Method for positioning up branch signal multi-frame and pointer
A pointer positioning and pointer position technology, which is applied in multiplexing communication, time division multiplexing systems, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of large logic and inappropriate cost performance of FPGA chips, and achieve the effect of reducing logic consumption.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0028] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
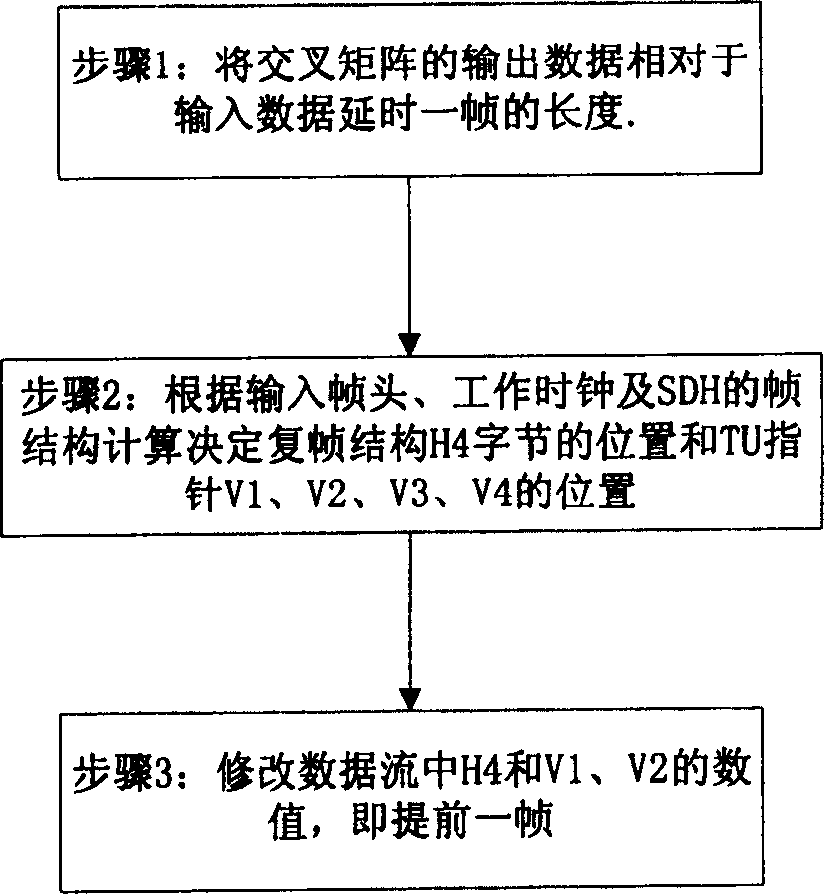
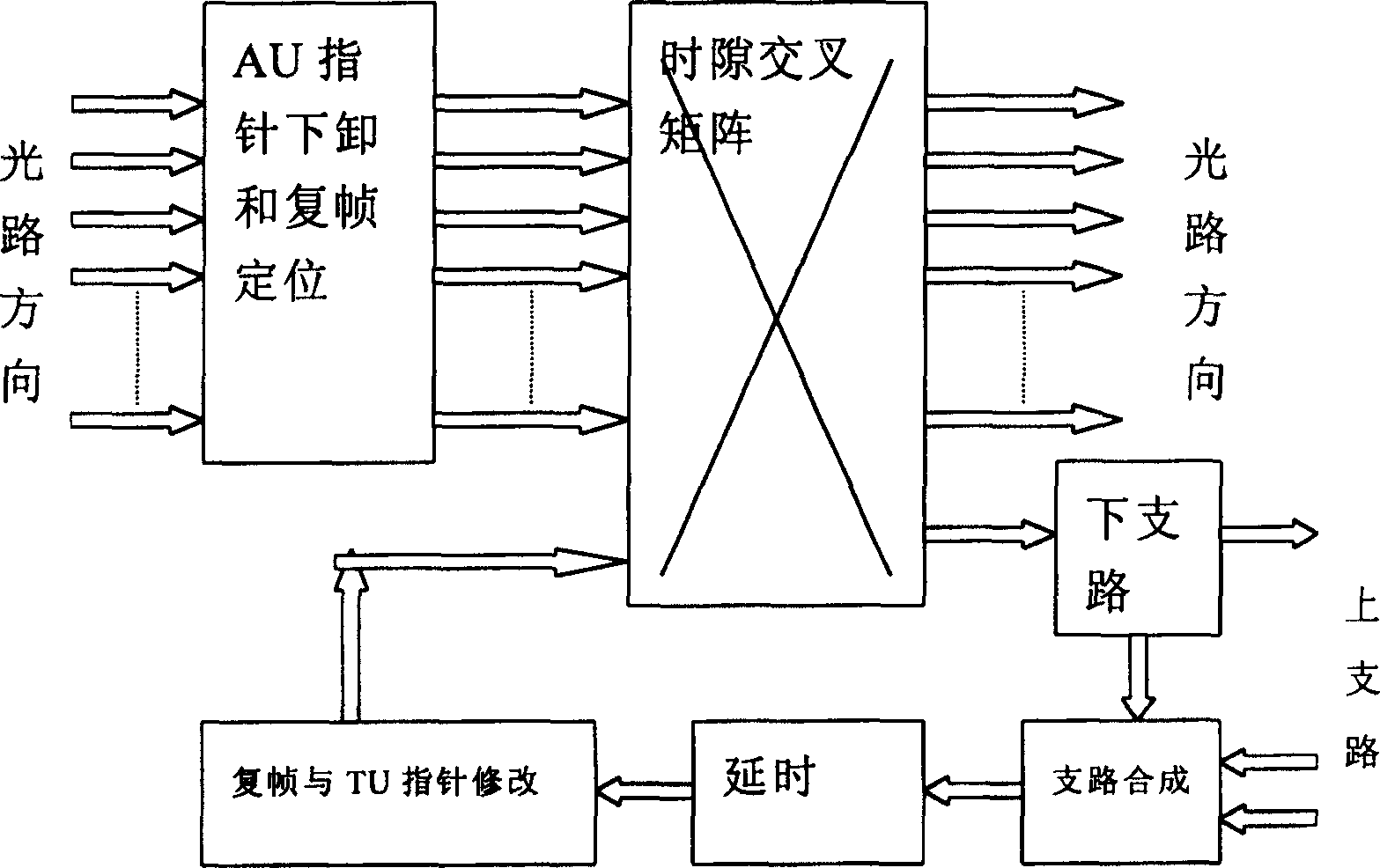
[0029] Such as figure 1 Shown, method of the present invention comprises the following steps at least:
[0030] Step 1: Delay the output data of the cross matrix relative to the input data by one frame length;
[0031] Step 2: Calculate and determine the position of the H4 byte of the multiframe structure and the positions of the TU pointers V1, V2, V3, and V4 according to the frame structure calculation of the input frame header, working clock and SDH;
[0032] Step 3: Modify the values of H4, V1, and V2 in the data stream, that is, one frame ahead, including: modifying the multiframe, modifying the position and value of the TU pointer.
