Artificial combined antibacterial engineering polypeptide and its preparation method
An engineering and artificial technology, applied in the field of artificially combined antibacterial engineering polypeptides and its preparation, can solve problems such as slow progress
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
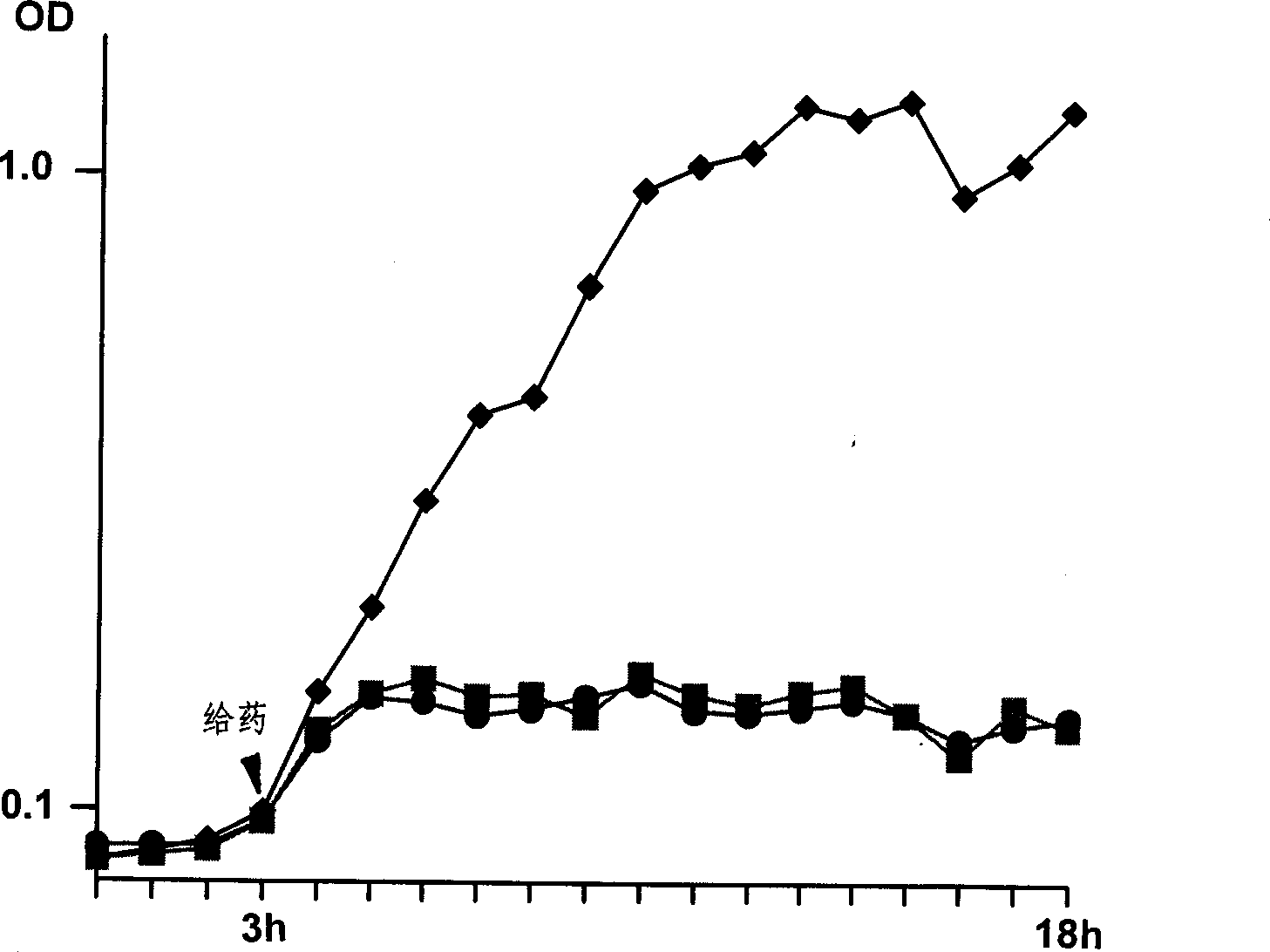
[0015] In this example, the Agr D signaling polypeptide of Staphylococcus aureus is linked to the carboxyl terminus of colistin Ia to prepare a plasmid for artificially combining anti-Staphylococcus aureus engineering polypeptide, and the mutated plasmid is transfected into In engineering bacteria with plasmids, multiply the bacteria in large quantities (4L FAB, 225rpm, 37°C, 6h), centrifuge and precipitate the bacteria (4°C, 6000g, 20min), take 4°C, 50mM boric acid buffer + 2mM EDTA + 2mM DTT 50 -80ml suspended cells, sonicate (4°C, 40W, 1-2min), high-speed centrifuge to crush the cells (4°C, 50000-70000g, 1.5h), take the supernatant and add streptomycin sulfate to precipitate DNA, 4°C, 50mM boric acid buffer + 2mM EDTA + 2mMDTT 2L dialyzed overnight, the supernatant was loaded on a CM ion exchange column, eluted at 4°C with 0.3M NaCl + 50 mM boric acid buffer to obtain an anti-Staphylococcus aureus engineering polypeptide, the molecular weight 63,000. In order to confirm th...
