Computational processor
A computing processing device and technology for computing data, which are applied in the fields of electrical digital data processing, digital data processing components, computing, etc., and can solve the problems such as the inability to realize cheap portable terminals, the inability to be monolithic, and the increase in cost.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
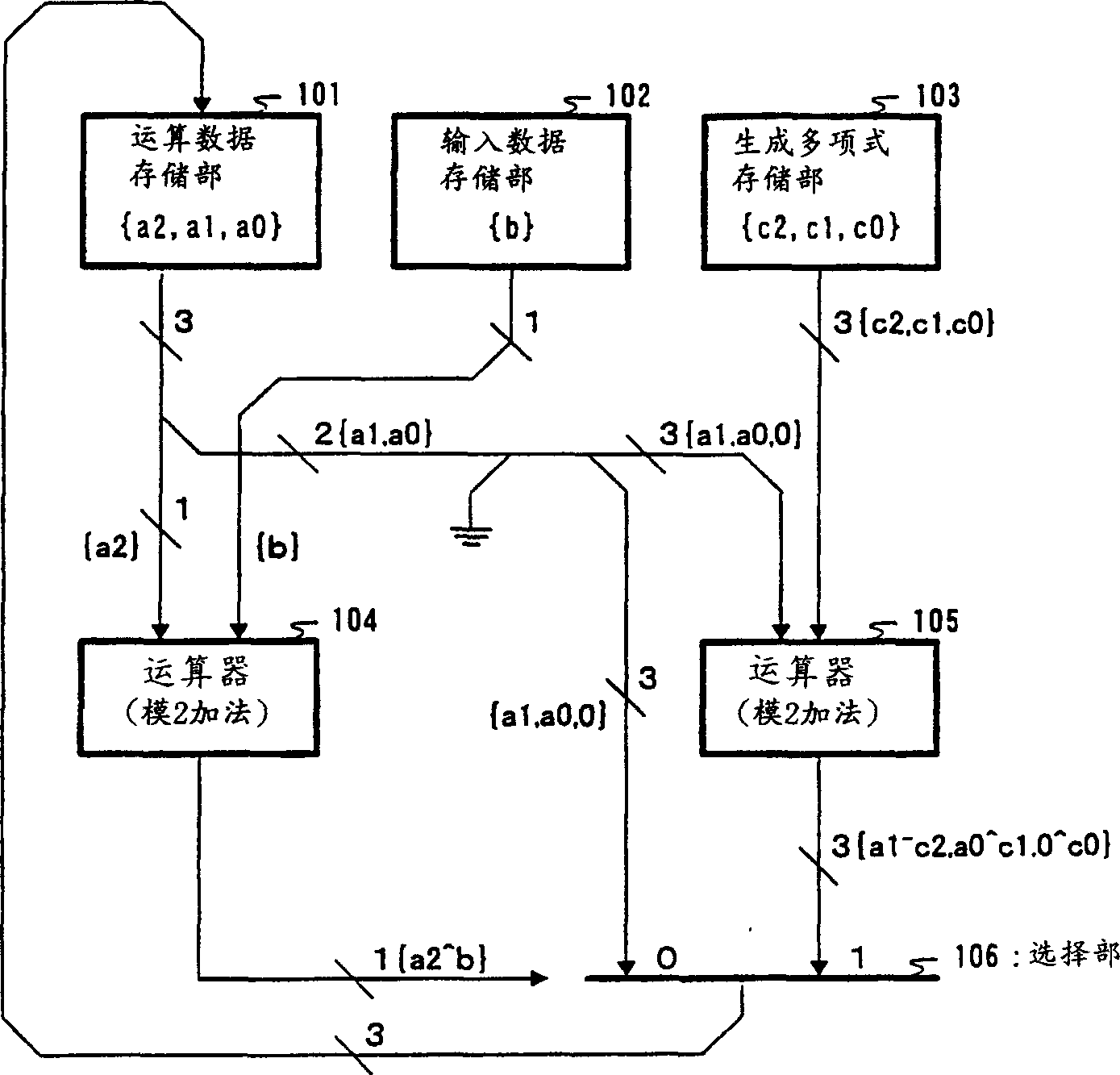
[0035] figure 2 is a block diagram showing the configuration of the arithmetic processing device of this embodiment.
[0036] exist figure 2 Among them, it mainly includes: operation data storage unit 101, which stores operation data; input data storage unit 102, which stores input data; generator polynomial storage unit 103, which stores coefficients of generator polynomial; arithmetic units 104, 105, carry out modulo 2 addition; and select The unit 106 outputs either one of the two input data.
