Fusion protein with reinforced erythrocytin activity in vivo
A fusion protein and generative technology, applied in the field of fusion proteins, can solve the problems of difficult to obtain target protein, reduction, loss of protein intrinsic activity, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0056] Example 1: Gene preparation
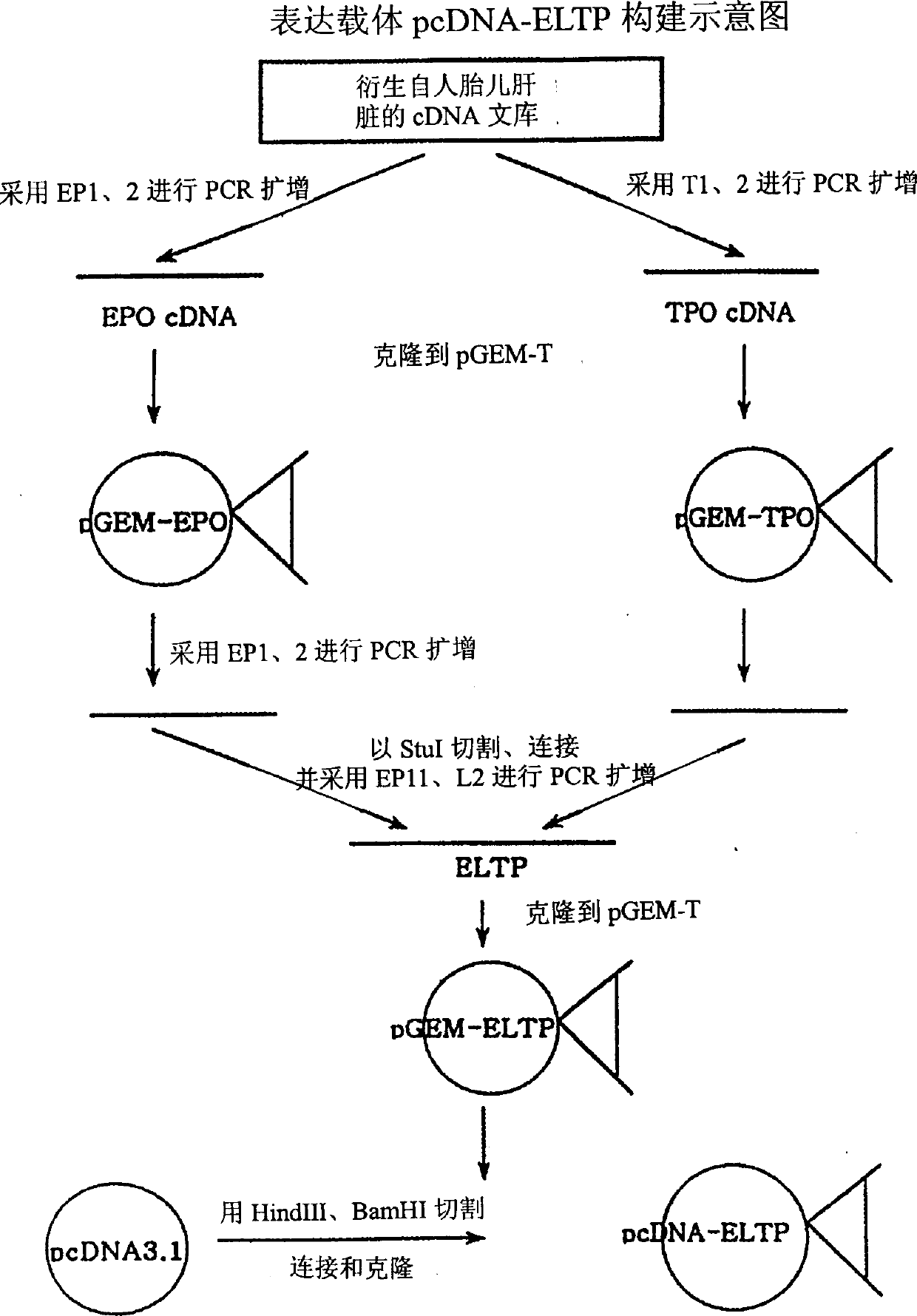
[0057] Using 50 pmol each of primers EP1 and EP2 complementary to the end of EPO cDNA, conventional PCR (PCR PreMix kit from Bioneer Company) was performed from a human-derived fetal liver cDNA library (Invitrogen Company) to obtain EPO cDNA. TPO cDNA was obtained in the same manner using primers T1 and T2 complementary to the ends of TPO cDNA. A total of 30 cycles of PCR were performed using the high-fidelity Taq system of BM Company. The reaction conditions were annealing at 52°C for 40 seconds, extension at 72°C for 55 seconds and denaturation at 94°C for 20 seconds to generate EPO cDNA and TPO cDNA. They were respectively cloned into the cloning vector pGEM-T (Promega Company). That is, the PCR product was eluted from 1% agarose gel, ligated to pGEM-T, and introduced into E. coli NM522. Transformed E. coli were grown overnight on LB-ampicillin plates containing X-gal / IPTG. Plasmids were purified from white colonies and treated with ...
