Method and apparatus for controlling the common mode impedance misbalance of an isolated sigle-ended circuit
A common-mode impedance and circuit technology, applied in the direction of amplifier input/output impedance improvement, amplifiers with semiconductor devices/discharge tubes, electrical components, etc., can solve common-mode current reduction, common-mode current imbalance, and common-mode impedance increase And other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
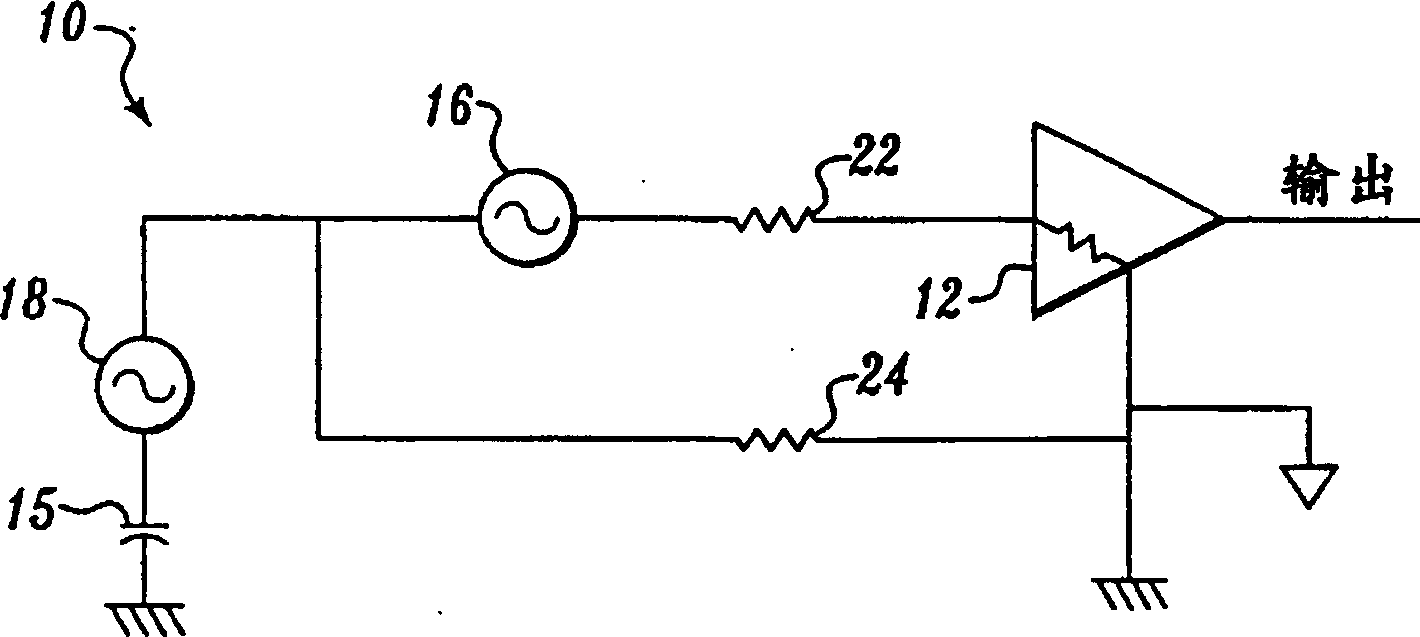
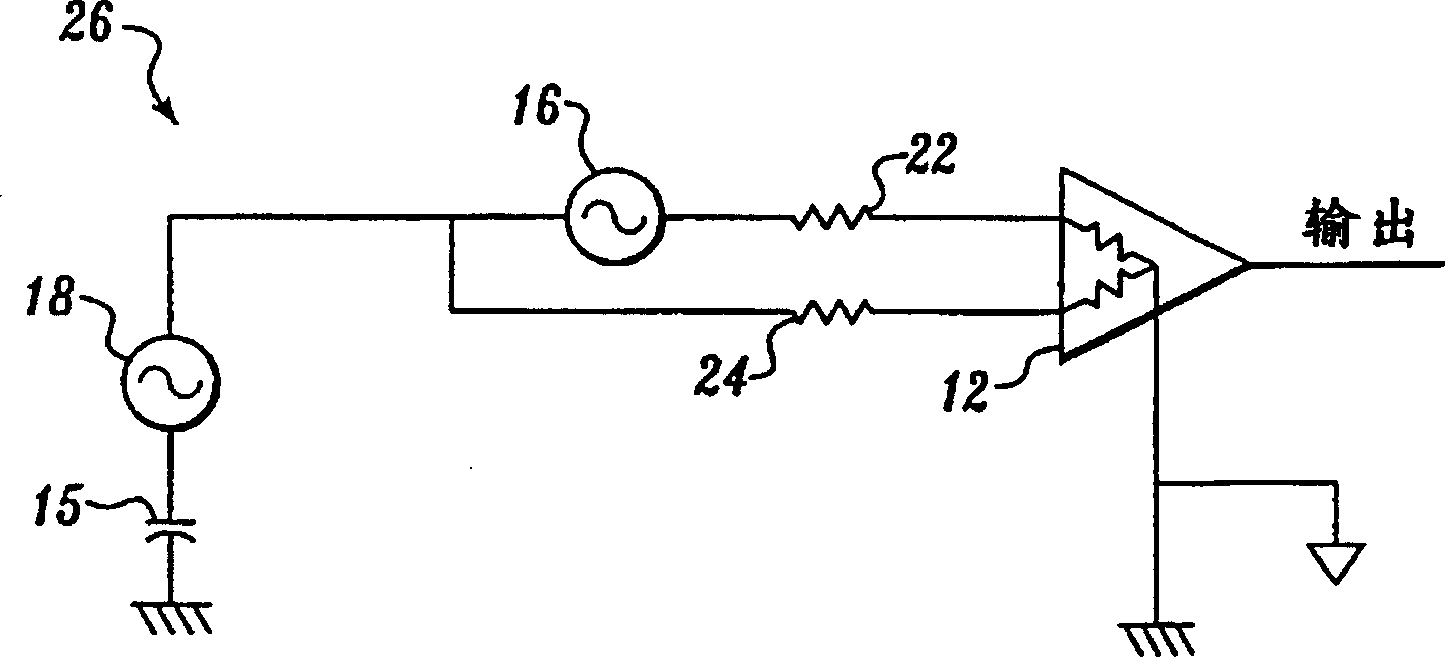
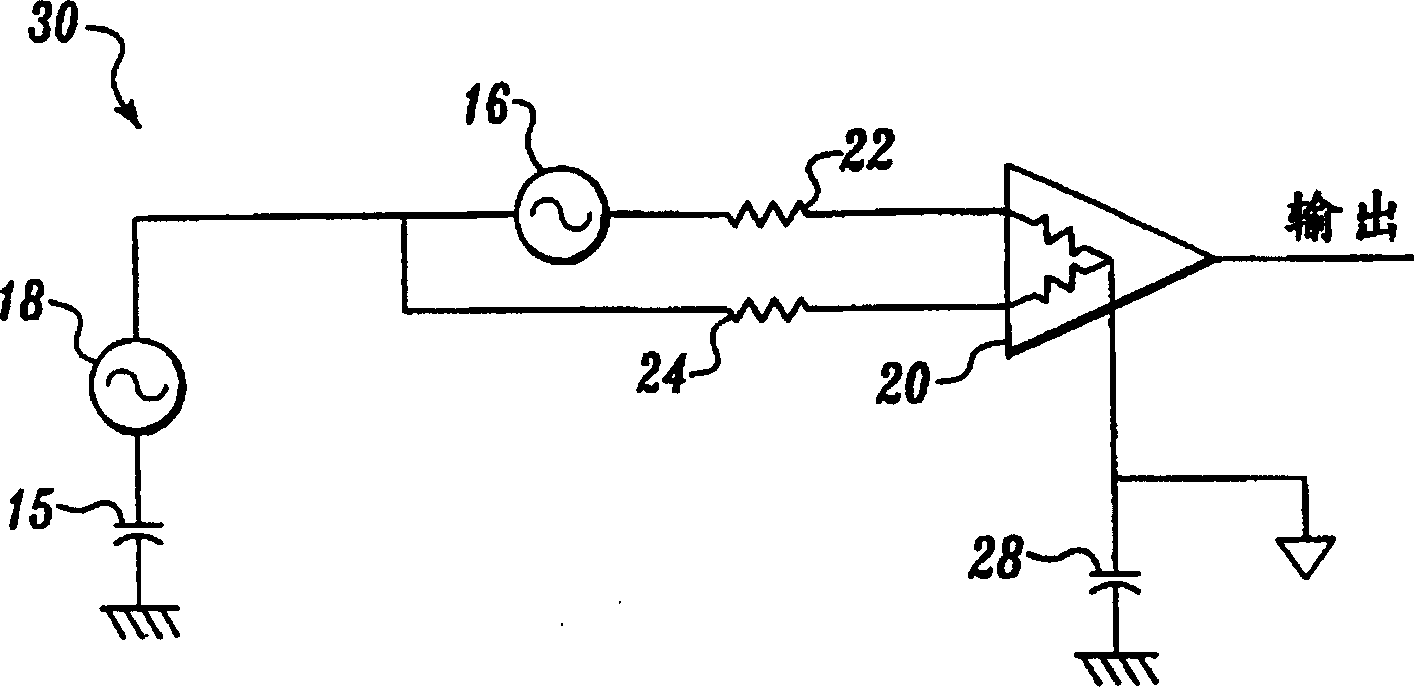
[0043] Figure 2A and 2B The described embodiment works by matching the discrete capacitors to the parasitic capacitance formed between the shield and the ground plane or with the internal shield. exist Figure 2A 34 is provided with a physical "outer" shield 42 enclosing an "inner" physical shield 46A, which in turn encloses amplifier 26. One end of a noise source 18 is coupled to a capacitor 15 representing a parasitic capacitance between ground ground and the noise source. The other end of noise source 18 is coupled in parallel at terminal A to one end of a resistive lead (represented by resistor 22 ) and one end of another resistive lead (represented by resistor 24 ). The other end of resistor 22 is coupled to the input of amplifier 26, and the other end of resistor 24 is coupled to the reference of amplifier 26, which reference is also circuit ground. Additionally, a small signal for amplification is provided by a small signal source (not shown) interposed between resis...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com