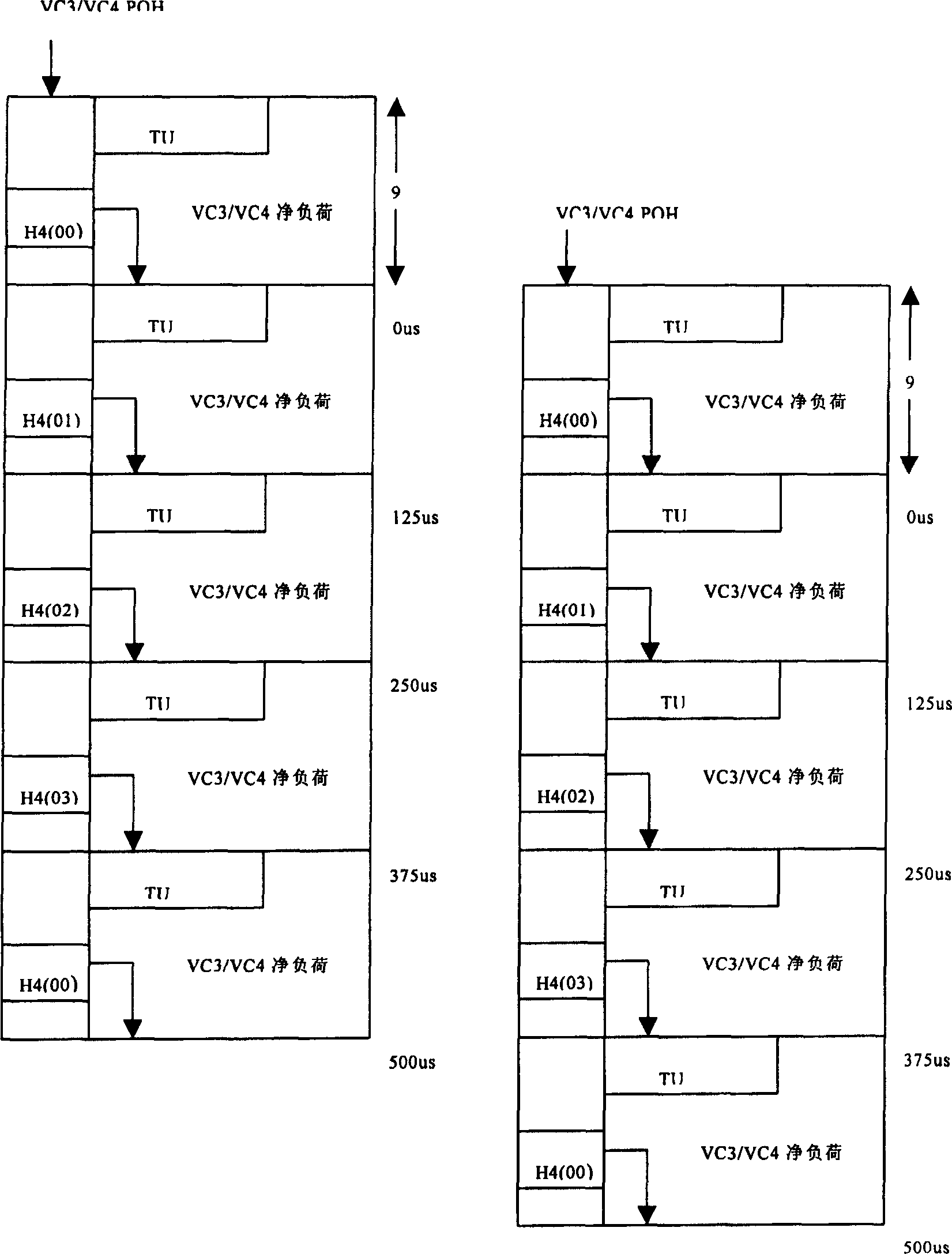
[0033] Such as figure 2 As shown, the signal multiframe and TU pointer after one frame delay are one frame behind the signal before the delay. Therefore, in order to have the same multiframe ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com