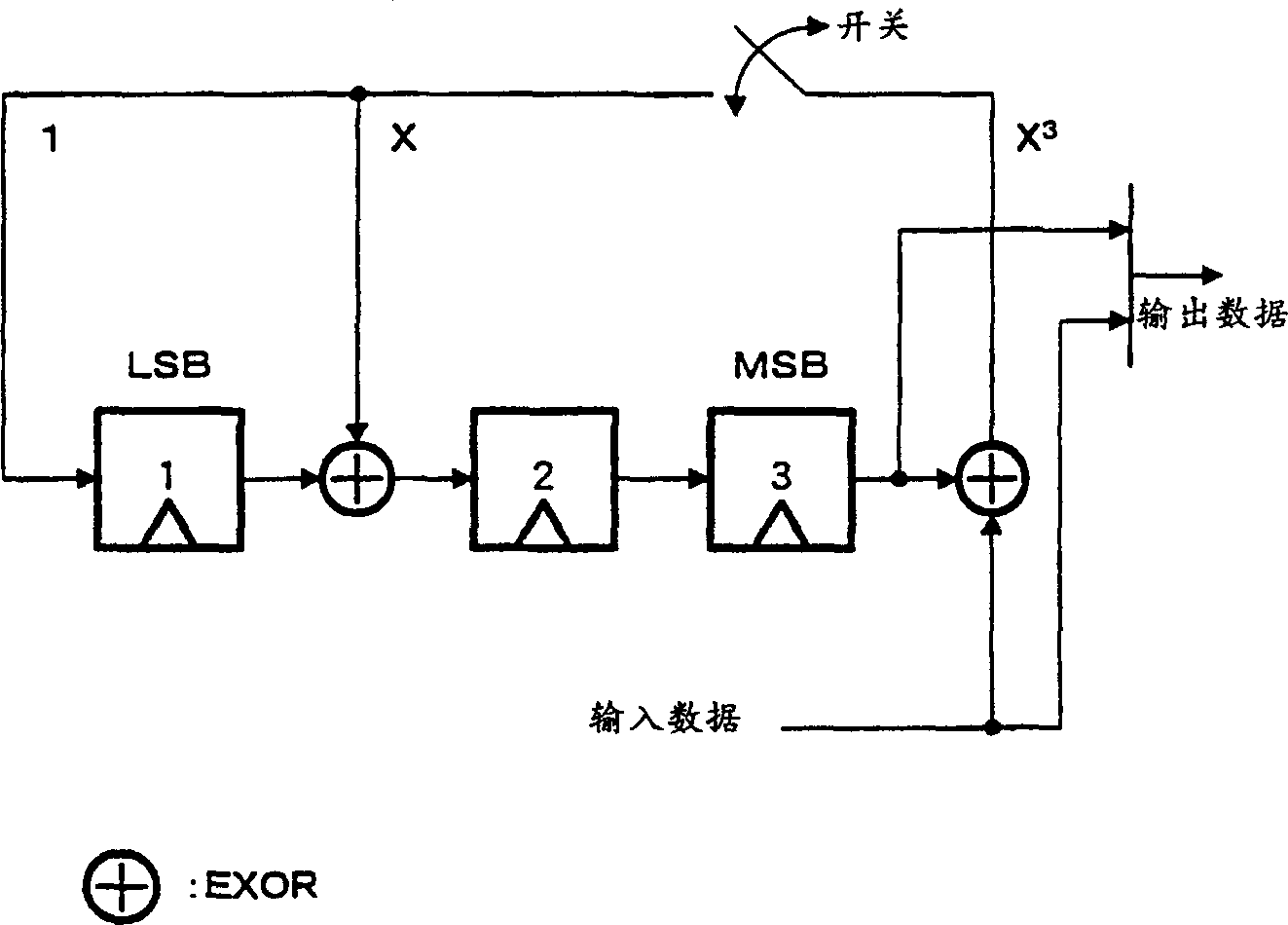
[0037] Hereinafter, a case of a 3-bit CRC will be taken as an example to specifically describe the processing performed by each component.
[0038] In the case of an N-bit CRC, the operation data storage unit 101 and the generator polynomial storage unit 103 need to be composed of at least N bits, and the arithmetic unit 105 needs to be able to perform at least N-bit modulo 2 addition. For example, in the case of a 3-bit CRC, the operation data storage unit 101 and the generator...