Embodiment 2
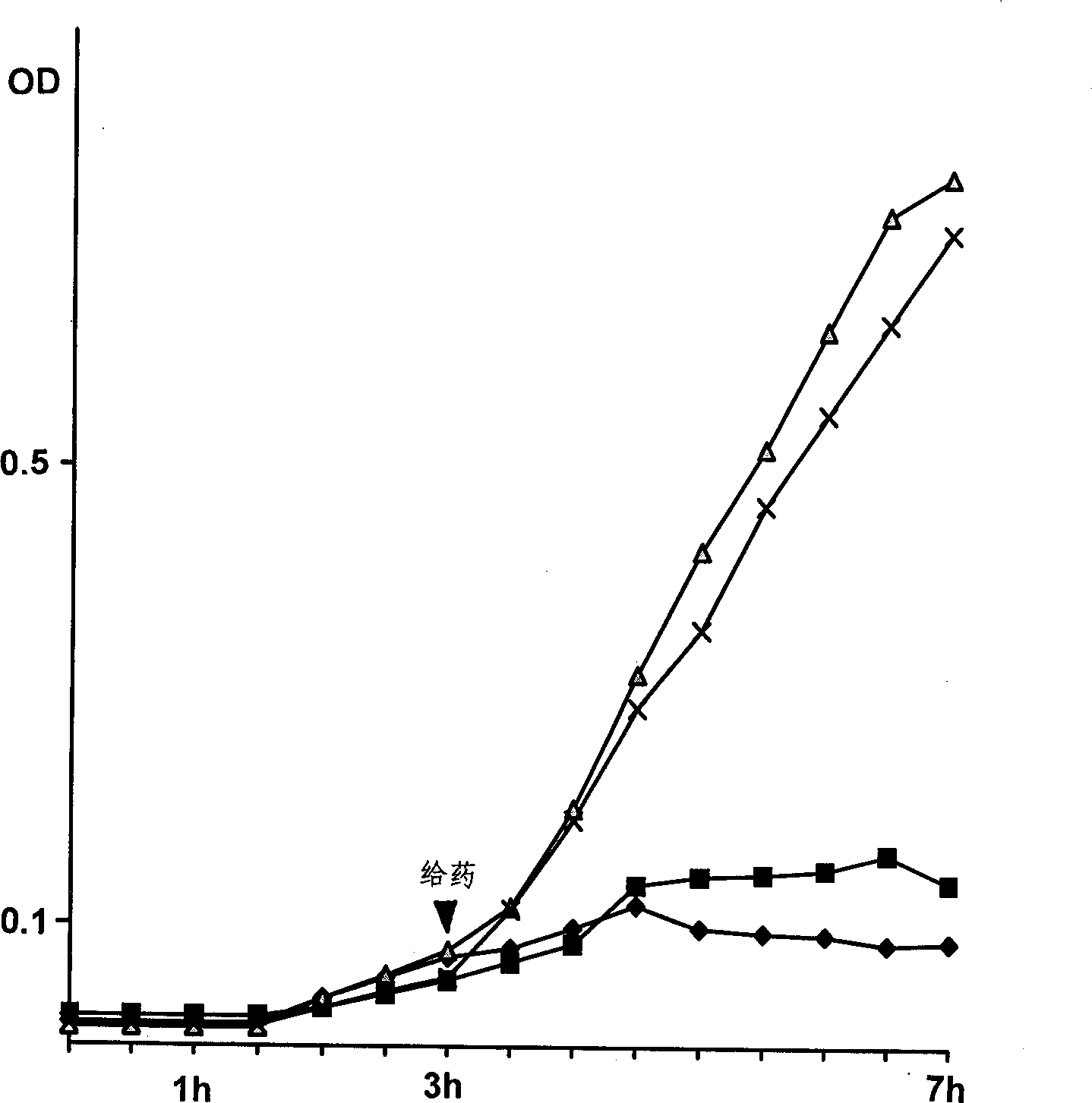
[0017] In this embodiment, the Agr D signaling polypeptide of Staphylococcus aureus is connected to the carboxyl terminus of the colistin Ia water-based pore structure domain, and a plasmid is prepared, and then through the technical steps used in the example one, it is smaller than the example one. Anti-Staphylococcus aureus engineering polypeptide with a molecular weight of 13,000. In order to confirm the antibacterial ability of the engineering polypeptide, 5 μl (10 8 CFUS / ml) into 10ml of LB culture medium, incubated at 225rpm, 37°C for three hours, then added the antibacterial engineering polypeptide (final concentration 0.5μg / ml), continued to incubate at 225pm, 37°C, sampled every hour by spectrophotometry Meter (A595nm) colorimetric test, ampicillin (Ampicillin, final concentration 0.5μg / ml) and Staphylococcus aureus-LB medium without adding any drugs were used as controls (see attached figure 2 ), the results showed that: after the Staphylococcus aureus in the control ...
Embodiment 3
[0018] This embodiment is based on the above-mentioned technical route. We connect the Agr D signaling polypeptide of Staphylococcus aureus to the amino terminal of the colicin Ia aqueous pore structure domain to prepare a plasmid, and then go through the technical steps used in Example 1 to obtain A smaller anti-Staphylococcus aureus engineering polypeptide with a molecular weight of 13,000 was obtained than Example 1. Preliminary experiments show that the polypeptide has the ability to resist Staphylococcus aureus.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com