Waste storage device
a technology for storage devices and receptacles, which is applied in the field of receptacles with receptacles, can solve the problems of inconvenient location of receptacles in a remote location, inconvenient use, and general unsatisfactory results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
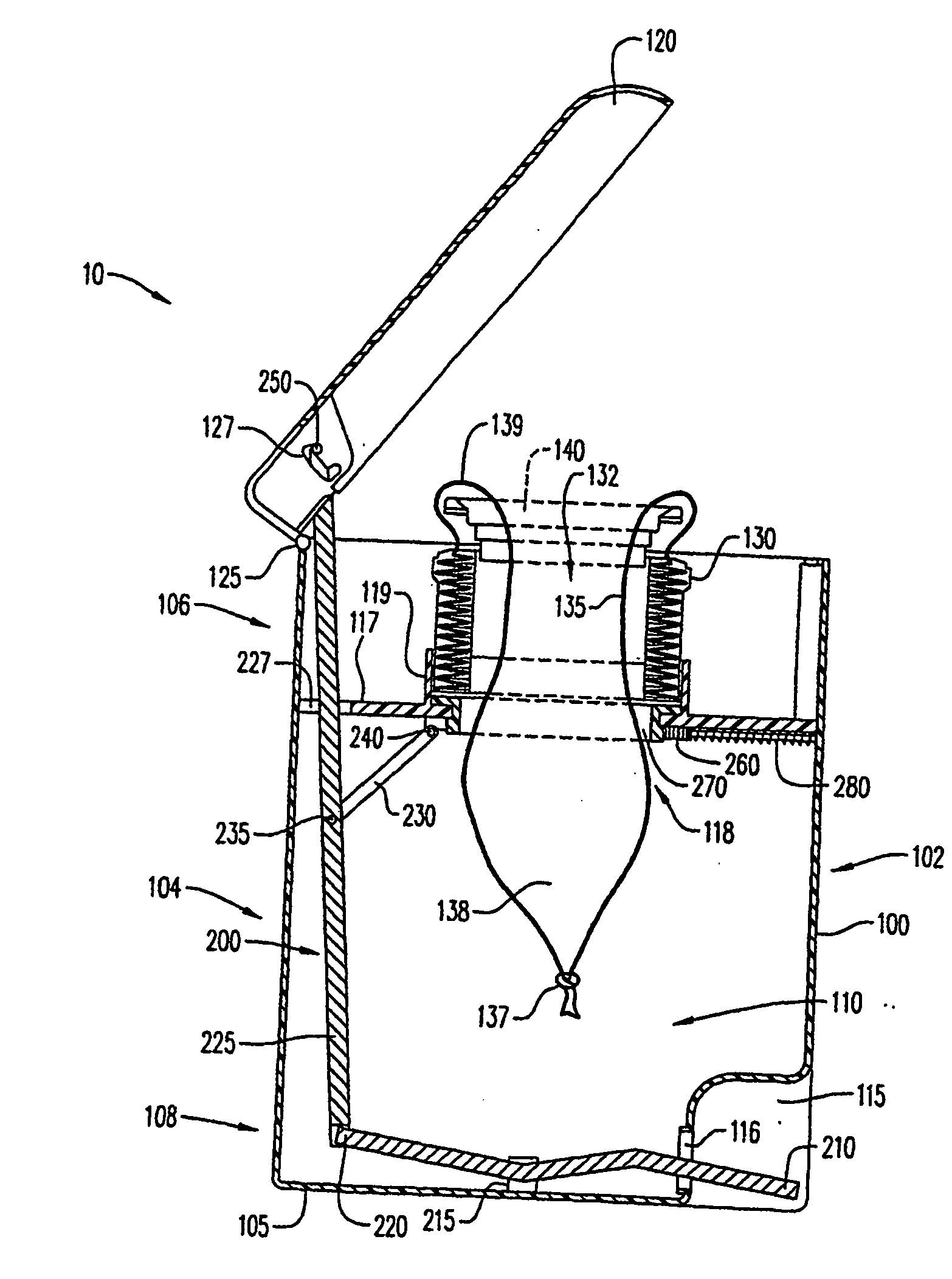
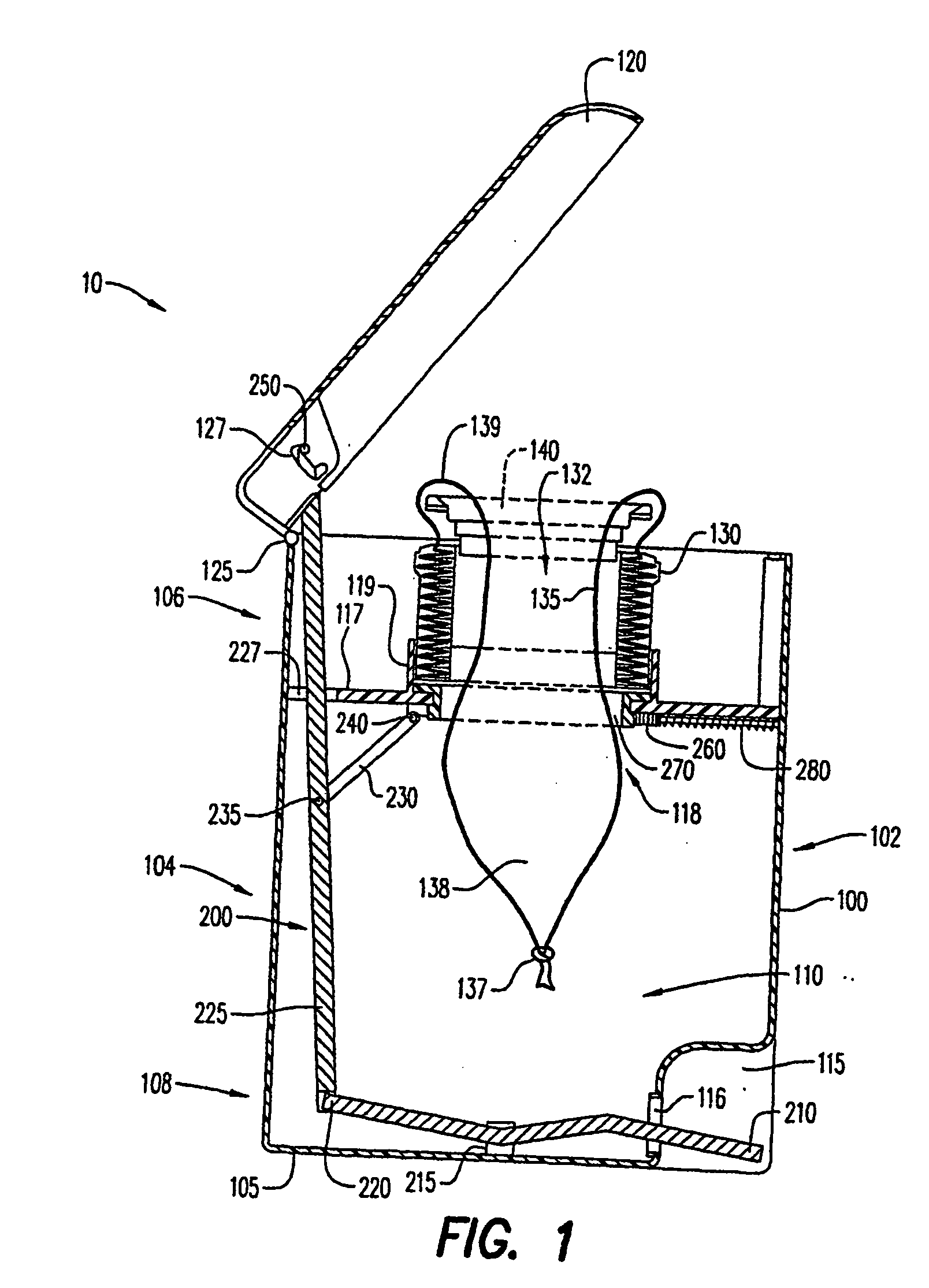
[0091] Referring to FIG. 1, there is shown an embodiment of a waste storage device having the sealing mechanism of the present invention, generally represented by reference numeral 10.
