Power consumption dispatching method for refrigerator body foaming constant-temperature unit
A scheduling method and constant temperature technology, which is applied in the field of electricity scheduling of refrigerator box foaming constant temperature units, can solve the problems of power matching waste and reduce the safety of power consumption, and achieve the effect of improving safety and avoiding waste
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
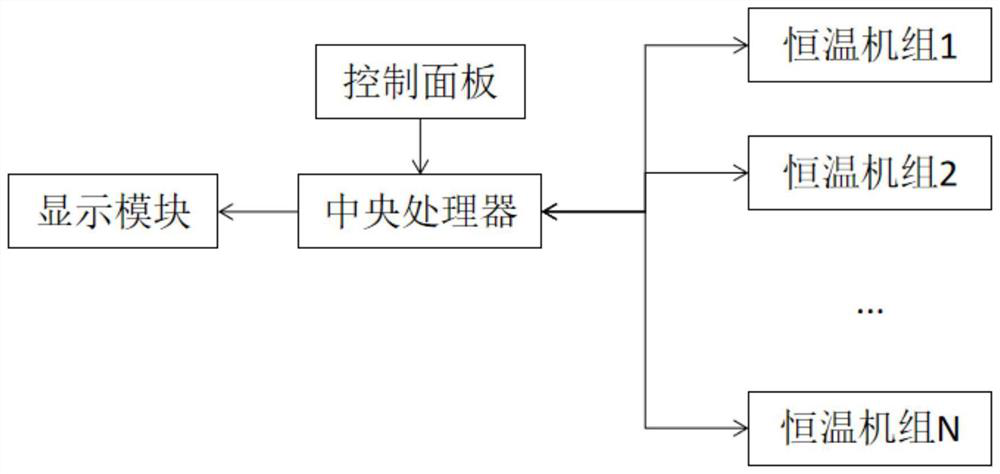
[0025] see figure 1 As shown, the present invention is a method for dispatching electricity for a refrigerator box foaming thermostatic unit, including a dispatching system; the dispatching system includes a central processing unit and a thermostatic unit; the central processing unit and the thermostatic unit are electrically connected;
[0026] The central processing unit is also electrically connected with a control panel and a display module, and the control panel transmits control instructions to the central processing unit; the display module adopts an LED display screen, and the display module displays the temperature data of the thermostatic unit received by the central processing unit;
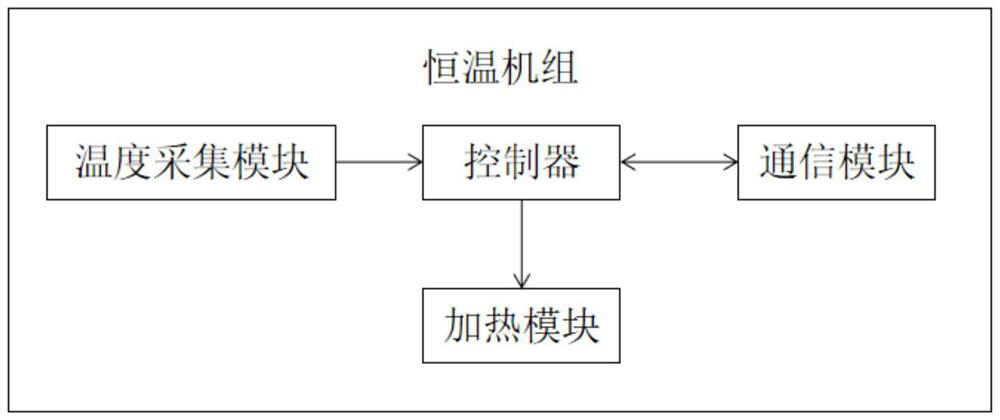
[0027] The thermostatic unit includes a controller, a temperature sensor, a heating module and a communication module. The controller is electrically connected to the temperature sensor, the heating module and the communication module respectively; the controller exchanges information w...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Embodiment 2: Based on Embodiment 1
[0029] This embodiment is a method for dispatching electricity for a refrigerator box foaming and constant temperature unit, and the dispatching system operates according to the following steps:
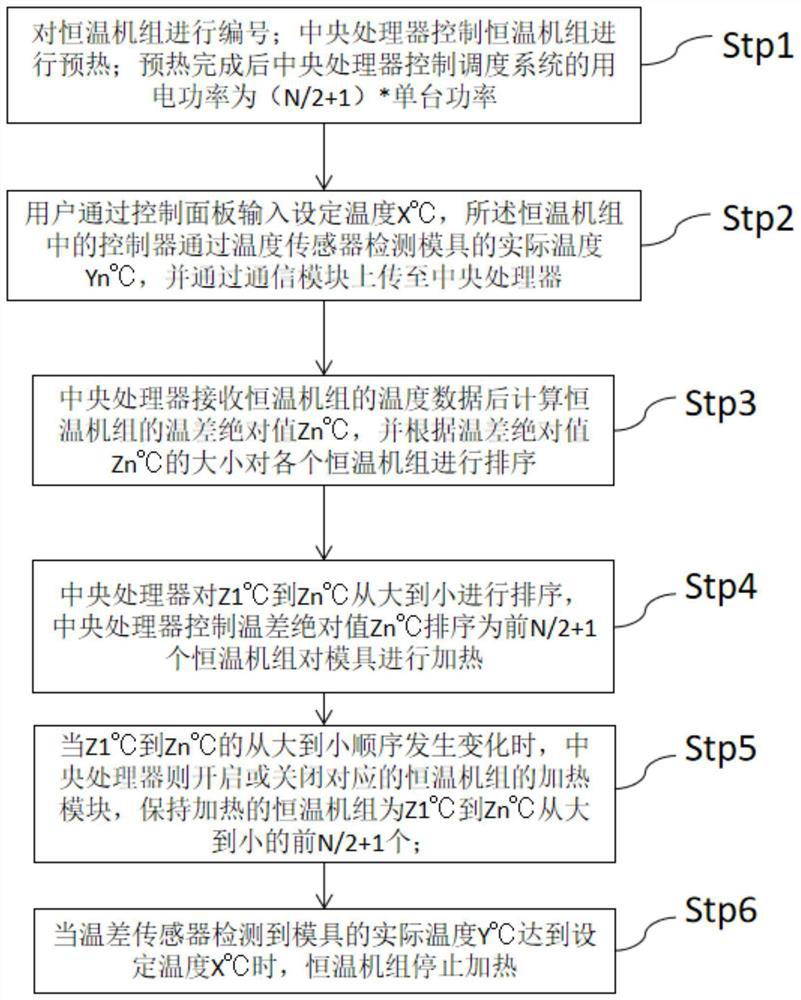
[0030] Stp1. Number the thermostatic unit; the central processor controls the thermostatic unit to preheat; the preheating time is 30-60min; after the preheating is completed, the power consumption of the central processor control scheduling system is (N / 2+1)*single unit Power, N is the number of constant temperature units, when N is an odd number, N / 2 is rounded up to 1;
[0031] Stp2. The user inputs the set temperature X°C through the control panel, and the range of the set temperature X°C is 30-60°C; the controller in the constant temperature unit detects the actual temperature Y°C of the mold through the temperature sensor, and uploads it to the center through the communication module processor;
[0032] Stp3. After receiving the te...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com