Method for synchronizing base stations
A technology for synchronizing base stations and base stations, which is applied in the direction of synchronization devices, communication between multiple stations, transmission systems, etc., and can solve problems such as loss of autocorrelation characteristics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
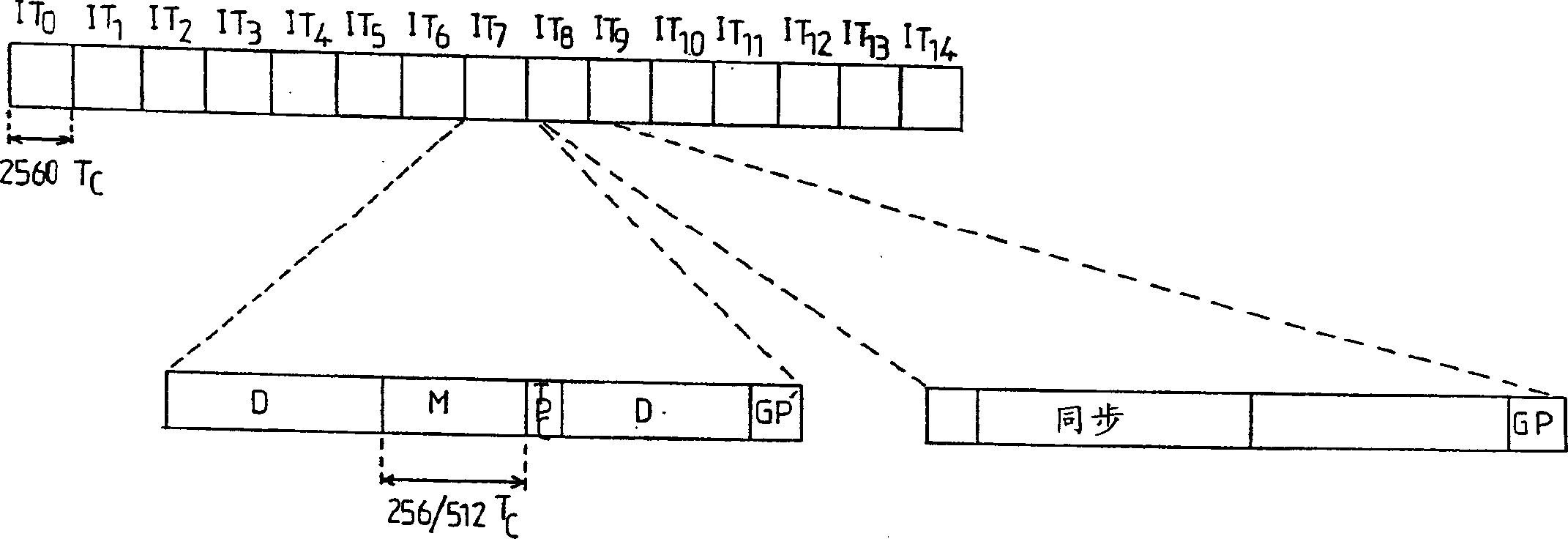
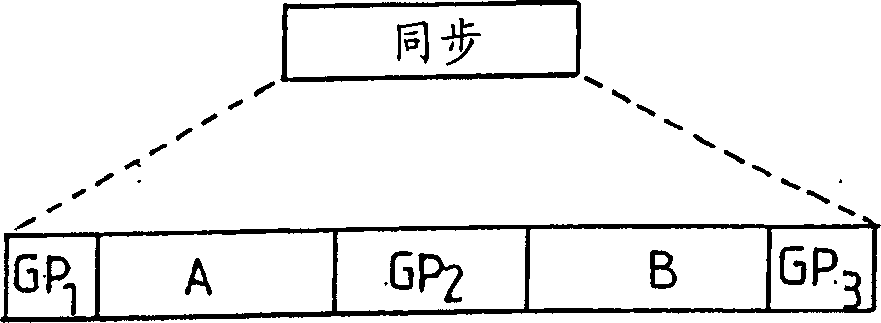
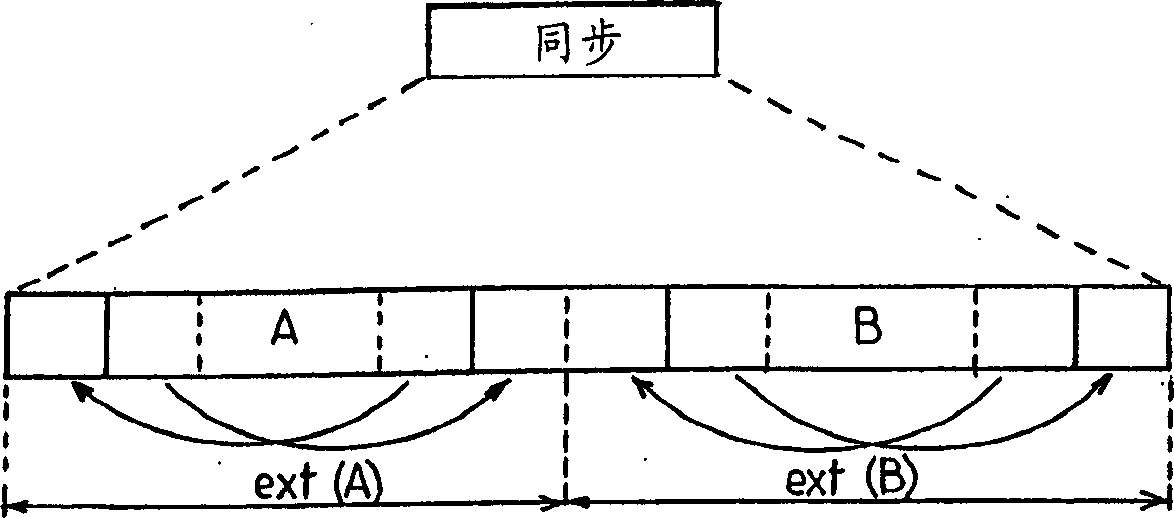
[0023] The general idea underlying the invention is to use a pair of complementary polyphase codes and more specifically a pair of Golay complementary codes for synchronizing neighboring base stations. In the rest of the description, it is not polyphase codes but Golay codes. However, it is clear that the invention is applicable to polyphase codes in general.
[0024] These complementary codes, as known herein, have the remarkable property that the sum of their aperiodic autocorrelation functions is a Dirac function. In other words, if a pair of such complementary codes is denoted as (A, B), we get AA (m)+ BB (m)=δ(m), where m is the time label, δ is the Kronecker symbol, and is the aperiodic autocorrelation function.
[0025] In addition, as in the article entitled "Efficient pulse compressor for Golay complementary sequences (Efficient pulse compressor for Golay complementary sequences)" in Eletronics Letters Vol.27 No.3, pp. 219-220, published in January 1991, S.Z. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com