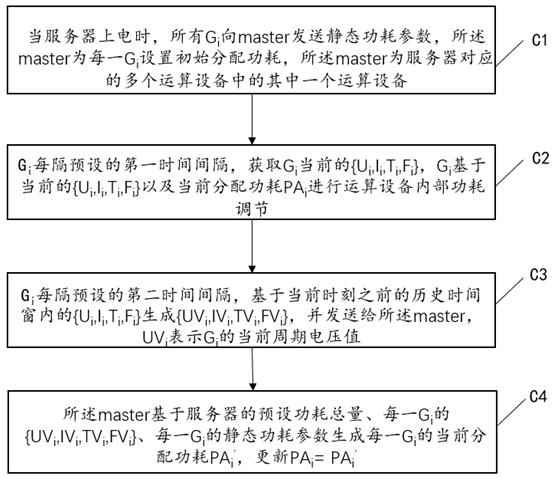
[0048] Embodiment 2 provides a method for allocating power consumption based on multiple computing devices, such as figure 2 shown, including:
[0049] Step C1. When the server is powered on, all G i Send static power consumption parameters to the master, the master is each G i Set the initial allocation power consumption, the master is one of the multiple computing devices corresponding to the server, G i is the i-th computing device in the server, the value of i ranges from 1 to N, and N is the total number of computing devices in the server;
[0050] where the initial allocated power can be based on G i The static power consumption parameters of the server and the total power consumption of the server can be directly allocated, or the default value can be set directly. Since the master can be quickly determined after power-on, the process of dynamically allocating power consumption will soon enter. Therefore, set a reasonable initial value. Allocate the power consumpti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com