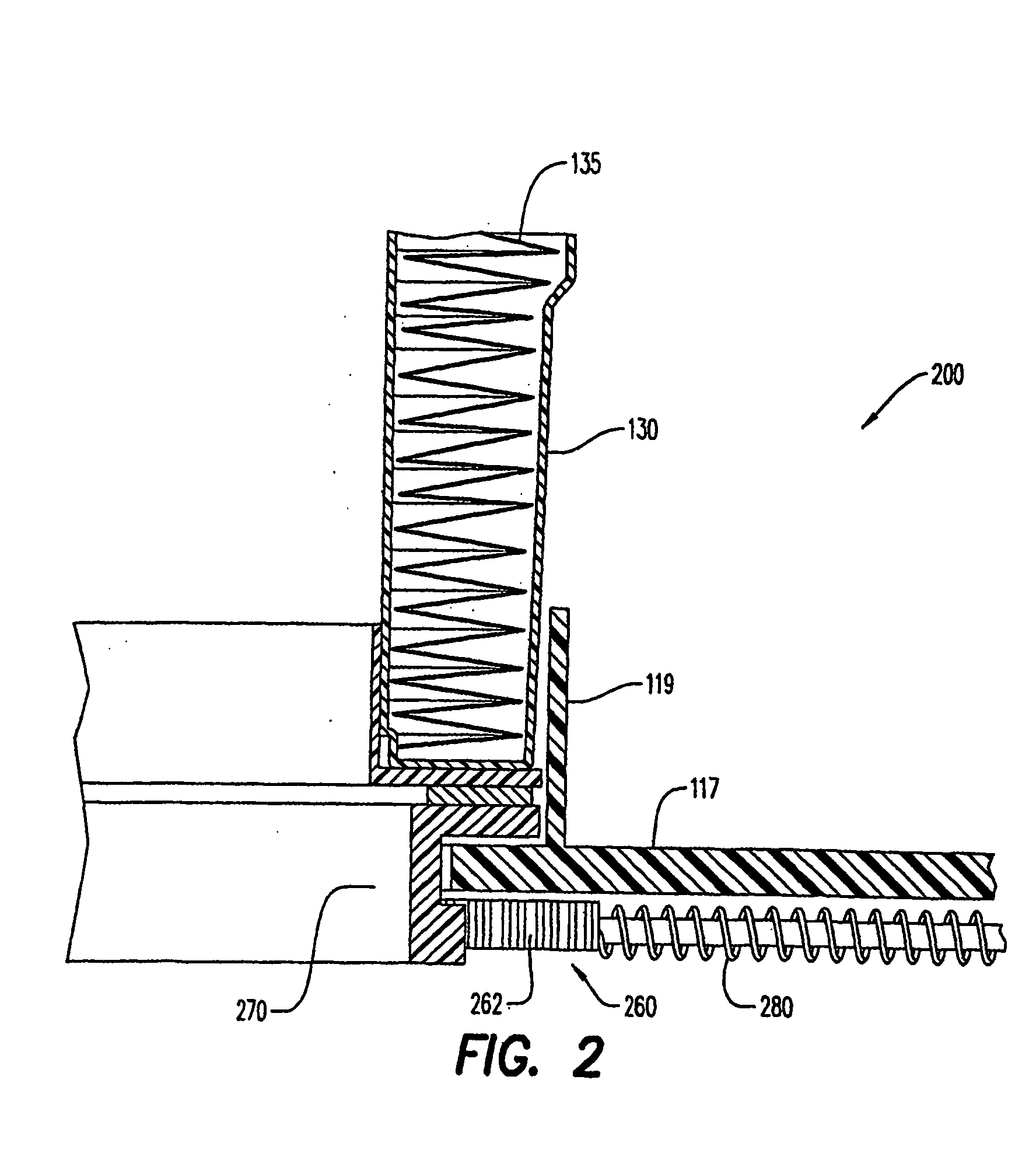
[0092] Waste storage device 10 has a body 100, a lid 120, a storage film cassette 130, a film ring 140 and a sealing mechanism 200. Body 100 has a base 105, an inner volume 110, front and rear portions 102, 104, and upper and lower portions 106, 108. Body 100 is substantially cylindrical in shape to maximize inner volume 110. However, alternative shapes for body 100 can also be used including rectangular or cubical. Lower portion 108 of body 100 has an indentation or pedal housing 115 that will be described later in greater detail. Preferably, pedal housing 115 is positioned along front portion 102.
[0093] Lid 120 is substantially cylindrical in shape and has a diameter substantially the same size as the diameter of body 100 to provide a sealing engagement of the lid with the body along upper portion ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| flexible | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com