Embodiment 2
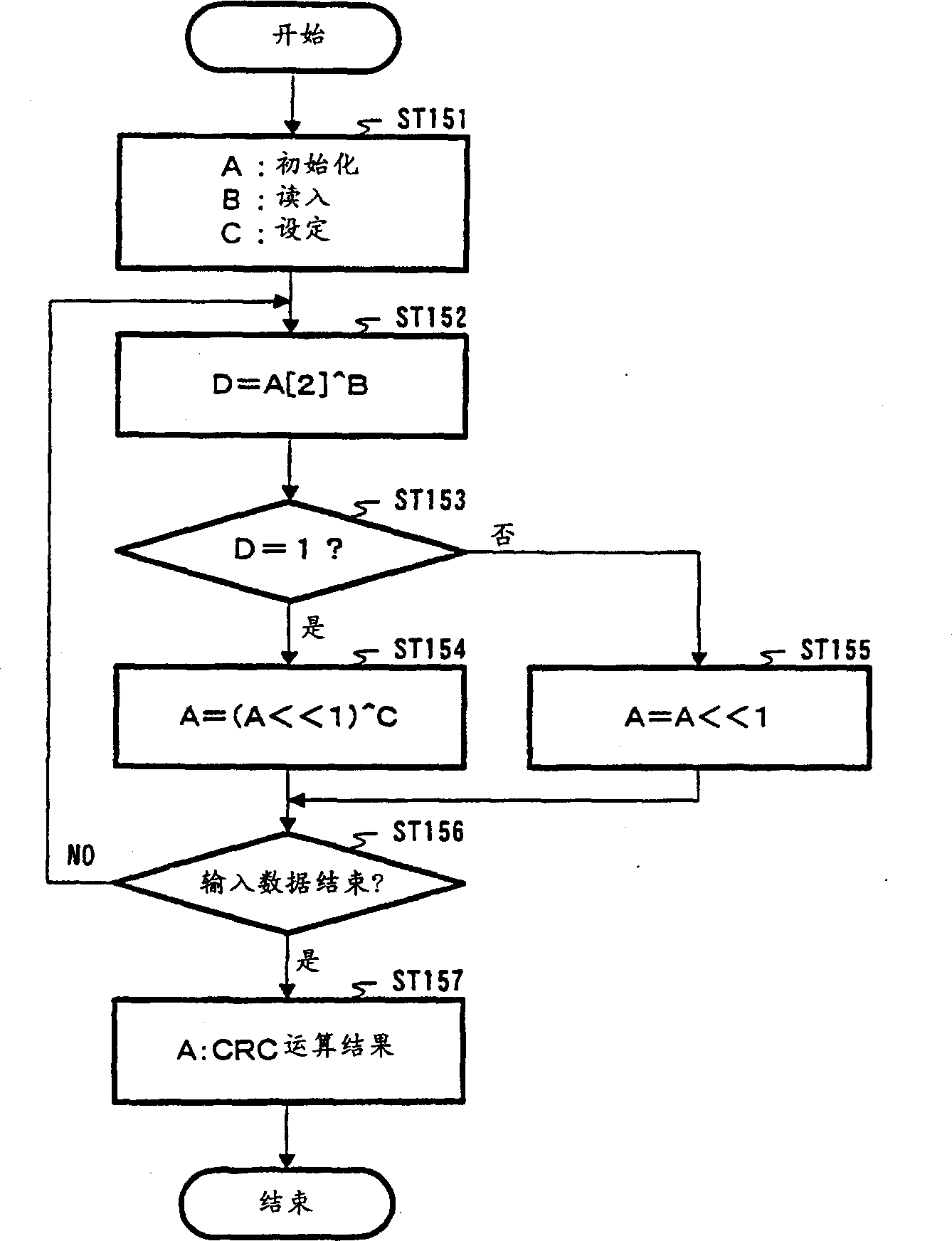
[0052] Figure 4 is a block diagram showing the configuration of the arithmetic processing device of this embodiment. exist Figure 4 in, right with figure 2 The same components are appended with figure 2 The same reference numerals are used, and descriptions thereof are omitted.
[0053] Figure 4 The arithmetic processing device shown with the figure 2 Compared with the arithmetic processing device shown, the configuration in which the arithmetic units 104 and 105 are replaced by the addition of selection units 201 and 202 , the arithmetic unit 203 and the arithmetic result storage unit 204 is employed.
[0054] Figure 4 The arithmetic processing device shown is carried out with arithmetic unit 203 figure 2 In the processing of the two arithmetic units 104 and 105 in the shown arithmetic processing device, a CRC operation is performed for each bit in two machine cycles. The selection unit 201 and the selection unit 202 switch the data input to the arithmetic uni...
Embodiment 3
[0062] Figure 5 is a block diagram showing the configuration of the arithmetic processing device of this embodiment. exist Figure 5 in, right with figure 2 The same components are appended with figure 2 The same reference numerals are used, and descriptions thereof are omitted.
[0063] Figure 5 The arithmetic processing device shown with the figure 2 Compared with the arithmetic processing device shown, the arithmetic unit 301 is added instead of the arithmetic units 104 and 105 .
[0064] Figure 5 The arithmetic processing device shown is carried out by using the arithmetic unit 301 figure 2 In the processing of the two arithmetic units 104 and 105 in the arithmetic processing device shown, two types of data are merged and then operated, and the CRC operation is performed for each bit in one machine cycle.
[0065] Hereinafter, a case of a 3-bit CRC will be taken as an example to specifically describe the processing performed by each component.
[0066] In t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com