Embodiment 2
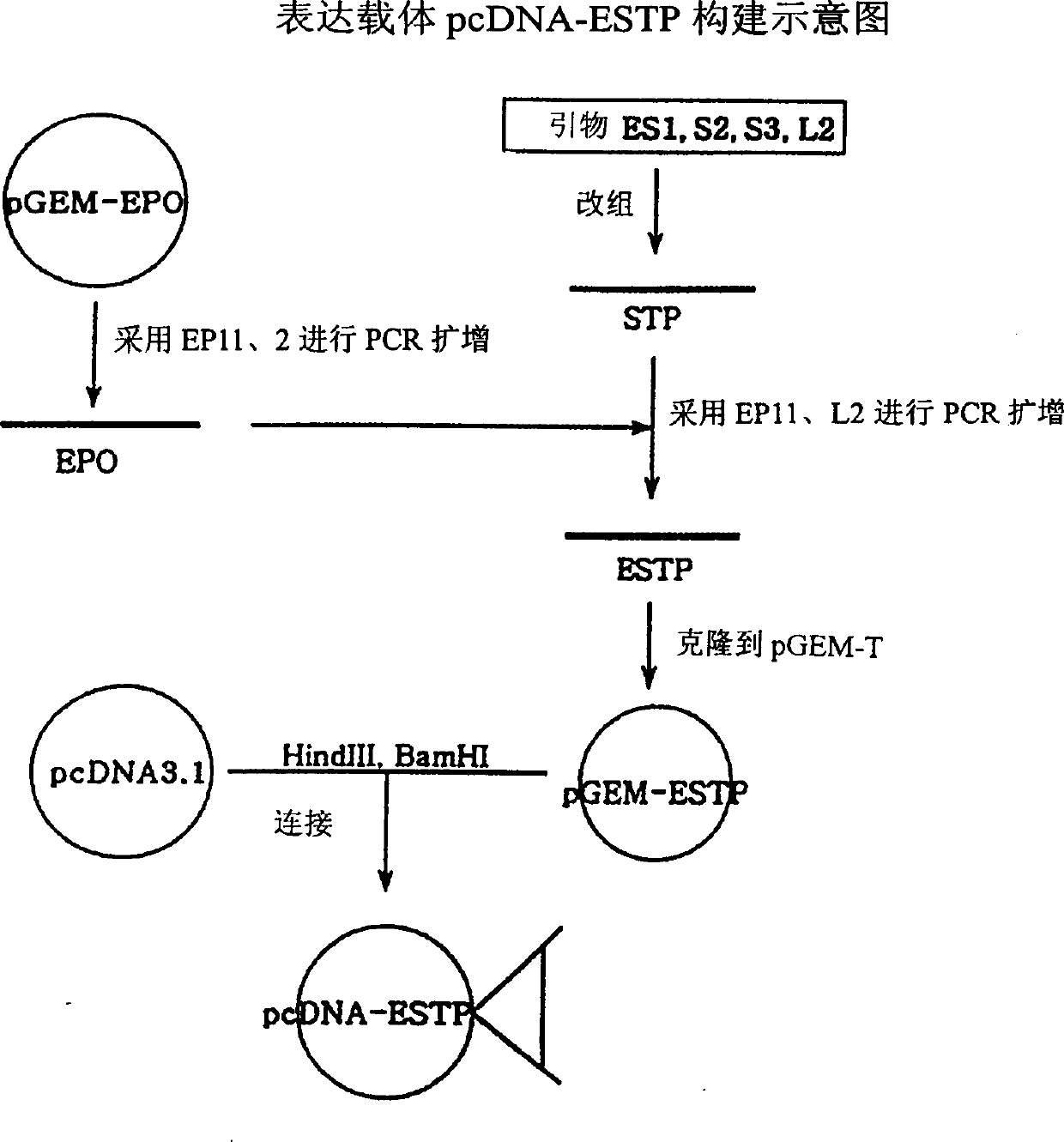
[0063] Invitrogen's pcDNA3-1 vector was used as the expression vector. The ELTP and ESTP genes cloned into the pGEM-T vector contain HindIII and BamHI recognition sites at the ends, respectively. pcDNA3.1, pGEM-ELTP and pGEM-ESTP were treated with restriction enzymes HindIII and BamHI, respectively. Linear pcDNA3.1, ELTP and ESTP genes were isolated on agarose gels using Qiagen extraction kits. After pcDNA3.1 was ligated with ELTP or ESTP, the ligated product was introduced into E.coli NM522. Plasmids were isolated from colonies of transformed E. coli grown overnight on LB-ampicillin plates and treated with restriction enzymes HindIII and BamHI. Colonies containing ELTP or ESTP genes were then screened out by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis. These plasmids were named pcDNA-ELTP and pcDNA-ESTP respectively (Fig. 3). Example 3: Transformation and expression of CHO cells
Embodiment 3
[0064]CHO cells (DG44) were cultured in 60mm cell culture dishes to 40-80% confluence (1-4×105 cells / 60mm dish). Mix 3 μl of superfection reagent (BM company) and 97 μl of cell culture medium (α-MEM with matrix, no serum, no antibody), and then add plasmid pcDNA-ELTP (=0.1 μg / μl, about 2 μg) and the vector pLTRdhfr26 (ATCC37295, 0.2 µg) having the dhfr gene. The mixture was reacted at room temperature for 5-10 minutes, and then added to the cells prepared above. One day later, the original medium was renewed with G418-containing medium (matrix-free α-MEM, 10% FBS) at a content of 500 μg / ml. The medium was then continuously refreshed with medium containing 500 μg / ml G418 for 7-10 days, during which time the cells without the G418 resistance gene and the negative control cells were completely killed. The screened cells were fully cultured on G418 medium, and the expressed ELTP protein was identified with the EPO ELISA kit of BM Company. The same method was applied to pcDNA-ES...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com